
State the electronic configuration for Neon $\left[ {P = 10,n = 10} \right]$
A. $2,{\text{ 6}}$
B. $2,{\text{ 7}}$
C. $2,{\text{ 9}}$
D. $2,{\text{ 8}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons into different shells, subshells and orbitals in an atom. The electronic configuration is governed by Aufbau’s principle and some other rules.
Complete step by step solution:
Aufbau’s principle helps in filling of electrons in various shells and subshells according to the energy of electrons a representation of the rule is drawn as,
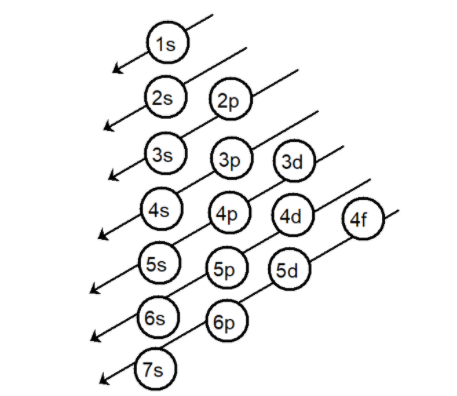
The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons hence the element has $10$ electrons. According to Aufbau’s principle the electrons are filled as,
Electronic configuration of element with atomic number $10$is,
\[{}_{10}Ne = \]$1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}$
From the above given information, we can calculate the electronic configuration of Neon.
The symbol of Neon is $Ne$, and the atomic number of Neon is $10$. Then the electronic configuration of Neon is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}$
The inner shell $\left( {n = 1} \right)$contains two electrons and outer shell $\left( {n = 2} \right)$contains eight electrons. Therefore, electronic configuration of Neon is$2,{\text{ 8}}$.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Addition information:
(i) Electronic configuration of the element is written in terms of ${s^x},{\text{ }}{{\text{p}}^y},{\text{ }}{{\text{d}}^z}$. In this type of notation, the subshells are represented by their respective symbol for example, $s$is written for the subshell with $l = 0$. $p$is written for subshell with $l = 1.$ In the notation, the letters $x,{\text{ y, z}}$….. represent the number of electrons present in the various subshells. For the complete electronic configuration, the principal quantum number is written before the respective subshell. For example: electronic configuration of $Mg\left( {12} \right) = 1{s^2}2{s^2}s{p^6}3{s^2}$
(ii) Orbital notation:
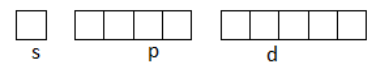
It is the other way of expressing the electronic configuration of an atom. In this notation, the orbitals of the subshell are represented by a box and electrons are represented by the arrows. Arrow $\left( \uparrow \right)$represents $ + \dfrac{1}{2}$i.e. positive spin and an arrow $\left( \downarrow \right)$represents$ - \dfrac{1}{2}$ i.e. negative spin.
For example: magnesium

Note: Aufbau’s principle: this principle states that the electrons are added one by one into the various orbitals in order of their increasing energy starting with the orbital of lowest energy. In other words, we can say that the electrons first occupy the lowest energy orbital available to them and only when these orbitals are filled, the only the electrons are filled in the higher energy orbitals. For multi-electron atoms, the following is the increasing order of the energy of the orbitals are 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s. For the prediction of orbitals, only three quantum numbers are required [$n,{\text{ l, m}}$] and for the prediction of electrons all quantum numbers are required [$n,{\text{ l, m}}$ and $s$].
Complete step by step solution:
Aufbau’s principle helps in filling of electrons in various shells and subshells according to the energy of electrons a representation of the rule is drawn as,

The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons hence the element has $10$ electrons. According to Aufbau’s principle the electrons are filled as,
Electronic configuration of element with atomic number $10$is,
\[{}_{10}Ne = \]$1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}$
From the above given information, we can calculate the electronic configuration of Neon.
The symbol of Neon is $Ne$, and the atomic number of Neon is $10$. Then the electronic configuration of Neon is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}$
The inner shell $\left( {n = 1} \right)$contains two electrons and outer shell $\left( {n = 2} \right)$contains eight electrons. Therefore, electronic configuration of Neon is$2,{\text{ 8}}$.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Addition information:
(i) Electronic configuration of the element is written in terms of ${s^x},{\text{ }}{{\text{p}}^y},{\text{ }}{{\text{d}}^z}$. In this type of notation, the subshells are represented by their respective symbol for example, $s$is written for the subshell with $l = 0$. $p$is written for subshell with $l = 1.$ In the notation, the letters $x,{\text{ y, z}}$….. represent the number of electrons present in the various subshells. For the complete electronic configuration, the principal quantum number is written before the respective subshell. For example: electronic configuration of $Mg\left( {12} \right) = 1{s^2}2{s^2}s{p^6}3{s^2}$
(ii) Orbital notation:

It is the other way of expressing the electronic configuration of an atom. In this notation, the orbitals of the subshell are represented by a box and electrons are represented by the arrows. Arrow $\left( \uparrow \right)$represents $ + \dfrac{1}{2}$i.e. positive spin and an arrow $\left( \downarrow \right)$represents$ - \dfrac{1}{2}$ i.e. negative spin.
For example: magnesium

Note: Aufbau’s principle: this principle states that the electrons are added one by one into the various orbitals in order of their increasing energy starting with the orbital of lowest energy. In other words, we can say that the electrons first occupy the lowest energy orbital available to them and only when these orbitals are filled, the only the electrons are filled in the higher energy orbitals. For multi-electron atoms, the following is the increasing order of the energy of the orbitals are 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s. For the prediction of orbitals, only three quantum numbers are required [$n,{\text{ l, m}}$] and for the prediction of electrons all quantum numbers are required [$n,{\text{ l, m}}$ and $s$].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




