
Out of soft iron and steel which has more coercivity, less retentivity.
(A) Iron
(B) Steel
(C) Both are equal
(D) Can’t say
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: First of all define the terms retentivity and coercivity. Then use the hysteresis curve of both soft iron and steel.
Retentivity is the amount of magnetization left when an external magnetizing field is removed. Coercivity is the reverse external magnetizing field which is required to demagnetize the substance completely.
Complete solution:
Hysteresis curve shows the pattern of change in the value magnetising force (H) with magnetic flux density (B). The area under hysteresis loop represents the loss in energy in one complete cycle of magnetising and demagnetising of a magnetic material.
With increase in the value of the magnetic field, there is an increase in the value of magnetism. When the values of B and H are zero then substance retains some amount of magnetism known as residual magnetism. The force required to remove the residual magnetism is known as Coercive force.
Hysteresis curve of steel is shown in figure (a) and the hysteresis curve of soft iron is shown in figure (b).
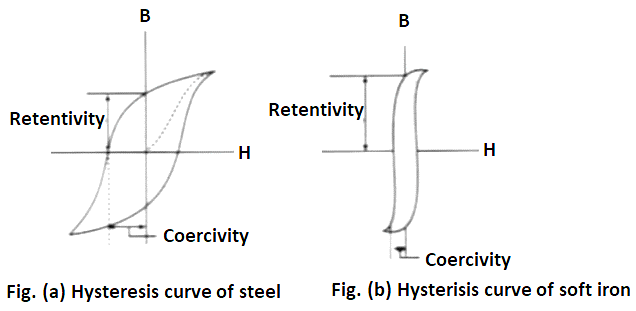
From the above figures it is clear that the steel has more coercivity and less retentivity as compared to the soft iron.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct choice.
Note: Retentivity of steel is more than the retentivity of soft iron. Soft iron is easily magnetized and demagnetized as compared to steel. The coercivity of soft iron is less than that of the coercivity of the steel. Energy loss in soft iron is less than energy loss in steel because of the small area of soft iron ( ${\text{B - H}}$ ) curve.
Retentivity is the amount of magnetization left when an external magnetizing field is removed. Coercivity is the reverse external magnetizing field which is required to demagnetize the substance completely.
Complete solution:
Hysteresis curve shows the pattern of change in the value magnetising force (H) with magnetic flux density (B). The area under hysteresis loop represents the loss in energy in one complete cycle of magnetising and demagnetising of a magnetic material.
With increase in the value of the magnetic field, there is an increase in the value of magnetism. When the values of B and H are zero then substance retains some amount of magnetism known as residual magnetism. The force required to remove the residual magnetism is known as Coercive force.
Hysteresis curve of steel is shown in figure (a) and the hysteresis curve of soft iron is shown in figure (b).

From the above figures it is clear that the steel has more coercivity and less retentivity as compared to the soft iron.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct choice.
Note: Retentivity of steel is more than the retentivity of soft iron. Soft iron is easily magnetized and demagnetized as compared to steel. The coercivity of soft iron is less than that of the coercivity of the steel. Energy loss in soft iron is less than energy loss in steel because of the small area of soft iron ( ${\text{B - H}}$ ) curve.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




