
The \[{{\left[ Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}\]complex ion:
(A) Exhibits planar geometry
(B) Is diamagnetic
(C) Should be very stable
(D) has 2 unpaired electrons.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The\[C{{N}^{-}}\]is a strong field ligand. \[{{\left[ Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}\]will form an inner orbital complex. Finding the oxidation state of iron will help in determining its hybridization.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given \[{{\left[ Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}\]as our coordination complex. Now first let us find out the oxidation number of iron. As you already know, the cyanide ion has an oxidation number of “$-1$”; taking iron atom’s oxidation state as “x” we form the following equation:
\[\begin{align}
& x+6(-1)=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow x=+3 \\
\end{align}\]
So iron can be seen as- $F{{e}^{3+}}$ . The atomic number of iron is $26$; its electronic configuration becomes: $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{6}}$. The arrangement of electrons in its orbital is as follows:
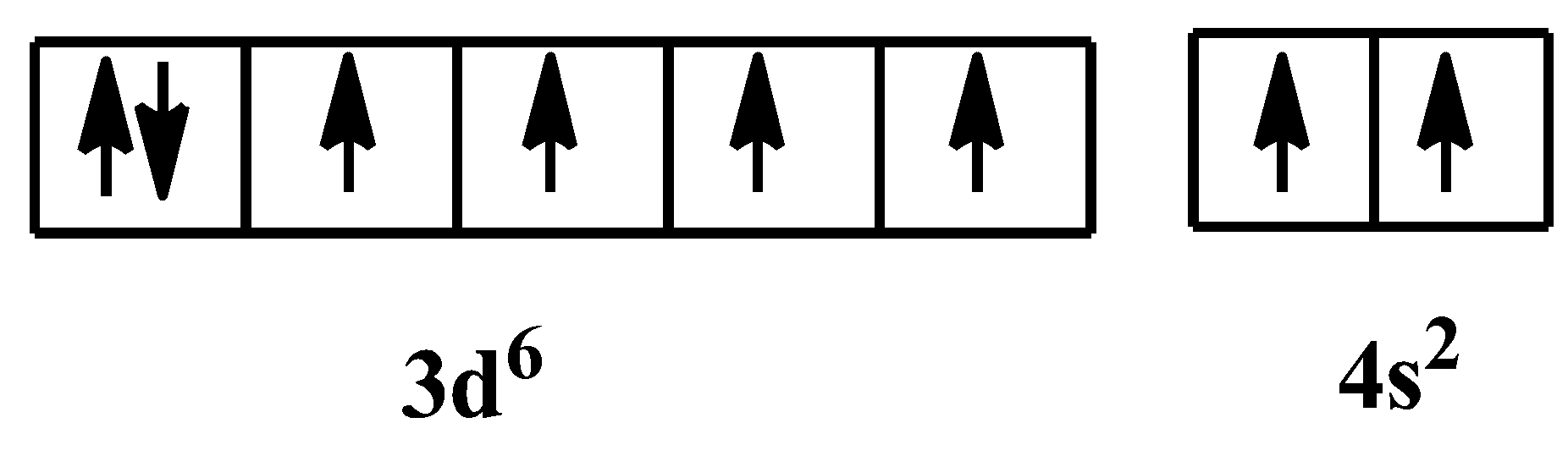
In $F{{e}^{3+}}$ state, its electronic configuration would be:
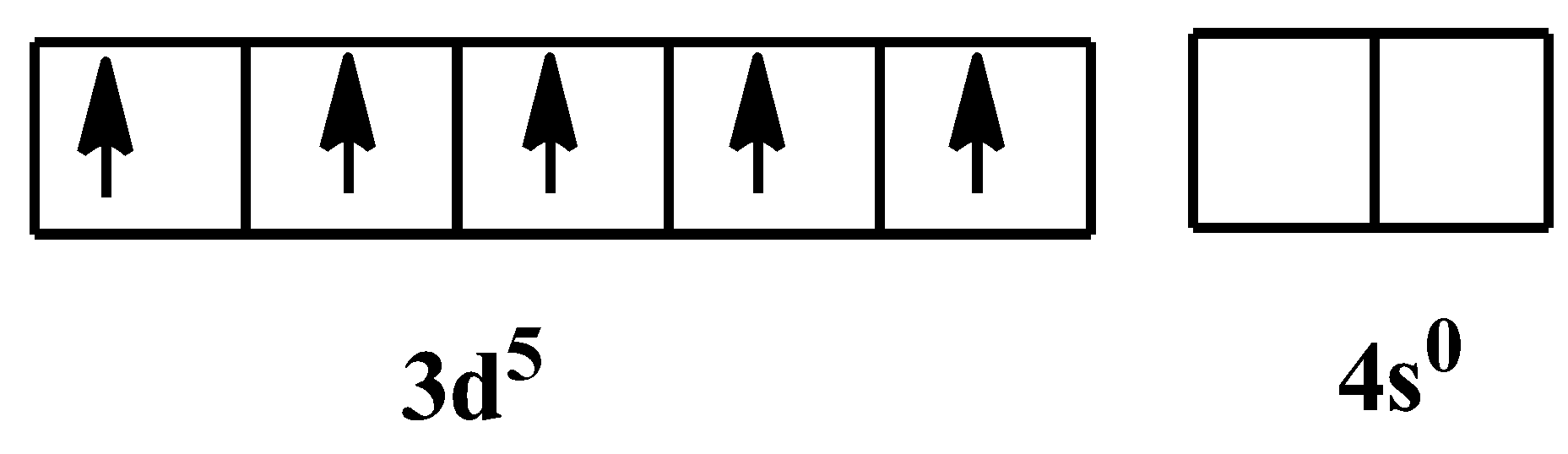
As it is mentioned already in the hint, that cyanide is a strong field ligand, which means it will always form low spin complexes. As there are six of them, so the hybridization would be ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$, which is for octahedral geometry. The orbital configuration in the presence of the ligand would be-

So, the orbital configuration when the ligands would have donated their electrons is:
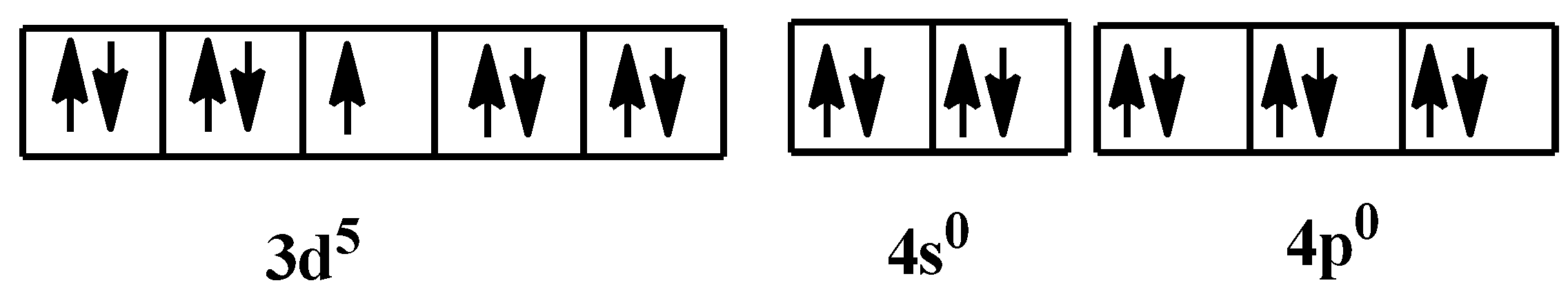
As you can see, there is one unpaired electron. This makes the coordinate complex paramagnetic in nature. From all the options, only option C is correct. Indeed, the compound is very stable.
Note:
Sometimes, these strong field ligands form low spin complexes. Although these occurrences are very rare, students are still advised to memorize some of these exceptions. Cyanide and CO are some of these.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given \[{{\left[ Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}\]as our coordination complex. Now first let us find out the oxidation number of iron. As you already know, the cyanide ion has an oxidation number of “$-1$”; taking iron atom’s oxidation state as “x” we form the following equation:
\[\begin{align}
& x+6(-1)=-3 \\
& \Rightarrow x=+3 \\
\end{align}\]
So iron can be seen as- $F{{e}^{3+}}$ . The atomic number of iron is $26$; its electronic configuration becomes: $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{6}}$. The arrangement of electrons in its orbital is as follows:

In $F{{e}^{3+}}$ state, its electronic configuration would be:

As it is mentioned already in the hint, that cyanide is a strong field ligand, which means it will always form low spin complexes. As there are six of them, so the hybridization would be ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$, which is for octahedral geometry. The orbital configuration in the presence of the ligand would be-

So, the orbital configuration when the ligands would have donated their electrons is:

As you can see, there is one unpaired electron. This makes the coordinate complex paramagnetic in nature. From all the options, only option C is correct. Indeed, the compound is very stable.
Note:
Sometimes, these strong field ligands form low spin complexes. Although these occurrences are very rare, students are still advised to memorize some of these exceptions. Cyanide and CO are some of these.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




