
Racemic mixture is formed by mixing two:
(A) Isomeric compounds
(B) Chiral compounds
(C) Meso compounds
(D) Enantiomers with chiral carbon
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A Racemic mixture is a mixture containing two enantiomers in equal amounts.
Step by step answer:
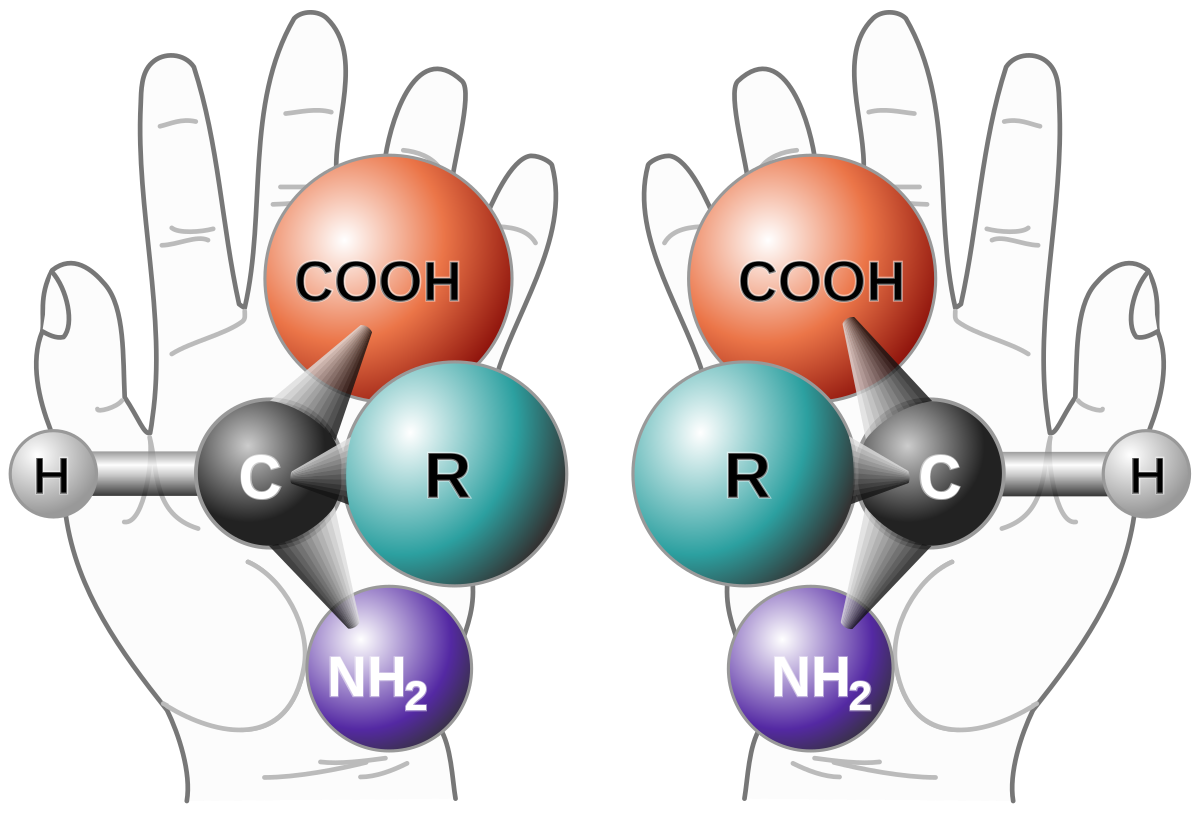
A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers. They often are distinguished as either right-handed or left-handed by their absolute configuration or some other criterion.
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate is one that has equal amounts of left-handed and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.

In case of racemic mixture, the net rotation of the plane-polarized light is zero. Although the two enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions, the rotations cancel because they are present in equal amounts.
In the above example, as you can see, both the enantiomers that are formed (R and S) are mirror images of each other. Thus we can say that the racemic mixture is formed by the mixture of two chiral compounds. So, Option D is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
We know that isomers are compounds that contain exactly the same number of atoms, that is they have the same empirical formula, but differ from each other by the way in which atoms are arranged.
Note: A Racemic mixture is optically inactive as the effect of one isomer gets cancelled by another isomer. The optical purity of a racemic mixture is . This signifies that there are no enantiomers present in excess.
Step by step answer:

A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers. They often are distinguished as either right-handed or left-handed by their absolute configuration or some other criterion.
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate is one that has equal amounts of left-handed and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule.

In case of racemic mixture, the net rotation of the plane-polarized light is zero. Although the two enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions, the rotations cancel because they are present in equal amounts.
In the above example, as you can see, both the enantiomers that are formed (R and S) are mirror images of each other. Thus we can say that the racemic mixture is formed by the mixture of two chiral compounds. So, Option D is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
We know that isomers are compounds that contain exactly the same number of atoms, that is they have the same empirical formula, but differ from each other by the way in which atoms are arranged.
Note: A Racemic mixture is optically inactive as the effect of one isomer gets cancelled by another isomer. The optical purity of a racemic mixture is . This signifies that there are no enantiomers present in excess.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




