




How Does a Domestic Electric Circuit Work? Functions and Safety Features
A domestic electric circuit describes the electrical wiring system that delivers power safely throughout a residence. It includes an arrangement of wires, protective devices, and connections to operate electrical appliances efficiently while prioritizing safety. Understanding the structure and functioning of the domestic electric circuit is essential for problems and conceptual clarity in JEE Main Physics.
Domestic Electric Circuit: Overview and Structure
A domestic electric circuit starts with the main supply entering the house through overhead lines or underground cables. The circuit comprises devices for protection, measurement, and distribution, ensuring safe and independent operation of appliances. Standard household circuits are designed for alternating current (AC), most commonly at 230 V and 50 Hz in India.
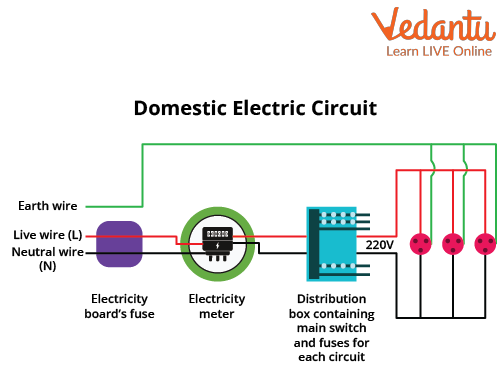
Key Components of a Domestic Electric Circuit
The main elements in a domestic electric circuit include the main fuse, energy meter, main switch, circuit breakers, distribution board, earthing, switches, sockets, and connected appliances. Each component serves a distinct function to maintain efficient operation and safety.
- Main fuse protects the entire installation
- Energy meter records consumed energy
- Main switch disconnects phase and neutral
- MCBs offer overload/short-circuit protection
- Distribution board separates lighting and power circuits
- Earthing diverts leakage current to the ground
- Switches and sockets control appliances
Typical Domestic Electric Circuit Diagram
A properly labelled domestic electric circuit diagram shows the flow of electric current from the main supply through the protective fuse and energy meter, followed by a double-pole main switch. The wiring is then distributed to lighting and power circuits through circuit breakers and switches.
Wiring and Color Coding Standards
Household wiring follows strict color codes for safety and identification. The live wire is either red or brown, the neutral wire is black or blue, and the earthing wire is green or yellow-green. Correct usage prevents connection errors and hazards.
| Wire Function | Standard Color |
|---|---|
| Live (Phase) | Red/Brown |
| Neutral | Black/Blue |
| Earth | Green/Yellow-Green |
AC Supply and Its Advantages in Domestic Circuits
Alternating current (AC) is supplied in homes due to its efficiency in transmission and ease of voltage transformation. In India, domestic supply is AC of 230 V at 50 Hz. This enables the connection of various appliances and efficient power distribution.
For a deeper look at current, refer to Understanding Current Electricity.
| Feature | AC (Domestic) |
|---|---|
| Type | Alternating Current |
| Voltage | 230 V (India) |
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Advantage | Low transmission loss |
Parallel vs Series Connections in Domestic Electric Circuits
Domestic appliances are always connected in parallel. Parallel wiring ensures that each device receives the full supply voltage and can be switched on or off independently. Series connection is avoided as it disrupts circuit functionality and voltage distribution.
| Parameter | Parallel |
|---|---|
| Voltage across appliances | Same for all |
| Current through appliances | Divided as per load |
| Appliance control | Independent |
Distribution of 5A and 15A Circuits
The domestic electric circuit is divided into lighting and power circuits. Circuits with 5A rating serve low-power devices such as lights and fans, while 15A circuits are allocated for high-power appliances like air conditioners and geysers. This segregation prevents overloading and enhances safety.
Resistance in these circuits influences current flow and is analyzed in Resistance in Electric Circuits.
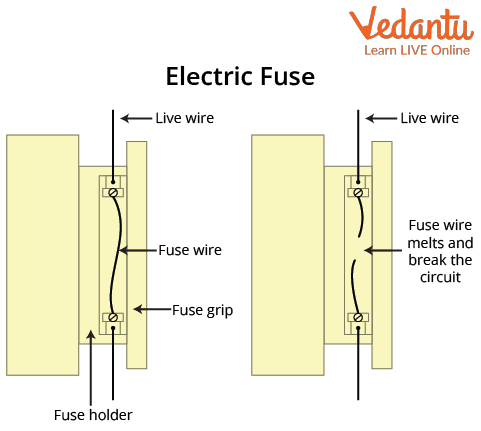
Fuse, Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), and Earthing
Fuses and MCBs are essential protective devices in domestic wiring. A fuse is a thin wire with a low melting point that breaks the circuit if excess current flows, preventing fire hazards. MCBs offer resettable protection by quickly turning off supply during overloads or faults.
Earthing provides a path for leakage current to flow directly to the ground, preventing electric shock from faulty appliances. Proper earthing is mandatory for any domestic electric installation.
Basic Calculation in Domestic Circuits
The current drawn by an appliance can be calculated using the formula $I = \dfrac{P}{V}$, where $I$ is current, $P$ is power, and $V$ is supply voltage. This calculation checks whether a given circuit can safely handle particular appliances.
- For a 1.5 kW appliance on 230 V: $I = \dfrac{1500}{230} \approx 6.52$ A
Safety Practices in Domestic Wiring
Domestic electric circuits are designed with multiple safety measures. Installation of proper fuses, MCBs, and earthing is essential for protection against shocks, short circuits, and fire hazards. Regular maintenance ensures continued safety.
Further study on electric safety can be related to Ohm's Law and Resistance.
Summary of Domestic Electric Circuit Essentials
A domestic electric circuit systematically supplies AC power in parallel to all appliances. Dedicated sub-circuits using 5A and 15A wiring handle low and high-power devices, ensuring safety and independent control. Color-coded wires and protective devices uphold safety standards.
Concepts such as electric field lines and circuit analysis play a vital role in understanding domestic circuits, as discussed in Electric Field Lines and Properties.
For theoretical background on electrostatics that supports domestic circuit work, consult Fundamentals of Electrostatics.
FAQs on Understanding Domestic Electric Circuits: Components and Safety
1. What is a domestic electric circuit?
A domestic electric circuit is the wiring system in homes that distributes electrical power to appliances and devices safely and efficiently. Key features include:
- Live wire (usually red or brown) supplying current
- Neutral wire (black or blue) ensuring a return path
- Earth wire for safety against electric shocks
- Fuse and MCB to protect against overload
2. Explain the components of a domestic electric circuit.
A standard domestic electric circuit includes essential components to ensure power supply and safety:
- Live wire: Delivers electric current
- Neutral wire: Completes the circuit by returning current
- Earth wire: Directs leakage current for safety
- Fuse/MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker): Prevents overload by breaking the circuit
- Main switch: Controls overall supply
3. What is the role of the earth wire in a domestic electric circuit?
The earth wire is a safety device that prevents electric shock by directing leakage current safely into the ground.
- Protects users from accidental contact with live wires
- Ensures appliances do not become live if there is insulation failure
- Works with the fuse/MCB to disconnect supply quickly in faults
4. Why is a fuse important in a domestic electric circuit?
A fuse protects the domestic electric circuit from overload and short circuits.
- It is a safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if excess current flows
- Prevents fires and damage to appliances
- Ensures only safe levels of current pass through
5. How is electricity supplied and distributed in a house?
Electricity enters a house through the main supply line and is then distributed to different circuits.
- Electric meter records consumption
- Main fuse or breaker offers protection
- Wires distribute power to lighting and power circuits
- Switches allow control over individual appliances
6. What is the difference between a live wire and a neutral wire?
The live wire and neutral wire serve different roles in a domestic circuit.
- Live wire: Carries current from the supply to the appliance (usually red/brown)
- Neutral wire: Returns current to the supply (usually black/blue)
7. What precautions should be taken while using domestic electric circuits?
To use domestic electric circuits safely, follow these precautions:
- Avoid overloading sockets
- Never touch electrical appliances with wet hands
- Regularly check the condition of wires and plugs
- Ensure earth connections are present
- Use appliances with intact insulation
8. What do you mean by overloading of an electric circuit?
Overloading in a domestic electric circuit occurs when too many appliances operate simultaneously on a single circuit.
- Excessive current flows, exceeding safe limits
- Can cause overheating of wires
- May result in melting of fuse or tripping of MCB
- Risks include fire and damage to appliances
9. What safety devices are used in a domestic electric circuit?
Domestic electric circuits use several safety devices for protection:
- Fuse: Melts and cuts off supply during excess current
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB): Trips automatically when overloaded
- Earth wire: Protects against electric shock
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB): Detects and interrupts leakage currents
10. Why do we use separate circuits for high-power appliances?
High-power appliances require separate circuits to maintain safety and prevent overloading.
- Ensures heavy devices get sufficient current without overloading common lines
- Protects against circuit overheating
- Reduces risk of accidents and appliance damage
11. How does the main switch work in a domestic electric circuit?
The main switch controls the electricity supply to the entire house.
- Acts as the master controller for flow of current
- Allows users to disconnect all circuits simultaneously during emergencies or repairs
- Enhances safety by cutting power quickly when needed
12. What is the function of a residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) in home wiring?
A Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) protects against electric shocks by detecting current leakage.
- Instantly disconnects supply when it senses leakage to earth
- Reduces the risk of fatal electric shocks
- Complements fuses and MCBs for comprehensive safety
























