
The thermocouple is based on the principle of:
A) Seebeck effect
B) Thomson effect
C) Peltier effect
D) Joule effect
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A thermocouple is a sensor for measuring temperature. This sensor consists of two dissimilar metal wires, joined at one end, and connected to a thermocouple thermometer or other thermocouple-capable device at the other end.
A small thermoelectric current is generated when two different metal wires are put into contact at both ends with their junctions having a different temperature.
Complete answer:
Two dissimilar metals ‘A’ and ‘B’ are joined at the two junctions ‘P’ and ‘Q’. Here the ‘P’ junction is a hot junction whereas the junction ‘Q’ is a cold junction and a galvanometer is connected in this arrangement as shown in Figure.
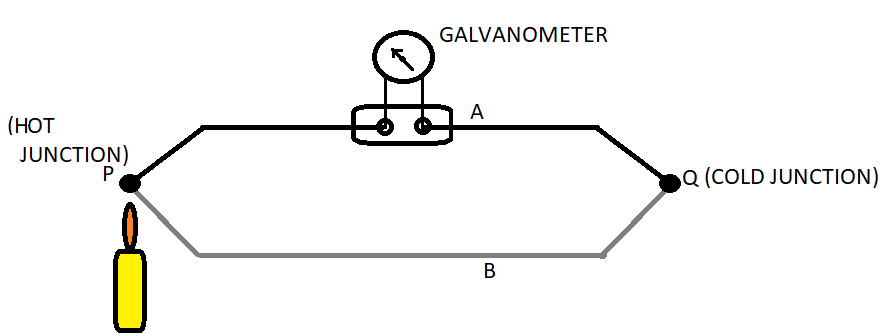
When these junctions are kept at different temperatures, generally cold junction is kept at $0^\circ $C and the hot junction is kept at an unknown temperature which we want to measure (i.e. the temperature of the junction is raised by heating it). An e.m.f. will be generated in this circuit due to the temperature gradient along the wire across the junctions.
When both the junctions are at different temperatures, a current will flow through the meter and the meter will show the deflection.
As the generated e.m.f. is proportional to the temperature difference, the amount of current flow will also be proportional to the temperature difference.
The working principle: Seebeck Effect
Seebeck Effect: This effect states that when a closed circuit is formed by joining two dissimilar metals at two junctions, and junctions are maintained at different temperatures then an electromotive force (e.m.f.) is induced in this closed circuit.
Final answer is A, Seebeck Effect.
We can see that in a thermocouple two dissimilar wires or electrical conductors are joined and a temperature difference is created between the junctions by heating one junction thus this temperature gradient produces a voltage difference between two junctions and the current starts flowing. This is the Seebeck effect.
Note: At the hot junction, electrons get energy and start moving towards the cold junction and this results in the flow of current in the thermocouple
When both the junctions are at the same temperature, e.m.f. generated at both junctions will be the same. No current will flow through the circuit. And there will be no deflection in the meter.
The amount of induced e.m.f. is different for different metal combinations and is proportional to the temperature difference of the junctions.
A small thermoelectric current is generated when two different metal wires are put into contact at both ends with their junctions having a different temperature.
Complete answer:
Two dissimilar metals ‘A’ and ‘B’ are joined at the two junctions ‘P’ and ‘Q’. Here the ‘P’ junction is a hot junction whereas the junction ‘Q’ is a cold junction and a galvanometer is connected in this arrangement as shown in Figure.

When these junctions are kept at different temperatures, generally cold junction is kept at $0^\circ $C and the hot junction is kept at an unknown temperature which we want to measure (i.e. the temperature of the junction is raised by heating it). An e.m.f. will be generated in this circuit due to the temperature gradient along the wire across the junctions.
When both the junctions are at different temperatures, a current will flow through the meter and the meter will show the deflection.
As the generated e.m.f. is proportional to the temperature difference, the amount of current flow will also be proportional to the temperature difference.
The working principle: Seebeck Effect
Seebeck Effect: This effect states that when a closed circuit is formed by joining two dissimilar metals at two junctions, and junctions are maintained at different temperatures then an electromotive force (e.m.f.) is induced in this closed circuit.
Final answer is A, Seebeck Effect.
We can see that in a thermocouple two dissimilar wires or electrical conductors are joined and a temperature difference is created between the junctions by heating one junction thus this temperature gradient produces a voltage difference between two junctions and the current starts flowing. This is the Seebeck effect.
Note: At the hot junction, electrons get energy and start moving towards the cold junction and this results in the flow of current in the thermocouple
When both the junctions are at the same temperature, e.m.f. generated at both junctions will be the same. No current will flow through the circuit. And there will be no deflection in the meter.
The amount of induced e.m.f. is different for different metal combinations and is proportional to the temperature difference of the junctions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




