
The equation for Freundlich adsorption isotherm is:
A. \[\dfrac{x}{m} = K{p^{1/n}}\]
B. \[x = mK{p^{1/n}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{x}{m} = K{p^{ - n}}\]
D. All of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: From the name itself, it becomes clear that Freundlich adsorption isotherm is a curve that expresses the variation in the amount of gas adsorbed by the adsorbent with the temperature at the constant pressure.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is an empirical relation between the concentrations of a solute on the surface of an adsorbent to the concentration of the solute present in the liquid. Freundlich equation is an expression which represents the isothermal variation of adsorption of a gas adsorbed on a unit mass solid adsorbent with pressure. Adsorption is an attractive interaction between atoms, molecules or ions of a gas or liquid to a surface or deposition of molecular species on a surface called adsorbent.
Its mathematical expression can be analysed as:
\[\dfrac{x}{m} = K{p^{1/n}}\](\[n > {\text{ }}1\])
Where, x is the mass of the adsorbent, k and n are constants that depend on the nature of adsorbent and the gas at a specific temperature .Adsorption factors consists of temperature, pore-volume, degree of saturation, molecular sieve, type of adsorbent, and surface area.
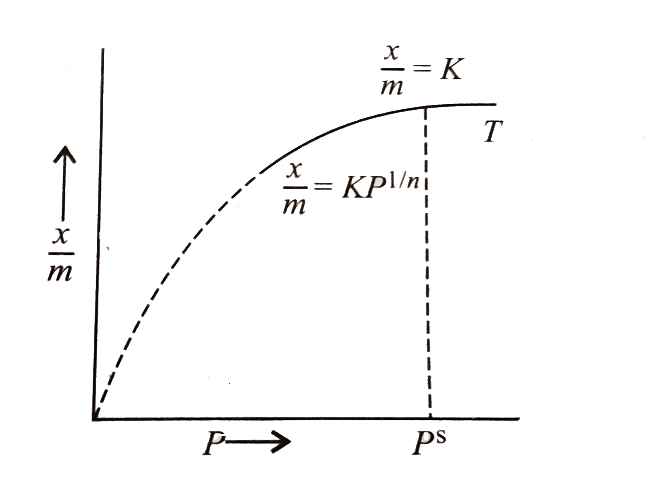
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: One might get confused between adsorption and absorption. They seem similar but are totally different as absorption is a bulk process in which the particles go into the bulk of the solvent while adsorption is a surface phenomenon in which the particles remain stuck to the surface of the solvent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Freundlich adsorption isotherm is an empirical relation between the concentrations of a solute on the surface of an adsorbent to the concentration of the solute present in the liquid. Freundlich equation is an expression which represents the isothermal variation of adsorption of a gas adsorbed on a unit mass solid adsorbent with pressure. Adsorption is an attractive interaction between atoms, molecules or ions of a gas or liquid to a surface or deposition of molecular species on a surface called adsorbent.
Its mathematical expression can be analysed as:
\[\dfrac{x}{m} = K{p^{1/n}}\](\[n > {\text{ }}1\])
Where, x is the mass of the adsorbent, k and n are constants that depend on the nature of adsorbent and the gas at a specific temperature .Adsorption factors consists of temperature, pore-volume, degree of saturation, molecular sieve, type of adsorbent, and surface area.

Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: One might get confused between adsorption and absorption. They seem similar but are totally different as absorption is a bulk process in which the particles go into the bulk of the solvent while adsorption is a surface phenomenon in which the particles remain stuck to the surface of the solvent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




