
Lower members of aliphatic carboxylic acid are soluble in water. This is due to
(a)Water is non electrolyte
(b)due to London forces
(c)formation of hydrogen bonds with water
(d)van der-waals interaction with water molecules
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: An organic acid is an organic compound which contains carboxylic groups. Their general formula is R-COOH. Where R represents any alkyl or phenyl group. Polarity means when a high electronegative atom pulls the electron density of a lesser electronegative atom leading to the formation of partial negative and positive charge on them.
Complete step by step solution:
-Acids that have a general formula R-COOH are organic acids, where R represents any organic chain. The OH (hydroxyl group) is polar in organic acids. This leads to polarity in organic acid. The OH being partial negative charge and C of COOH has partial positive charge. Two poles are formed. These polar groups can now form hydrogen bonding with the water molecules easily. This is only in the case of lower carboxylic acids. In case of higher carboxylic acids, the organic chain R increases, this decreases the polarity of the compound, thus it solubility decreases.
-Carboxylic acids up to four carbon atoms can mix with water in any proportion. When you mix them, the energy released during the formation of new bonds is almost the same as the energy required to break the hydrogen bonds in the pure liquid.
-The solubility of organic acids decreases rapidly with its increase in size. The longer hydrocarbon chair, ‘tails’ comes in between the water molecules and breaks the hydrogen bond, that is, it does not allow the formation of hydrogen bonds. The broken hydrogen bonds are replaced by weaker van der-waals forces dispersion forces.
-Energetics of soluble carboxylic acids are very complex.
Let us consider RCOOH and how it forms hydrogen bonds.
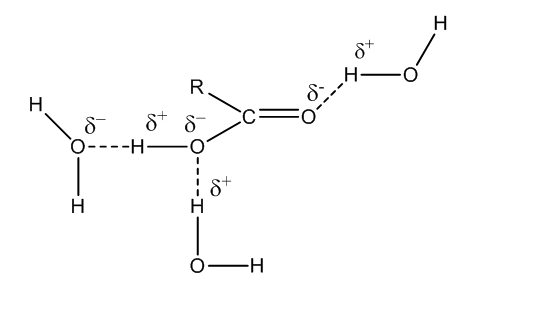
Therefore, the correct answer for the question is option (c).
Note: It is due to the presence of a polar OH group which has the ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, lower carboxylic acids are soluble. Even in higher organic acids, the COOH group has polarity, but their R will be very long chain, preventing them from the formation of hydrogen bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
-Acids that have a general formula R-COOH are organic acids, where R represents any organic chain. The OH (hydroxyl group) is polar in organic acids. This leads to polarity in organic acid. The OH being partial negative charge and C of COOH has partial positive charge. Two poles are formed. These polar groups can now form hydrogen bonding with the water molecules easily. This is only in the case of lower carboxylic acids. In case of higher carboxylic acids, the organic chain R increases, this decreases the polarity of the compound, thus it solubility decreases.
-Carboxylic acids up to four carbon atoms can mix with water in any proportion. When you mix them, the energy released during the formation of new bonds is almost the same as the energy required to break the hydrogen bonds in the pure liquid.
-The solubility of organic acids decreases rapidly with its increase in size. The longer hydrocarbon chair, ‘tails’ comes in between the water molecules and breaks the hydrogen bond, that is, it does not allow the formation of hydrogen bonds. The broken hydrogen bonds are replaced by weaker van der-waals forces dispersion forces.
-Energetics of soluble carboxylic acids are very complex.
Let us consider RCOOH and how it forms hydrogen bonds.

Therefore, the correct answer for the question is option (c).
Note: It is due to the presence of a polar OH group which has the ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, lower carboxylic acids are soluble. Even in higher organic acids, the COOH group has polarity, but their R will be very long chain, preventing them from the formation of hydrogen bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




