
The basic structural unit of silicates is:
A. $Si{{O}^{-}}$
B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$
C. $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$
D. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{2-}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Think about the ores in which silicate compounds are formed and recall the general formula for silicates. They are usually structures made up of silicon and oxygen and arranged in tetrahedral units which are joined together. Silicon is at the center and oxygen atoms are present at the corners of the tetrahedron.
Complete step by step solution:
The general formula for silicates is defined to be ${{[Si{{O}_{(4-x)}}^{(4-2x)-}]}_{n}}$ for $0\le x<2$. From this formula, we can safely rule out options ‘A. $Si{{O}^{-}}$’ and ‘D. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{2-}$’ as the correct answers.
Silicates include orthosilicates, metasilicates, and pyrosilicates with the structural formulae of $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$, $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$, and $S{{i}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}^{6-}$ respectively Usually when referring to silicates, the most standard form of a silicate is referred to, the orthosilicate which is tetrahedrally arranged.
The silicon atom in orthosilicate is $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized and the 4 oxygen atoms are present at 4 corners of the tetrahedron. Orthosilicate compounds are found in various ores of minerals like granite, feldspar, and others.
The structure of the orthosilicate anion is:
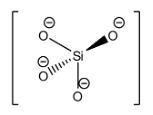
Hence, the answer to this question is ‘B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$’
Additional information:
The bond length in the orthosilicate anion is 162pm and the bond angle is $109.5{}^\circ $. This is exactly the bond angle that is predicted for tetrahedral structures that do not have any lone pairs or dipole moments.
Note: Although options ‘B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$’ and ‘C. $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$’ are both considered to be silicates, the correct answer is ‘B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$’ since $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$ is always explicitly described to be a metasilicate and not just a silicate.
Complete step by step solution:
The general formula for silicates is defined to be ${{[Si{{O}_{(4-x)}}^{(4-2x)-}]}_{n}}$ for $0\le x<2$. From this formula, we can safely rule out options ‘A. $Si{{O}^{-}}$’ and ‘D. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{2-}$’ as the correct answers.
Silicates include orthosilicates, metasilicates, and pyrosilicates with the structural formulae of $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$, $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$, and $S{{i}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}^{6-}$ respectively Usually when referring to silicates, the most standard form of a silicate is referred to, the orthosilicate which is tetrahedrally arranged.
The silicon atom in orthosilicate is $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized and the 4 oxygen atoms are present at 4 corners of the tetrahedron. Orthosilicate compounds are found in various ores of minerals like granite, feldspar, and others.
The structure of the orthosilicate anion is:

Hence, the answer to this question is ‘B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$’
Additional information:
The bond length in the orthosilicate anion is 162pm and the bond angle is $109.5{}^\circ $. This is exactly the bond angle that is predicted for tetrahedral structures that do not have any lone pairs or dipole moments.
Note: Although options ‘B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$’ and ‘C. $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$’ are both considered to be silicates, the correct answer is ‘B. $Si{{O}_{4}}^{4-}$’ since $Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$ is always explicitly described to be a metasilicate and not just a silicate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




