
The maximum tendency to form unipositive ion is for the element with the electronic configuration:
(A) $1{s^2},2{s^2},2{p^6},3{s^2}$
(B) $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}3{p^1}$
(C) $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}3{p^2}$
(D) $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}3{p^3}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Stability of molecule can be explained the basis of symmetry.
Therefore, all orbitals of the same subshell are either completely filled or are exactly half filled and are more stable because there is a symmetrical distribution of electrons.
This can be explained by the following diagram.
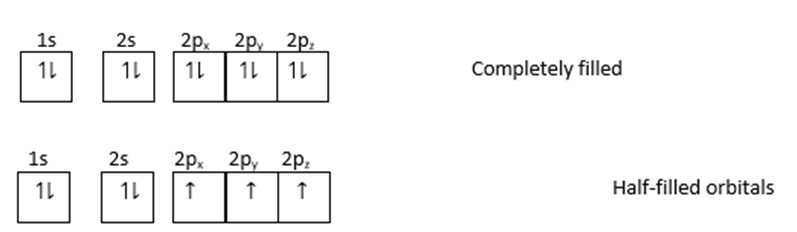
The above orbitals show stability.
Complete step by step answer:
Unipositive ions are those ions which are formed by dissing one electron from its outermost orbit.
For example:
$Na - 2,8,1$lose electron
$N{a^ + } - 2,8$unipositive ion
Atoms lose ions and form positive ions in such a way that it can attain stable configuration.
Stable configurations either have completely filled orbitals or half-filled orbitals.
Therefore, from above discusses we conclude that the maximum tendency to form unipositive ion is
(1) For element:$1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}$
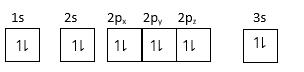
As $3s$ orbital is completely filled, so it forms stable configuration.
(2) For element: $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}3{p^1}$
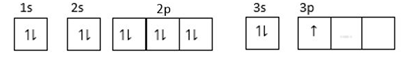
$3p$ is orbital is incompletely filled so does not form unipositive ions.
(3) For element: $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^2}$
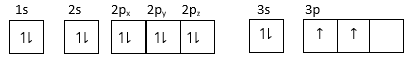
3p orbital has one unpaired electron so it can form a unipositive ion by closing one electron and attaining stable configuration.
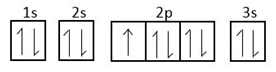
Element in form of unipositive ion.
Not completely filled so it does not form a unipositive ion.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (B)
Note: Filling of orbitals explain with the help of Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity. This rule deals with filling of electrons into a degenerate [equal energy] orbital of the same subshell like p. d. f.
Electron pairs in p, d and f orbitals cannot occur until each orbital contains one electron each. The term maximum multiplicity means that the total spin of an unpaired electron is maximum.
Therefore, all orbitals of the same subshell are either completely filled or are exactly half filled and are more stable because there is a symmetrical distribution of electrons.
This can be explained by the following diagram.

The above orbitals show stability.
Complete step by step answer:
Unipositive ions are those ions which are formed by dissing one electron from its outermost orbit.
For example:
$Na - 2,8,1$lose electron
$N{a^ + } - 2,8$unipositive ion
Atoms lose ions and form positive ions in such a way that it can attain stable configuration.
Stable configurations either have completely filled orbitals or half-filled orbitals.
Therefore, from above discusses we conclude that the maximum tendency to form unipositive ion is
(1) For element:$1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}$

As $3s$ orbital is completely filled, so it forms stable configuration.
(2) For element: $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6},3{s^2}3{p^1}$

$3p$ is orbital is incompletely filled so does not form unipositive ions.
(3) For element: $1{s^2},2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^2}$

3p orbital has one unpaired electron so it can form a unipositive ion by closing one electron and attaining stable configuration.

Element in form of unipositive ion.
Not completely filled so it does not form a unipositive ion.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (B)
Note: Filling of orbitals explain with the help of Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity. This rule deals with filling of electrons into a degenerate [equal energy] orbital of the same subshell like p. d. f.
Electron pairs in p, d and f orbitals cannot occur until each orbital contains one electron each. The term maximum multiplicity means that the total spin of an unpaired electron is maximum.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




