
Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq.NaOH yields:
A. o-Cresol
B. m-Cresol
C. 2,4-Dihydroxytoluene
D. Benzyl alcohol
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests monochlorination means chlorination with a single chlorine atom where multiple chlorination would be possible. As we know toluene also known as ‘toluol’ is an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know halogenation in the presence of light follows a free radical pathway. Thus toluene will react with the alkyl group to give product haloalkyl and therefore, it will form haloalkyl in the presence of alkaline medium will undergo substitution at side chain rather than at the hydrogen of the aromatic ring and will form alcohol by replacing halogen atom in haloalkyl group.
Monochlorination of toluene to form benzyl alcohol by following two steps:
In the first step reaction,toluene reacts with chlorine in presence of sunlight at 383k to give Benzyl Chloride which is also called Chlorophenyl methane by substituting at side
chain rather than at hydrogen of the aromatic ring.
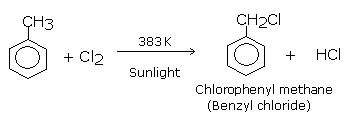
Now in the second step, this product Benzyl chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to yield Benzyl alcohol via nucleophilic substitution reaction.
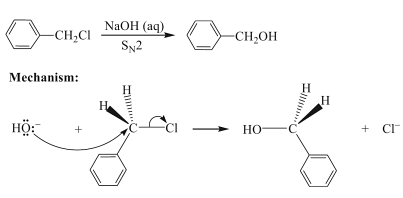
In this mechanism, the nucleophile which is -OH will attack the electrophilic carbon of haloalkane through oxygen and substitutes chloride to give Benzyl alcohol and the reaction is called Nucleophilic substitution reaction in which this benzyl chloride reacts with aqueous NaOH, as a result the NaCl formed will be eliminated and the remaining end product is Benzyl alcohol.
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Additional information:
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\]
It is colourless liquid with a mild pleasant aromatic odour and it is a very useful solvent due to its polarity, low vapour pressure and low toxicity.
It is mild soluble in water and miscible in alcohols and diethyl ether. Benzyl alcohol is used for waxes, inks, paints, etc and it is also a precursor to a variety of esters and ethers which can be used in soap, perfume, etc.
Note: The benzyl group is abbreviated as ‘’Bn’’ not to be confused with ‘’Bz’’ which is used for benzoyl thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH not BzOH.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know halogenation in the presence of light follows a free radical pathway. Thus toluene will react with the alkyl group to give product haloalkyl and therefore, it will form haloalkyl in the presence of alkaline medium will undergo substitution at side chain rather than at the hydrogen of the aromatic ring and will form alcohol by replacing halogen atom in haloalkyl group.
Monochlorination of toluene to form benzyl alcohol by following two steps:
In the first step reaction,toluene reacts with chlorine in presence of sunlight at 383k to give Benzyl Chloride which is also called Chlorophenyl methane by substituting at side
chain rather than at hydrogen of the aromatic ring.

Now in the second step, this product Benzyl chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to yield Benzyl alcohol via nucleophilic substitution reaction.

In this mechanism, the nucleophile which is -OH will attack the electrophilic carbon of haloalkane through oxygen and substitutes chloride to give Benzyl alcohol and the reaction is called Nucleophilic substitution reaction in which this benzyl chloride reacts with aqueous NaOH, as a result the NaCl formed will be eliminated and the remaining end product is Benzyl alcohol.
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Additional information:
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\]
It is colourless liquid with a mild pleasant aromatic odour and it is a very useful solvent due to its polarity, low vapour pressure and low toxicity.
It is mild soluble in water and miscible in alcohols and diethyl ether. Benzyl alcohol is used for waxes, inks, paints, etc and it is also a precursor to a variety of esters and ethers which can be used in soap, perfume, etc.
Note: The benzyl group is abbreviated as ‘’Bn’’ not to be confused with ‘’Bz’’ which is used for benzoyl thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH not BzOH.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




