
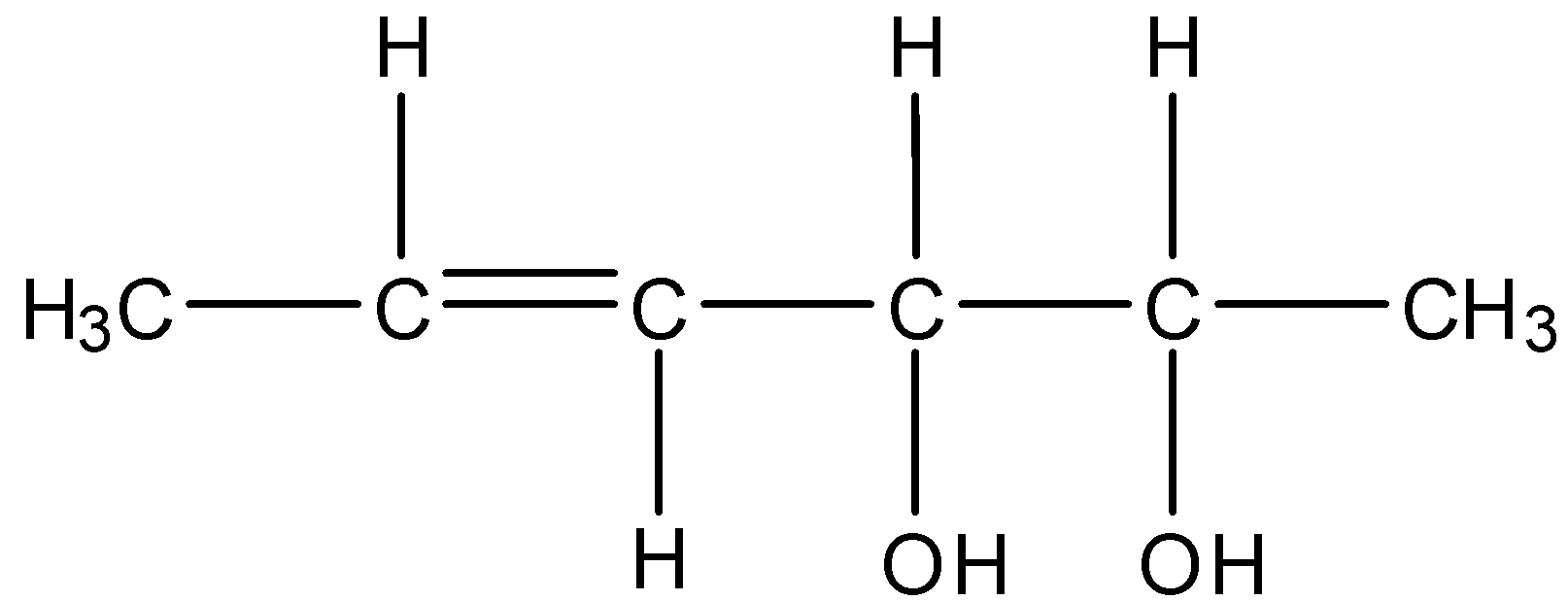
The total number of configurational isomers of the given compound are:
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Configurational isomers are the stereoisomers that cannot be converted into one another by rotation around a single bond in the molecule. There are two types of Configurational isomers. 1) Geometrical isomers and 2) optical isomers.
Complete step by step solution:
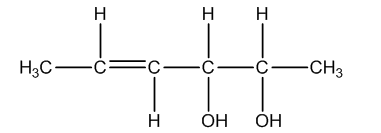
Total number of configurational isomers = geometrical isomers + optical isomers.
So, totally 8 configurational isomers are going to form by the given compound.
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Don’t be confused between geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism. The compounds that have double bonds will show geometrical isomerism and the compounds which have chiral centers show the optical isomerism. Both the isomerisms combined are called geometrical isomerism.
Complete step by step solution:
Geometrical isomerism is going to show by unsaturated compounds and optical isomerism is going to exhibit by the molecules that are having chiral carbons.
The given molecule contains six carbons, one double bond and two chiral centers.

Now we will talk about geometrical isomerism.
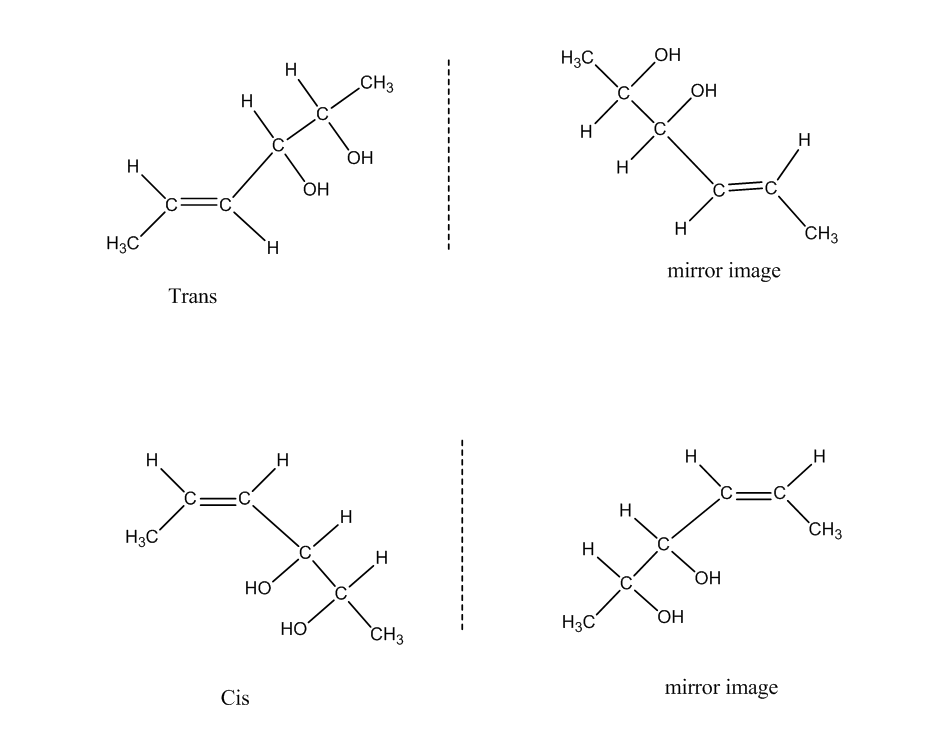
The following are the geometrical isomers of the given compound.

Now there are two forms called Trans and Cis they have mirror images also. So, the geometrical isomers formed are four.
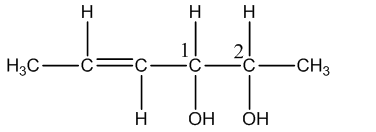
Coming to optical isomers, the given compound has two chiral centers and shown in the below image.

The numbers 1 and 2 represent two chiral centers.
There is a formula to calculate the number of isomers from chiral centers.
Optical isomers = \[{{2}^{n}}\], here n = number of chiral centers.
We know that in the given compound there are two chiral centers.
Therefore the number of optical isomers = \[{{2}^{2}}=4\].
Total number of configurational isomers = geometrical isomers + optical isomers.
= 4 +4
= 8.
So, totally 8 configurational isomers are going to form by the given compound.
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Don’t be confused between geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism. The compounds that have double bonds will show geometrical isomerism and the compounds which have chiral centers show the optical isomerism. Both the isomerisms combined are called geometrical isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




