
The condition for obtaining secondary maxima in the diffraction pattern due to single slit is:
A) $a\sin \theta = \dfrac{{n\lambda }}{2}$
B) $a\sin \theta = \dfrac{{(2n - 1)\lambda }}{2}$
C) $a\sin \theta = n\lambda $
D) $a\sin \theta = (2n - 1)\lambda $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Diffraction of light is the property of light bending around the corners such that it spreads out and illuminates areas. Diffraction is really hard to distinguish from interference as both occur simultaneously.
Complete answer:
The diffraction from a single slit gives a characteristics pattern. Diffusion effects are usually noticeable with the slit with size not very much larger than the wavelength.

The above diagram represents a laser illuminating a single slit and a double slit and the resultant pattern is projected on the screen. The pattern is maximum at centre as the light travels from an equal distance from the slit .The central pattern is broad and is equally spaced from either side with weaker maxima.
For calculating first order minima, assuming a slit width a and divide it in two equal halves .From Huygens principle and considering parallel rays from the both sides at angle to the axis of symmetry.
The ray that will come from a distance of a/2 from below will travel extra distance $\left( {a\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$ when the distance is half the wavelength then $a\sin \theta = \lambda .$
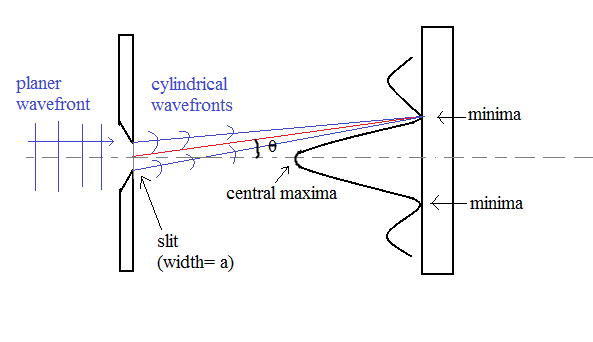 For maxima, the distance between two nth second maxima with central maxima is calculated
For maxima, the distance between two nth second maxima with central maxima is calculated
as: ${x_n} = D\theta = \dfrac{{(2n + 1)}}{{2b}} = \dfrac{{(2n + 1)\lambda f}}{{2b}}$
Where \[b = a\] (width of the slit)
Therefore the diffraction pattern due to single slit for secondary maxima is:
$a\sin \theta = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Where, $n = 2,3,4,..$
Hence option (B) is the correct option.
Note: Diffractions are only observed with waves travelling in two dimension or three dimension. Diffraction is interference phenomenon where interference of an infinite number of waves emitted by a continuous distribution of source points in two or three dimensions.
Complete answer:
The diffraction from a single slit gives a characteristics pattern. Diffusion effects are usually noticeable with the slit with size not very much larger than the wavelength.

The above diagram represents a laser illuminating a single slit and a double slit and the resultant pattern is projected on the screen. The pattern is maximum at centre as the light travels from an equal distance from the slit .The central pattern is broad and is equally spaced from either side with weaker maxima.
For calculating first order minima, assuming a slit width a and divide it in two equal halves .From Huygens principle and considering parallel rays from the both sides at angle to the axis of symmetry.
The ray that will come from a distance of a/2 from below will travel extra distance $\left( {a\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$ when the distance is half the wavelength then $a\sin \theta = \lambda .$
 For maxima, the distance between two nth second maxima with central maxima is calculated
For maxima, the distance between two nth second maxima with central maxima is calculated as: ${x_n} = D\theta = \dfrac{{(2n + 1)}}{{2b}} = \dfrac{{(2n + 1)\lambda f}}{{2b}}$
Where \[b = a\] (width of the slit)
Therefore the diffraction pattern due to single slit for secondary maxima is:
$a\sin \theta = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Where, $n = 2,3,4,..$
Hence option (B) is the correct option.
Note: Diffractions are only observed with waves travelling in two dimension or three dimension. Diffraction is interference phenomenon where interference of an infinite number of waves emitted by a continuous distribution of source points in two or three dimensions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




