
Make an analysis of the amplitude-modulated wave. Plot the frequency spectrum
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The process of changing the amplitude or frequency or phase of the carrier in accordance with the intensity of the signal is known as modulation. Accordingly, the types of modulations are amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), and phase modulation (PM).
Complete step by step solution:
Let us represent a carrier wave as
${e_c} = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t$
where ${e_c}$ stands for the instantaneous voltage, ${E_c}$ stands for the amplitude, and ${\omega _c}$ stands for the angular frequency of the carrier wave.
The modulating signal can be written as,
${e_s} = {E_s}\cos {\omega _s}t$
where ${e_s}$ represent the instantaneous voltage, ${E_s}$ stands for the amplitude, and ${\omega _s}$ stands for the angular frequency of the signal wave.
In an amplitude modulated wave the amplitude of the carrier wave is adjusted in accordance with the intensity of the audio signal.
Therefore the modulated signal can be written as,
$e = \left( {{E_c} + {E_s}\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)\cos {\omega _c}t$
Taking ${E_c}$ outside the bracket, we get
$e = {E_c}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{E_s}}}{{{E_c}}}\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)\cos {\omega _c}t$
The ratio $\dfrac{{{E_s}}}{{{E_c}}} = m$, where $m$ stands for the modulation factor.
Now the above equation can be written as,
$e = {E_c}\left( {1 + m\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)\cos {\omega _c}t$
Opening the bracket, we get
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + m{E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t.\cos {\omega _s}t$
Multiplying and dividing with $2$in the second half of the above equation, we get
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\left( {2\cos {\omega _c}t.\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)$
This can be written as,
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\left[ {\cos \left( {{\omega _c} + {\omega _s}} \right)t + \cos \left( {{\omega _c} - {\omega _s}} \right)t} \right]$
Opening the square bracket, we get
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} + {\omega _s}} \right)t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} - {\omega _s}} \right)t$
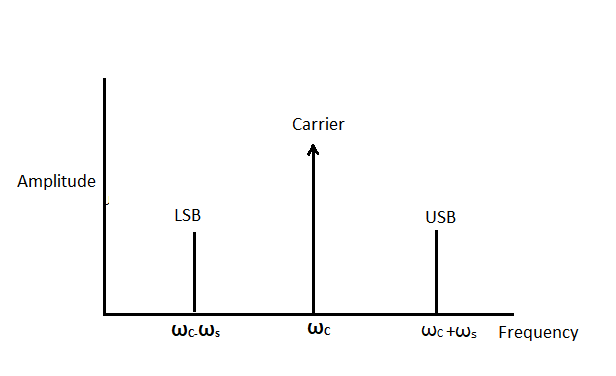
From this expression, we can understand that there are three components in the modulated wave. They are:
${E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t$ : this component is the same as the carrier wave.
$\dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} + {\omega _s}} \right)t$: The frequency of this component is greater than the carrier and is called the upper side band.
$\dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} - {\omega _s}} \right)t$: The frequency of this component is lesser than that of the carrier and is called the lower side band.
Frequency spectrum:
Both the lower side band and the upper side band are located on either side of the carrier wave.
Note:
The modulation index or modulation factor is the ratio of change of the amplitude of the carrier wave after modulation to the amplitude of the unmodulated carrier wave. The process of recovering the audio frequency signal from the modulated carrier wave is known as demodulation or detection.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us represent a carrier wave as
${e_c} = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t$
where ${e_c}$ stands for the instantaneous voltage, ${E_c}$ stands for the amplitude, and ${\omega _c}$ stands for the angular frequency of the carrier wave.
The modulating signal can be written as,
${e_s} = {E_s}\cos {\omega _s}t$
where ${e_s}$ represent the instantaneous voltage, ${E_s}$ stands for the amplitude, and ${\omega _s}$ stands for the angular frequency of the signal wave.
In an amplitude modulated wave the amplitude of the carrier wave is adjusted in accordance with the intensity of the audio signal.
Therefore the modulated signal can be written as,
$e = \left( {{E_c} + {E_s}\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)\cos {\omega _c}t$
Taking ${E_c}$ outside the bracket, we get
$e = {E_c}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{E_s}}}{{{E_c}}}\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)\cos {\omega _c}t$
The ratio $\dfrac{{{E_s}}}{{{E_c}}} = m$, where $m$ stands for the modulation factor.
Now the above equation can be written as,
$e = {E_c}\left( {1 + m\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)\cos {\omega _c}t$
Opening the bracket, we get
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + m{E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t.\cos {\omega _s}t$
Multiplying and dividing with $2$in the second half of the above equation, we get
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\left( {2\cos {\omega _c}t.\cos {\omega _s}t} \right)$
This can be written as,
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\left[ {\cos \left( {{\omega _c} + {\omega _s}} \right)t + \cos \left( {{\omega _c} - {\omega _s}} \right)t} \right]$
Opening the square bracket, we get
$e = {E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} + {\omega _s}} \right)t + \dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} - {\omega _s}} \right)t$
From this expression, we can understand that there are three components in the modulated wave. They are:
${E_c}\cos {\omega _c}t$ : this component is the same as the carrier wave.
$\dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} + {\omega _s}} \right)t$: The frequency of this component is greater than the carrier and is called the upper side band.
$\dfrac{{m{E_c}}}{2}\cos \left( {{\omega _c} - {\omega _s}} \right)t$: The frequency of this component is lesser than that of the carrier and is called the lower side band.
Frequency spectrum:
Both the lower side band and the upper side band are located on either side of the carrier wave.

Note:
The modulation index or modulation factor is the ratio of change of the amplitude of the carrier wave after modulation to the amplitude of the unmodulated carrier wave. The process of recovering the audio frequency signal from the modulated carrier wave is known as demodulation or detection.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




