
The correct curve between admittance (Y) and frequency (f) in an anti-resonant circuit will be
A)
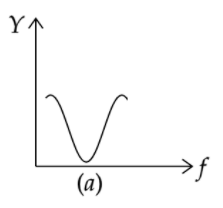
B)
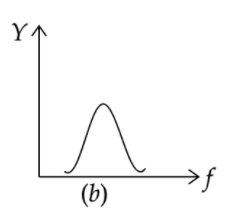
C)
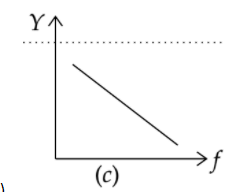
D)
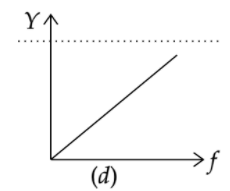
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Let us discuss in brief about an anti-resonant circuit. A parallel circuit containing a resistor, an inductor and a capacitor will produce an anti-resonance circuit (also called parallel resonance circuit) if the net current through the combination is in phase with the voltage. The remarkable point is that at resonance, the anti-resonant circuit produces the same equation as for the series resonance circuit.
Formula Used:
\[Y=\dfrac{1}{Z}\] , \[Z=\dfrac{V}{I}\]
Complete step by step solution:
In the hint section, we mentioned that the formula for the anti-resonant circuit is the same as that for a series resonance circuit. As such, it should make no difference if the inductor or capacitor are connected in parallel or series. But that is not the case.
In the anti-resonant circuit, the reactance (which is the resistance due to capacitor and inductor) of the circuit is maximum. If the impedance of a circuit is at its maximum, then consequently, the admittance must be at its minimum. The relation between admittance and impedance can be given as \[Y=\dfrac{1}{Z}\] where \[Y\] is the admittance and \[Z\] is the impedance. The current and the impedance can be related as \[Z=\dfrac{V}{I}\] where \[V\] denotes the voltage and \[I\] denotes the current. The admittance can hence be written as \[Y=\dfrac{I}{V}\] . Thus, if the reactance of the circuit is at maximum, it implies that the current in the circuit will be at a minimum.
Among the options given above, option (A) is the only option that depicts admittance attaining a minimum value.
Therefore, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: In contrast to the series resonance circuit, the resistor in an anti-resonant circuit has a damping effect on the circuit bandwidth. Also, since the current is constant for any value of impedance, the waveform of the voltage for an anti-resonant circuit will have the same shape as that of the total impedance.
Formula Used:
\[Y=\dfrac{1}{Z}\] , \[Z=\dfrac{V}{I}\]
Complete step by step solution:
In the hint section, we mentioned that the formula for the anti-resonant circuit is the same as that for a series resonance circuit. As such, it should make no difference if the inductor or capacitor are connected in parallel or series. But that is not the case.
In the anti-resonant circuit, the reactance (which is the resistance due to capacitor and inductor) of the circuit is maximum. If the impedance of a circuit is at its maximum, then consequently, the admittance must be at its minimum. The relation between admittance and impedance can be given as \[Y=\dfrac{1}{Z}\] where \[Y\] is the admittance and \[Z\] is the impedance. The current and the impedance can be related as \[Z=\dfrac{V}{I}\] where \[V\] denotes the voltage and \[I\] denotes the current. The admittance can hence be written as \[Y=\dfrac{I}{V}\] . Thus, if the reactance of the circuit is at maximum, it implies that the current in the circuit will be at a minimum.
Among the options given above, option (A) is the only option that depicts admittance attaining a minimum value.
Therefore, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: In contrast to the series resonance circuit, the resistor in an anti-resonant circuit has a damping effect on the circuit bandwidth. Also, since the current is constant for any value of impedance, the waveform of the voltage for an anti-resonant circuit will have the same shape as that of the total impedance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




