
The ratio of its rotational kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy of a sphere, which is rolling without slipping on a horizontal plane, will be:
(A) $5:2$
(B) $2:5$
(C) $7:5$
(D) $5:7$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint The kinetic energy of the body is the sum of its rotational kinetic energy and the translational kinetic energy about the center of mass of the rigid sphere. Here the center of mass is at the point $O$. Also, it has been given that there is no slip, i.e. the relative velocity of the point $A$ on both the sphere and the ground $0$. Therefore we have $v = \omega R$.
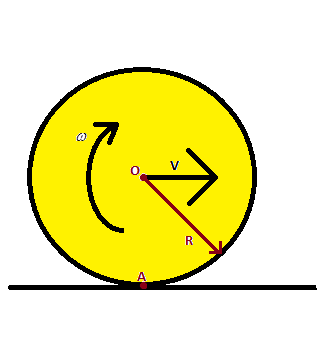
Complete Step by step solution We will separately calculate the rotational kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy and find their ratios. The rotational energy of any body is given by $\dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}$, where $I$ is the mass moment of inertia, and $\omega $ is the angular velocity about the center of mass of the body $O$.
This energy will vary with different objects as for various objects, the moment of inertia $I$ will vary.
For this solid sphere, $K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}(\dfrac{2}{5}M{r^2}){\omega ^2}$
Therefore, substituting $v = \omega R$ in $K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}(\dfrac{2}{5}M{r^2}){\omega ^2}$, we get
$ \Rightarrow K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}(\dfrac{2}{5}M{r^2}){(\dfrac{v}{r})^2}$,
$ \Rightarrow K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{5}M{v^2}$, where $v$ is the translational velocity at the center of mass of the body $O$.
Now we will find the translational kinetic energy of the solid sphere.
Translational kinetic energy is given by $K.E{._{translational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2}$
Now the ratio of the rotational kinetic energy to the translational kinetic energy is, $\dfrac{{K.E{._{rotational}}}}{{K.E{._{translational}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{5}M{v^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2}}} = \dfrac{2}{5}$
Hence the correct answer is an option (B).
Note Here we consider the sphere as a solid body. If the sphere would have been hollow, then the moment of inertia would be $\dfrac{{2M{R^2}}}{3}$, in which case the answer would be $\dfrac{{K.E{._{rotational}}}}{{K.E{._{translational}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{3}M{v^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2}}} = \dfrac{2}{3}$. The velocity at the contact between the ground and the sphere is $0$ and at the top, most point of the sphere is $v + R\omega $, which is equal to $2v$ , and is the fastest moving point on the sphere.

Complete Step by step solution We will separately calculate the rotational kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy and find their ratios. The rotational energy of any body is given by $\dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}$, where $I$ is the mass moment of inertia, and $\omega $ is the angular velocity about the center of mass of the body $O$.
This energy will vary with different objects as for various objects, the moment of inertia $I$ will vary.
For this solid sphere, $K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}(\dfrac{2}{5}M{r^2}){\omega ^2}$
Therefore, substituting $v = \omega R$ in $K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}(\dfrac{2}{5}M{r^2}){\omega ^2}$, we get
$ \Rightarrow K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}(\dfrac{2}{5}M{r^2}){(\dfrac{v}{r})^2}$,
$ \Rightarrow K.E{._{rotational}} = \dfrac{1}{5}M{v^2}$, where $v$ is the translational velocity at the center of mass of the body $O$.
Now we will find the translational kinetic energy of the solid sphere.
Translational kinetic energy is given by $K.E{._{translational}} = \dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2}$
Now the ratio of the rotational kinetic energy to the translational kinetic energy is, $\dfrac{{K.E{._{rotational}}}}{{K.E{._{translational}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{5}M{v^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2}}} = \dfrac{2}{5}$
Hence the correct answer is an option (B).
Note Here we consider the sphere as a solid body. If the sphere would have been hollow, then the moment of inertia would be $\dfrac{{2M{R^2}}}{3}$, in which case the answer would be $\dfrac{{K.E{._{rotational}}}}{{K.E{._{translational}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{3}M{v^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2}}} = \dfrac{2}{3}$. The velocity at the contact between the ground and the sphere is $0$ and at the top, most point of the sphere is $v + R\omega $, which is equal to $2v$ , and is the fastest moving point on the sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




