
The cyclopentadienyl cation is antiaromatic while the cyclopentadienyl anion is aromatic. If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: (1) A compound is said to be aromatic if it is cyclic and has planar ring, and also it must have cyclic delocalized pi-electron clouds lying above and below the plane of the ring.
(2) It must also follow Huckel’s $(4n+2)\pi$ electron rule where n is any integer.
(3) For antiaromaticity, the rule is that the molecule must have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons where n is any integer.
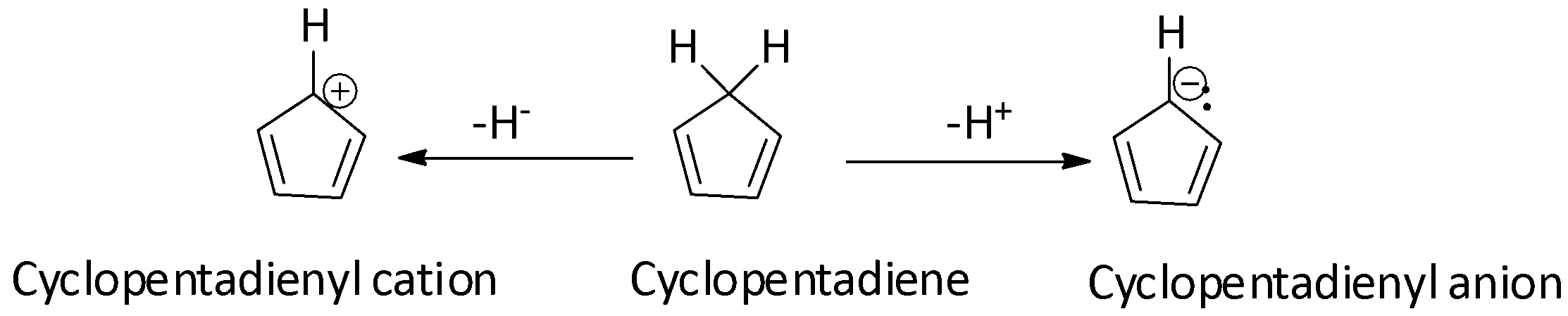
Complete step-by-step answer: Both the cyclopentadienyl cation and cyclopentadienyl anion are formed from cyclopentadiene by the loss of a hydride ion and the abstraction of a proton respectively. Cyclopentadiene is not an aromatic compound because of the presence of a ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon on its ring due to which it does not contain an uninterrupted cyclic pi-electron cloud. When a hydride anion $\left( {{{\text{H}}^{\text{ - }}}} \right)$ is removed from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl cation will be formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$to${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl cation formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. However, it fails to meet the Huckel’s rule of aromaticity as it does not have $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons and so it is not aromatic. But, it does have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 4 pi electrons). Hence, it is antiaromatic.
When a proton is abstracted from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl anion is formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ to ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl anion formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. Moreover, it also satisfies the Huckel’s rule for aromaticity as it has $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 6 pi electrons) and so it is aromatic. Thus, the cyclopentadienyl anion is an aromatic compound.
Thus, the given statement is true and so 1.
Note: In the $(4n+2)\pi$ rule, n is not a property of the molecule. This rule is applied just to generate a series: n is equal to 2, 6, 10, 14 etc. and if our pi electron value matches any number in this series, then it possesses aromaticity.
(2) It must also follow Huckel’s $(4n+2)\pi$ electron rule where n is any integer.
(3) For antiaromaticity, the rule is that the molecule must have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons where n is any integer.
Complete step-by-step answer: Both the cyclopentadienyl cation and cyclopentadienyl anion are formed from cyclopentadiene by the loss of a hydride ion and the abstraction of a proton respectively. Cyclopentadiene is not an aromatic compound because of the presence of a ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon on its ring due to which it does not contain an uninterrupted cyclic pi-electron cloud. When a hydride anion $\left( {{{\text{H}}^{\text{ - }}}} \right)$ is removed from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl cation will be formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$to${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl cation formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. However, it fails to meet the Huckel’s rule of aromaticity as it does not have $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons and so it is not aromatic. But, it does have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 4 pi electrons). Hence, it is antiaromatic.
When a proton is abstracted from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl anion is formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ to ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl anion formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. Moreover, it also satisfies the Huckel’s rule for aromaticity as it has $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 6 pi electrons) and so it is aromatic. Thus, the cyclopentadienyl anion is an aromatic compound.

Thus, the given statement is true and so 1.
Note: In the $(4n+2)\pi$ rule, n is not a property of the molecule. This rule is applied just to generate a series: n is equal to 2, 6, 10, 14 etc. and if our pi electron value matches any number in this series, then it possesses aromaticity.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




