




What Are the Main Uses and Benefits of Nuclear Fission?
Nuclear fission is a fundamental process in which the nucleus of a heavy atom splits into two or more lighter nuclei, accompanied by the release of a significant amount of energy. This released energy is harnessed in nuclear reactors to generate electricity. Understanding the principles of nuclear fission and the functioning of nuclear reactors is essential for JEE Main physics.
Nuclear Fission: Definition and Mechanism
Nuclear fission involves the splitting of a heavy nucleus such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239 when it absorbs a slow-moving neutron. This process produces two lighter nuclei, additional neutrons, and a large amount of energy in the form of kinetic energy and radiation.
The general fission reaction of uranium-235 can be represented as: $^{235}\text{U} + ^{1}\text{n} \rightarrow \text{Fission Fragments} + 2\ \text{or}\ 3\ ^{1}\text{n} + Q$, where $Q$ is the energy released.
The energy released in a single fission of uranium-235 is approximately 200 MeV, which is significantly higher than that released in chemical reactions. This yield makes nuclear fission suitable for large-scale power generation.
Typically, the fission fragments are barium and krypton or similar pairs, along with two or three free neutrons. These additional neutrons are key to sustaining a chain reaction required in a nuclear reactor.
The Nuclear Chain Reaction
A chain reaction occurs when the neutrons produced in one fission event induce additional fission events. If exactly one neutron from each reaction causes further fission, the reaction is self-sustaining and steady.
Uncontrolled chain reactions release energy explosively, as in atomic bombs. In nuclear reactors, the reaction is controlled to maintain a steady output of energy for electricity generation.
The multiplication factor $k$ determines the behavior of the chain reaction. If $k = 1$, the chain reaction is critical and self-sustaining; if $k > 1$, it is supercritical; and if $k < 1$, it is subcritical.
The process of nuclear fission in reactors is described in detail in Nuclear Reactor Overview.
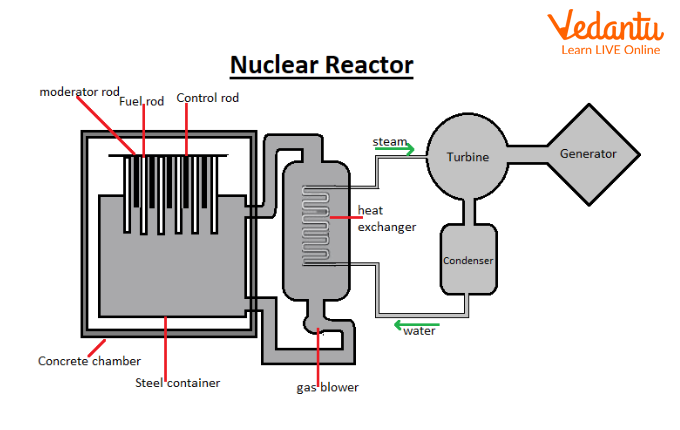
Working Principle of a Nuclear Reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device that initiates and controls nuclear fission chain reactions. Its main function is to provide controlled energy output for power generation or research.
The reactor core contains fissionable material, typically uranium-235 or plutonium-239, which serves as the fuel. When neutrons strike these nuclei, fission occurs, releasing energy that is harvested for electricity production.
Key components of a nuclear reactor include the fuel, moderator, control rods, coolant, and shielding. Each serves a specific role in sustaining and regulating the reaction while ensuring safety.
For foundational atomic concepts, visit Understanding Atomic Structure.
Main Components of a Nuclear Reactor
The fuel is composed of fissionable isotopes such as $^{235}\text{U}$, $^{239}\text{Pu}$, or $^{232}\text{Th}$. These nuclei are capable of sustaining a chain reaction under appropriate conditions.
Moderators slow down fast neutrons, increasing the probability of fission. Common moderators include ordinary water, heavy water, and graphite due to their low neutron absorption cross-section.
Control rods made of neutron-absorbing materials such as boron or cadmium are inserted or withdrawn from the reactor core to regulate the neutron population and thus control the rate of fission.
Coolants circulate through the core to remove the heat generated by fission. Water, heavy water, and gases like carbon dioxide are widely used coolants in various reactor designs.
A protective shield surrounds the reactor core to prevent harmful radiation from escaping, ensuring safety for personnel and the environment. Concrete and lead are typical shielding materials.
Common Nuclear Fission Reactions
The most frequently used nuclear fission reactions in reactors involve uranium-235 and plutonium-239. When bombarded with a neutron, these isotopes split into two lighter nuclei and release additional neutrons and energy.
- Splitting of $^{235}$U nucleus by neutron absorption
- Splitting of $^{239}$Pu nucleus by neutron absorption
- Energy release is about 200 MeV per event
- 2 or 3 neutrons are emitted per fission
The energy released in these reactions is used in various nuclear reactors for electricity generation and research applications.
Types of Nuclear Reactors
Power reactors and research reactors are the two primary classifications. Power reactors are designed for electricity generation, while research reactors are used for neutron production and isotope synthesis.
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR): Water boils inside the reactor vessel
- Pressurised Water Reactor (PWR): Water is heated but kept under high pressure
- Pressurised Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR): Utilizes natural uranium and heavy water
Indian nuclear power plants include both BWR and PHWR designs. For detail on different reactor types, see Nuclear Reactor Overview.
Applications of Nuclear Reactors
Nuclear reactors are primarily used for electricity production. Additional uses include the production of radioisotopes for medicine, industry, and agriculture.
- Electric power generation for grids
- Production of radioactive isotopes
- Neutron beam generation for scientific research
- Research in reactor physics and nuclear engineering
Reactors are also crucial in the manufacture of plutonium-239, which has defense and research applications.
Differences: Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fission involves splitting heavy nuclei, whereas nuclear fusion is the process of combining light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process. Fusion requires extremely high temperatures, while fission occurs at lower energy thresholds.
| Nuclear Fission | Nuclear Fusion |
|---|---|
| Splitting of heavy nuclei | Combining light nuclei |
| Occurs at lower temperatures | Requires extremely high temperatures |
| Used in reactors | Used in stars and hydrogen bombs |
| Produces radioactive waste | Produces minimal long-lived waste |
For more on nuclear decay and reactions, review Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay.
Sample Calculation: Energy Released in Fission
The energy released in the fission of one uranium-235 nucleus is calculated using the mass defect and Einstein’s mass-energy relation $E = \Delta m c^2$.
If $1$ amu $= 931$ MeV and the mass defect per fission is approximately $0.2$ amu, then $E = 0.2 \times 931 = 186.2$ MeV, closely matching actual values in practice.
An in-depth explanation of nuclear binding energy can be found at Binding Energy Explained.
Nuclear Reactor Safety and Shielding
All reactors are designed with safety features such as control rods, moderation systems, coolants, and shielding to minimize radiation risks and maintain a stable reaction rate.
Thick concrete or lead shields protect operating personnel and the environment from radiation exposure originating from the reactor core during operation.
Summary of Key Points
Nuclear fission splits heavy nuclei, releasing high energy suitable for electricity generation in reactors. Reactors utilize a controlled chain reaction, moderated neutrons, and safety systems to ensure efficient and safe operation.
FAQs on Understanding Nuclear Fission and How Nuclear Reactors Work
1. What is nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission is a process in which the nucleus of a heavy atom, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, splits into two lighter nuclei, releasing a significant amount of energy.
Main points:
- It involves the bombardment of a heavy nucleus by a neutron.
- Results in two lighter nuclei and two or three more neutrons.
- Releases large amounts of energy in the form of heat.
- The process can lead to a chain reaction if neutrons continue to split further nuclei.
2. What is a nuclear reactor?
A nuclear reactor is a device that controls the process of nuclear fission to safely produce energy.
Key features:
- It maintains a controlled chain reaction.
- Uses moderators to slow down neutrons and control rods to absorb excess neutrons.
- The heat released from fission is used to produce steam that drives turbines for electricity generation.
3. What happens during a nuclear fission reaction?
During nuclear fission, a heavy nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei and releases energy.
Process highlights:
- Neutron collides with a heavy nucleus (e.g., uranium-235).
- Nucleus splits, producing two smaller nuclei and free neutrons.
- Extra neutrons cause a chain reaction by splitting more nuclei.
- Large energy release in the form of heat.
4. What are the main components of a nuclear reactor?
The main components of a nuclear reactor are essential for controlling the fission process safely.
They include:
- Fuel rods (usually uranium-235 or plutonium-239)
- Moderator (e.g., graphite or heavy water) to slow down neutrons
- Control rods (e.g., cadmium or boron) to absorb neutrons
- Coolant to transfer heat
- Containment vessel to prevent radiation leakage
5. What is a chain reaction in nuclear fission?
A chain reaction in nuclear fission occurs when neutrons produced from one fission event cause further fission reactions.
Main features:
- Can be controlled (in reactors) or uncontrolled (in nuclear bombs).
- Continuous release of energy as long as enough fissile material is present.
- Crucial for energy generation in nuclear reactors.
6. What are the uses of nuclear reactors?
Nuclear reactors have several important applications in modern society.
Key uses:
- Generating electricity in power plants
- Producing radioisotopes for medical, industrial, and agricultural purposes
- Conducting scientific research
- Propelling submarines and ships
7. What safety measures are required in a nuclear reactor?
Safety measures in nuclear reactors are critical to prevent accidents and radiation leakage.
Key actions include:
- Use of robust containment buildings
- Automatic shutdown systems using control rods
- Continuous cooling to avoid overheating
- Monitoring and alarm systems for radiation
- Strict safety protocols for workers
8. What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion?
The primary difference is that fission splits heavy nuclei, while fusion joins light nuclei.
Nuclear Fission:
- Splits a heavy nucleus (e.g., uranium-235)
- Releases large energy and neutrons
- Used in nuclear reactors
- Combines light nuclei (e.g., hydrogen isotopes)
- Releases even more energy
- Occurs naturally in stars
9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy from fission?
Nuclear energy from fission has both benefits and drawbacks.
Advantages:
- Produces vast amounts of energy
- Low greenhouse gas emissions
- Reliable electricity supply
- Radioactive waste disposal is challenging
- High initial costs and risks of accidents
- Potential for nuclear proliferation
10. What is meant by moderators in a nuclear reactor?
Moderators in a nuclear reactor are materials that slow down neutrons to sustain the chain reaction.
Main points:
- Common moderators are graphite and heavy water.
- They reduce the speed of neutrons without absorbing them.
- Slower neutrons are more effective in causing fission of U-235 nuclei.
11. What is controlled and uncontrolled chain reaction?
A controlled chain reaction is regulated to produce energy safely, while an uncontrolled chain reaction leads to a rapid, explosive energy release.
- Controlled chain reactions occur in nuclear reactors for power generation.
- Uncontrolled chain reactions occur in nuclear bombs, resulting in explosions.
12. Name two isotopes used as nuclear fuel.
Two commonly used isotopes as nuclear fuel are:
- Uranium-235 (U-235)
- Plutonium-239 (Pu-239)
























