
The melting points of amino-acids are higher than the corresponding halo-acids because?
(a) Amino acids exist as zwitterion resulting in strong dipole-dipole interaction.
(b) Amino acids are optically active.
(c) Due to higher molecular mass of $-{ NH }_{ 2 }$ group molecular mass of amino acids is higher.
(d) They interact with water more than halo-acids and have salt-like structure.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:In Amino acids, $ -{ NH }_{ 2 }$ (basic) and $ -COOH$ (acidic) groups are present as functional groups and they can be classified as $ \alpha -,\quad \beta -,\quad \gamma -,\quad \delta -,$ etc. depending upon the relative position of the $ -{ NH }_{ 2 }$ group with respect to the $ -COOH$ group .
Complete step by step answer:
There are a total of twenty six $\alpha -$amino acids that are found in proteins and they differ based on the nature of their side chain groups that determines the properties of the protein.
$\alpha -$amino acids possess the following properties:
-They are colourless, non-volatile crystalline solids.
-They melt with decomposition at very high temperatures.
-They are soluble in water but are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
-They exist as internal salt or zwitterion: Since amino acids contain both an acidic group (carboxyl group) and a basic group (amino group), they neutralise each other through the transfer of a proton from the carboxyl group to the amino group present in the molecule. The resultant ion is called a dipolar ion.
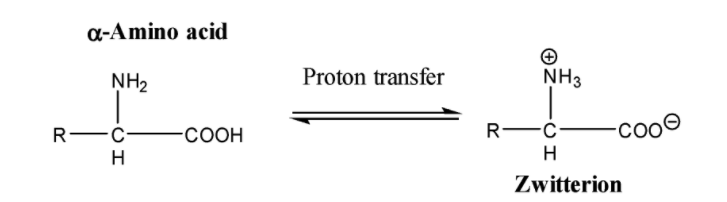
It is because of this zwitterion structure that the $\alpha -$amino acids have a crystalline structure and possess a high melting point.
Halo-acids are halogen derivatives of the carboxylic acids example 2-Chlorocarboxylic acids. Because they do comprise of halogen and –COOH groups, these molecules will possess dipole-dipole interactions but amino acids consist of stronger dipole-dipole interactions as well as electrostatic forces of attractions because of their dipolar nature.
Hence the correct answer is (a) Amino acids exist as zwitterion resulting in strong dipole-dipole interaction.
Note:
The chemical properties of the members of a homologous series similar though the first member may vary considerably from the rest of the members. The successive members of a homologous series differ by a \[C{{H}_{2}}\] group or by 14 mass units.
Complete step by step answer:
There are a total of twenty six $\alpha -$amino acids that are found in proteins and they differ based on the nature of their side chain groups that determines the properties of the protein.
$\alpha -$amino acids possess the following properties:
-They are colourless, non-volatile crystalline solids.
-They melt with decomposition at very high temperatures.
-They are soluble in water but are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
-They exist as internal salt or zwitterion: Since amino acids contain both an acidic group (carboxyl group) and a basic group (amino group), they neutralise each other through the transfer of a proton from the carboxyl group to the amino group present in the molecule. The resultant ion is called a dipolar ion.

It is because of this zwitterion structure that the $\alpha -$amino acids have a crystalline structure and possess a high melting point.
Halo-acids are halogen derivatives of the carboxylic acids example 2-Chlorocarboxylic acids. Because they do comprise of halogen and –COOH groups, these molecules will possess dipole-dipole interactions but amino acids consist of stronger dipole-dipole interactions as well as electrostatic forces of attractions because of their dipolar nature.
Hence the correct answer is (a) Amino acids exist as zwitterion resulting in strong dipole-dipole interaction.
Note:
The chemical properties of the members of a homologous series similar though the first member may vary considerably from the rest of the members. The successive members of a homologous series differ by a \[C{{H}_{2}}\] group or by 14 mass units.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




