
The radius of the bore of a capillary tube is $r$ and the angle of contact is $\theta $. When the tube of sufficient length is dipped in the liquid, the radius of curvature of the meniscus of the liquid rising in the tube is
(A) \[r\sin \theta \]
(B) $rcos\theta $
(C) $\dfrac{r}{{\sin \theta }}$
(D) $\dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint We proceed to solve this question by drawing a triangle in the meniscus region. Using properties of a triangle as well as trigonometry we find the radius of curvature of the meniscus. We can say that the meniscus formed is a concave meniscus because the liquid is rising in the tube. In the case of the convex meniscus, the liquid in the tube goes below the surface of the liquid.
Complete Step by step solution
The meniscus formed is a concave meniscus because from the question the liquid is rising in the capillary tube.
Pictorial representation of the meniscus
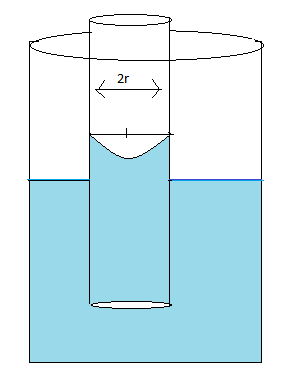
Here,
Radius of the capillary tube is represented by $r$
The same diagram can be made as follows
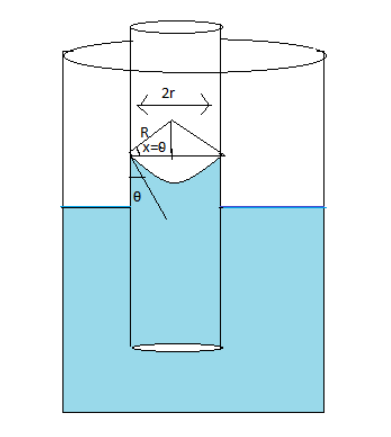
The radius of curvature of the meniscus is represented by $R$
The angle of contact is represented by $\theta $
From the angle of contact angle \[x\] is equal to $\theta $
From the diagram, the bigger triangle is a combination of two right-angled triangles
Taking the triangle on the left side under consideration and using \[cos\theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{hyp}}\] equal to \[cos\theta = \dfrac{r}{R}\]
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$
Hence radius of curvature of the meniscus is equal to $\dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$
Option (D) $\dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$is the correct answer.
Additional information A concave meniscus is formed when the adhesive force (between liquid and container) is greater than the cohesive force (intermolecular forces). Due to this, a concave meniscus is formed. Also, when the liquid is placed in a capillary tube it rises due to the adhesive force being greater than the cohesive force.
In the case of a liquid with a greater cohesive force than adhesive force, a convex meniscus is formed.
Note One might make the mistake of taking the meniscus as a convex meniscus. A convex meniscus is formed when the liquid in the capillary tube goes below the surface level of the remaining liquid. This question mentions that the liquid in the capillary tube is rising hence it is a concave meniscus.
Complete Step by step solution
The meniscus formed is a concave meniscus because from the question the liquid is rising in the capillary tube.
Pictorial representation of the meniscus

Here,
Radius of the capillary tube is represented by $r$
The same diagram can be made as follows

The radius of curvature of the meniscus is represented by $R$
The angle of contact is represented by $\theta $
From the angle of contact angle \[x\] is equal to $\theta $
From the diagram, the bigger triangle is a combination of two right-angled triangles
Taking the triangle on the left side under consideration and using \[cos\theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{hyp}}\] equal to \[cos\theta = \dfrac{r}{R}\]
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$
Hence radius of curvature of the meniscus is equal to $\dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$
Option (D) $\dfrac{r}{{cos\theta }}$is the correct answer.
Additional information A concave meniscus is formed when the adhesive force (between liquid and container) is greater than the cohesive force (intermolecular forces). Due to this, a concave meniscus is formed. Also, when the liquid is placed in a capillary tube it rises due to the adhesive force being greater than the cohesive force.
In the case of a liquid with a greater cohesive force than adhesive force, a convex meniscus is formed.
Note One might make the mistake of taking the meniscus as a convex meniscus. A convex meniscus is formed when the liquid in the capillary tube goes below the surface level of the remaining liquid. This question mentions that the liquid in the capillary tube is rising hence it is a concave meniscus.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




