
There are two identical small holes of area of cross section a on the opposite sides of a tank containing a liquid of density $\rho$. The difference in height between the holes is h. Tank is resting on a smooth horizontal surface. Horizontal force which has to be applied on the tank to keep it in equilibrium is:
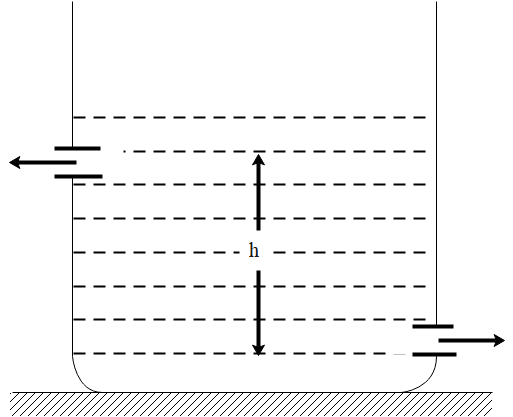
A. $g h \rho a$
B. $\dfrac{2gh}{\rho a}$
C. $2\rho agh$
D. $\dfrac{\rho gh}{a}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
HintWe know that Newton's second law states that a net force acting on an object causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the force. The third law can be understood this way for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. The net force is the vector sum of all the forces that act upon an object. That is to say, the net is the sum of all the forces, taking into account the fact that a force is a vector and two forces of equal magnitude and opposite direction will cancel each other out.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the net force reaction is:
Where,
$\text{F}={{\text{F}}_{\text{B}}}-{{\text{F}}_{\text{A}}}=\dfrac{\text{d}{{\rho }_{\text{B}}}}{\text{dt}}-\dfrac{\text{d}{{\rho }_{\text{A}}}}{\text{dt}}$
$={{\operatorname{av}}_{\text{B}}}\rho \times {{\text{v}}_{\text{B}}}-{{\operatorname{av}}_{\text{A}}}\rho \times {{\text{v}}_{\text{A}}}$
$\rho$is the density
v is the velocity
F is force
a is area
h is height
Therefore, we can derive the equation of net force.
$\therefore \text{F}=\operatorname{ap}\left( \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}-\text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2} \right)\ldots \ldots (i)$
According to Bernoulli’s theorem,
${{\rho }_{\text{A}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho \text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2}+\text{pgh}={{\rho }_{\text{B}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}+0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \left( \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}-\text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2} \right)=\rho \text{gh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}-\text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2}=2\text{gh}\ldots \ldots \text{(ii)}$
From the given equations (i) and (ii), we get the equation,
$\text{F}=\operatorname{a}\rho (2\text{gh})=2\text{a}\rho \text{gh}$
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We know that Bernoulli’s theorem states that within a horizontal flow of fluid, points of higher speed will have less pressure than points of slower fluid speed. We can say that the sum of pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy per unit mass of an incompressible, non-viscous fluid in a streamlined flow remains constant. For example, this principle explains why airplane wings are curved along the top and why ships have to steer away from each other as they pass. The pressure above the wing is lower than below it, providing life from underneath the wing.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the net force reaction is:
Where,
$\text{F}={{\text{F}}_{\text{B}}}-{{\text{F}}_{\text{A}}}=\dfrac{\text{d}{{\rho }_{\text{B}}}}{\text{dt}}-\dfrac{\text{d}{{\rho }_{\text{A}}}}{\text{dt}}$
$={{\operatorname{av}}_{\text{B}}}\rho \times {{\text{v}}_{\text{B}}}-{{\operatorname{av}}_{\text{A}}}\rho \times {{\text{v}}_{\text{A}}}$
$\rho$is the density
v is the velocity
F is force
a is area
h is height
Therefore, we can derive the equation of net force.
$\therefore \text{F}=\operatorname{ap}\left( \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}-\text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2} \right)\ldots \ldots (i)$
According to Bernoulli’s theorem,
${{\rho }_{\text{A}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho \text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2}+\text{pgh}={{\rho }_{\text{B}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}+0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \left( \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}-\text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2} \right)=\rho \text{gh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{v}_{\text{B}}^{2}-\text{v}_{\text{A}}^{2}=2\text{gh}\ldots \ldots \text{(ii)}$
From the given equations (i) and (ii), we get the equation,
$\text{F}=\operatorname{a}\rho (2\text{gh})=2\text{a}\rho \text{gh}$
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We know that Bernoulli’s theorem states that within a horizontal flow of fluid, points of higher speed will have less pressure than points of slower fluid speed. We can say that the sum of pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy per unit mass of an incompressible, non-viscous fluid in a streamlined flow remains constant. For example, this principle explains why airplane wings are curved along the top and why ships have to steer away from each other as they pass. The pressure above the wing is lower than below it, providing life from underneath the wing.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




