
The coordination number of an atom in a fcc lattice is:
(A) 12
(B) 8
(C) 4
(D) 6
Answer
522.1k+ views
Hint:
In a fcc lattice there is one constituent particle at each corner and one at the centre of each face. The number of nearest neighbours is called coordination number.
Complete step by step answer:
A face centred cubic unit cell contains atoms at all the corners of the unit cell and at the centre of all the faces of the cube.
Coordination number is the number of other atoms that each atom in a crystalline solid contacts. In simple words the number of nearest neighbours of an atom forms the coordination number.
In an fcc unit cell the total number of atoms is:
(a) 8 corner atoms with each one contributing $1/8$ of it to the unit cell = 1 atom
(b) 6 face centre atoms with each one contributing $1/2$ of it to the unit cell = 3 atoms
So, a total of 4 atoms in an fcc unit cell.
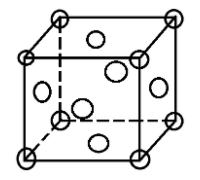
In an fcc structure atoms are packed as closely to each other as possible and the 4 atoms occupy 74% of the volume of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α = β = γ = 90$^{\circ}$
In an fcc lattice the face centre atoms are the nearest atoms and one corner atom is surrounded by 4 faces in the x-plane, 4 faces in the y-plane and 4 faces in the z-plane. So, every corner atom is surrounded by (4 × 3) = 12 face centre atoms. Since they are the nearest they form the coordination number.
Also if we consider the atom at the face centre, it is surrounded by 4 corner atoms of its own plane and the 8 adjacent face centred atoms (4 from above and 4 from below). This also makes the coordination number to be 12.
Hence, the coordination number of an fcc lattice is 12.
So, the correct option is (A).
Note:
While imagining the structure of the fcc unit cell, always be precise regarding the position of the atoms. Also remember that there are 4 faces associated with the 3 axes.
In a fcc lattice there is one constituent particle at each corner and one at the centre of each face. The number of nearest neighbours is called coordination number.
Complete step by step answer:
A face centred cubic unit cell contains atoms at all the corners of the unit cell and at the centre of all the faces of the cube.
Coordination number is the number of other atoms that each atom in a crystalline solid contacts. In simple words the number of nearest neighbours of an atom forms the coordination number.
In an fcc unit cell the total number of atoms is:
(a) 8 corner atoms with each one contributing $1/8$ of it to the unit cell = 1 atom
(b) 6 face centre atoms with each one contributing $1/2$ of it to the unit cell = 3 atoms
So, a total of 4 atoms in an fcc unit cell.

In an fcc structure atoms are packed as closely to each other as possible and the 4 atoms occupy 74% of the volume of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α = β = γ = 90$^{\circ}$
In an fcc lattice the face centre atoms are the nearest atoms and one corner atom is surrounded by 4 faces in the x-plane, 4 faces in the y-plane and 4 faces in the z-plane. So, every corner atom is surrounded by (4 × 3) = 12 face centre atoms. Since they are the nearest they form the coordination number.
Also if we consider the atom at the face centre, it is surrounded by 4 corner atoms of its own plane and the 8 adjacent face centred atoms (4 from above and 4 from below). This also makes the coordination number to be 12.
Hence, the coordination number of an fcc lattice is 12.
So, the correct option is (A).
Note:
While imagining the structure of the fcc unit cell, always be precise regarding the position of the atoms. Also remember that there are 4 faces associated with the 3 axes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




