
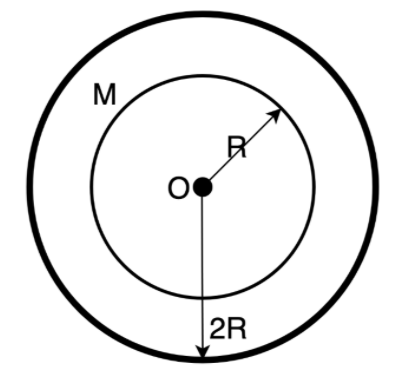
There is a concentric hole of the radius $R$ in a solid sphere of radius $2R$ . Mass of the remaining portion is $M$ . What is the gravitational potential at the center?
A) $ - \dfrac{{5GM}}{{7R}}$
B) $ - \dfrac{{7GM}}{{14R}}$
C) $ - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{7R}}$
D) $ - \dfrac{{9GM}}{{14R}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To solve the above question you should be familiar with gravitational potential. Let us define gravitational potential first. The gravitational potential is defined as the work done to move a unit of mass from infinity to the gravitational field of another body. In the above question, the gravitational field is of the earth. We know the formula for the gravitational potential of a solid sphere at the center, that is, $ - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{2R}}$ , where $M$ is the mass of the solid sphere and $R$ is the radius of the sphere. But the problem here is that we are not concerned with a solid sphere. Therefore first we will calculate the mass of the remaining sphere of radius $2R$ and then that of the solid sphere of radius $2R$. Once we get these two then we can easily calculate the desired gravitational potential.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1: First calculate the mass of the remaining sphere of the radius $2R$ in terms of volume and density. Let us assume the density of the sphere is $\rho $ ,
$\therefore M = \rho \times V$
We know that the volume of a sphere of the radius $2R$ will be $\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {(2R)^3}$ . But the hole in the sphere is of the radius $R$ . Therefore we will subtract the volume of the hole from the volume of the solid sphere to get the volume of the remaining part.
$\therefore M = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi [{(2R)^3} - {R^3}]$
$ \Rightarrow M = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \times 7{R^3}$
………… equation (1).
Step 2: Similarly calculate the mass of the solid sphere of the radius $2R$ in terms of volume and density. Let the mass of the solid sphere of radius $2R$ be $M'$ .
$\therefore M' = \rho \times {V_2}$
\[ \Rightarrow M' = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {(2R)^3}\]
$ \Rightarrow M' = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \times 8{R^3}$
…………equation (2)
Step 3: Divide equation (2) by equation (1).
$\therefore \dfrac{{M'}}{M} = \dfrac{8}{7}$
$ \Rightarrow M' = \dfrac{8}{7}M$
This is the mass of the solid sphere of radius $2R$ .
Step 4: To find the mass of the sphere of the radius $R$ of the same matter we will subtract the mass of the remaining part $M$from the mass of the solid sphere of the radius $2R$ . Let the mass of the sphere of the radius $R$ is $M''$ . then,
$\therefore M'' = - [\dfrac{8}{7}M - M]$
$ \Rightarrow M'' = - \dfrac{1}{7}M$
Here mass will be taken negatively because the negative mass is imposed.
Step 5: We know that the formula for the gravitational potential of a solid sphere is $ - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{2R}}$ . Therefore the gravitational potential of the remaining sphere $U$ will be
$\therefore U = - \dfrac{{3GM'}}{{2R}} - \dfrac{{3GM''}}{{2R}}$
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{3G}}{2}[\dfrac{{M'}}{{2R}} + \dfrac{{M''}}{R}]$
Substitute the values of $M'$ and $M''$
$\therefore U = - \dfrac{{3G}}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{\dfrac{8}{7}M}}{{2R}} - \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{7}M}}{R}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{3G}}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{4M}}{{7R}} - \dfrac{M}{{7R}}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{9GM}}{{14R}}$
Hence option D is correct.
Note: We know the formula for gravitational potential of only slandered shapes like sphere, circular disk, cube, etc. but in this case, the sphere was not solid. While solving this problem always remember that if you are taking the mass of the imagined sphere as negative then you have to add the gravitational potential of both. But if you are taking that mass as positive then you have to subtract the gravitational potential of the imagined sphere from the potential of the solid bigger sphere.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1: First calculate the mass of the remaining sphere of the radius $2R$ in terms of volume and density. Let us assume the density of the sphere is $\rho $ ,
$\therefore M = \rho \times V$
We know that the volume of a sphere of the radius $2R$ will be $\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {(2R)^3}$ . But the hole in the sphere is of the radius $R$ . Therefore we will subtract the volume of the hole from the volume of the solid sphere to get the volume of the remaining part.
$\therefore M = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi [{(2R)^3} - {R^3}]$
$ \Rightarrow M = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \times 7{R^3}$
………… equation (1).
Step 2: Similarly calculate the mass of the solid sphere of the radius $2R$ in terms of volume and density. Let the mass of the solid sphere of radius $2R$ be $M'$ .
$\therefore M' = \rho \times {V_2}$
\[ \Rightarrow M' = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {(2R)^3}\]
$ \Rightarrow M' = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \times 8{R^3}$
…………equation (2)
Step 3: Divide equation (2) by equation (1).
$\therefore \dfrac{{M'}}{M} = \dfrac{8}{7}$
$ \Rightarrow M' = \dfrac{8}{7}M$
This is the mass of the solid sphere of radius $2R$ .
Step 4: To find the mass of the sphere of the radius $R$ of the same matter we will subtract the mass of the remaining part $M$from the mass of the solid sphere of the radius $2R$ . Let the mass of the sphere of the radius $R$ is $M''$ . then,
$\therefore M'' = - [\dfrac{8}{7}M - M]$
$ \Rightarrow M'' = - \dfrac{1}{7}M$
Here mass will be taken negatively because the negative mass is imposed.
Step 5: We know that the formula for the gravitational potential of a solid sphere is $ - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{2R}}$ . Therefore the gravitational potential of the remaining sphere $U$ will be
$\therefore U = - \dfrac{{3GM'}}{{2R}} - \dfrac{{3GM''}}{{2R}}$
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{3G}}{2}[\dfrac{{M'}}{{2R}} + \dfrac{{M''}}{R}]$
Substitute the values of $M'$ and $M''$
$\therefore U = - \dfrac{{3G}}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{\dfrac{8}{7}M}}{{2R}} - \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{7}M}}{R}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{3G}}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{4M}}{{7R}} - \dfrac{M}{{7R}}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{9GM}}{{14R}}$
Hence option D is correct.
Note: We know the formula for gravitational potential of only slandered shapes like sphere, circular disk, cube, etc. but in this case, the sphere was not solid. While solving this problem always remember that if you are taking the mass of the imagined sphere as negative then you have to add the gravitational potential of both. But if you are taking that mass as positive then you have to subtract the gravitational potential of the imagined sphere from the potential of the solid bigger sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




