
The magnetic field is made radial in a galvanometer
(A) To make field stronger
(B) To make field weaker
(C) To make scale linear
(D) To reduce its resistance
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The magnetic field is made radial in a galvanometer to concentrate the field in a circular region uniformly in all directions and hence, make it linear in angular direction.
Complete step by step solution
Let us briefly recap what the purpose and design goal of a galvanometer is and what is the purpose of the radial magnetic field in it. The moving coil galvanometer consists of a rectangular coil with a huge number of windings of a thin insulated copper wire. This coil is suspended between the poles of a permanent magnet having hemispherical poles (like in a horseshoe magnet). The purpose of making the poles hemispherical is to apply a uniform radial magnetic field over the coil.
Had the magnetic field not been radial, the magnetic field and eventually, the magnetic flux through the coil would vary at different angular positions of the coil. Hence there would be unnecessary spikes and unresponsiveness in the galvanometer. We need the rotation to be smooth i.e. the angle of rotation should increase linearly with increase in the current.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Here is a diagram of a moving coil galvanometer for better understanding.
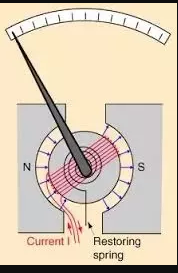
As you can see from the diagram, a radial magnetic field will ensure that there is always a component of magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the coil to ensure maximum magnetic flux/field/torque.
Complete step by step solution
Let us briefly recap what the purpose and design goal of a galvanometer is and what is the purpose of the radial magnetic field in it. The moving coil galvanometer consists of a rectangular coil with a huge number of windings of a thin insulated copper wire. This coil is suspended between the poles of a permanent magnet having hemispherical poles (like in a horseshoe magnet). The purpose of making the poles hemispherical is to apply a uniform radial magnetic field over the coil.
Had the magnetic field not been radial, the magnetic field and eventually, the magnetic flux through the coil would vary at different angular positions of the coil. Hence there would be unnecessary spikes and unresponsiveness in the galvanometer. We need the rotation to be smooth i.e. the angle of rotation should increase linearly with increase in the current.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Here is a diagram of a moving coil galvanometer for better understanding.

As you can see from the diagram, a radial magnetic field will ensure that there is always a component of magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the coil to ensure maximum magnetic flux/field/torque.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




