
The formal charges of C and O atoms in $C{O_2}$ are respectively:
A. 1,-1
B. -1,1
C. 2,-1
D. 0,0
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Chemical bonding refers to the formation of a chemical bond between two or more atoms, molecules, or ions to give rise to a chemical compound. These chemical bonds are what keeps the atoms together in the resulting compound. Moreover, formal charge is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity.
Complete step by step answer:
Formal charge is used to predict the most correct structure. Now, in the question we are given $C{O_2}$ molecule. Now, let’s draw all the resonating structures.
These are the resonating structures:
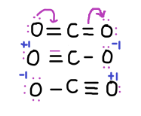
Now, $C{O_2}$ is a neutral molecule with 16 valence electrons. A valence electron is an outer shell electron that is associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed.
Further, let us consider all the three ways possible.
First, carbon single bonded to both oxygen atoms. (Carbon+2, oxygen-1 each, so total formal charge is 0)
Second, carbon single bonded to one oxygen and double bonded to another. (Carbon= $ + 1$, oxygen double=0, oxygen single= -1, so total formal charge is 0)
Third, carbon double bonded to both oxygen atoms (carbon=0, oxygen=0 so formal charge=0
Therefore, the formal charge of the C and O atom in $C{O_2}$ molecule is zero.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Carbon dioxide becomes a poisonous gas when inhaled in large amounts. It can lead to many respiratory disorders and can cause severe damage to the nervous system. $C{O_2}$ in the form of liquid and solid is used for refrigeration and cooling. It is used as an inert gas in various chemical processes. It is also used in the manufacture of casting molds in order to enhance their hardness.
Complete step by step answer:
Formal charge is used to predict the most correct structure. Now, in the question we are given $C{O_2}$ molecule. Now, let’s draw all the resonating structures.
These are the resonating structures:
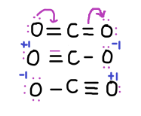
Now, $C{O_2}$ is a neutral molecule with 16 valence electrons. A valence electron is an outer shell electron that is associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed.
Further, let us consider all the three ways possible.
First, carbon single bonded to both oxygen atoms. (Carbon+2, oxygen-1 each, so total formal charge is 0)
Second, carbon single bonded to one oxygen and double bonded to another. (Carbon= $ + 1$, oxygen double=0, oxygen single= -1, so total formal charge is 0)
Third, carbon double bonded to both oxygen atoms (carbon=0, oxygen=0 so formal charge=0
Therefore, the formal charge of the C and O atom in $C{O_2}$ molecule is zero.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Carbon dioxide becomes a poisonous gas when inhaled in large amounts. It can lead to many respiratory disorders and can cause severe damage to the nervous system. $C{O_2}$ in the form of liquid and solid is used for refrigeration and cooling. It is used as an inert gas in various chemical processes. It is also used in the manufacture of casting molds in order to enhance their hardness.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




