
Two light sources with equal luminous intensity are lying at a distance of 1.2 m from each other. Where should a screen be placed between them such that illuminance on one of its faces is four times that on another face?
A. \[0.2{\text{ }}m\]
B. \[0.4{\text{ }}m\]
C. \[0.8{\text{ }}m\]
D. \[1.6{\text{ }}m\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: First think how light propagates through any surface. Then find out the relation between intensity of light with distance. Now you can draw the picture to make the question easier. At last, assume a distance x m form source and solve the equations.
Formula used:
The expression of intensity of wave is,
$I = \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light }}}}{{{\text{area }}}}$
\[{E_2} = 4{E_1}.{\text{ }}If{\text{ }}x{\text{ is distance from 1st source}},\]
Here ${E_1} = {\text{ intensity of light of 1st source}}$ and ${E_2} = {\text{ intensity of light of 2nd source}}$
Complete step by step solution:
First make a diagram for proper visualization
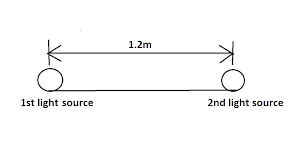
light intensity and distance are inversely proportional with each other. as the distance increases, the light intensity decreases. if the light source moves farther away, the light spreads over to more area. So light decreases in specific proportion with distance of light. Up to this all we say is general observation. Now let’s check this out scientifically. how light propagates through a medium. Let’s see it with a picture.
So now we can easily observe how light is really propagated. But it is a 2D view in 3D it obviously looks like a sphere. Now come to the point : what is the intensity of light? Intensity of light means the amount of light (lumens) falling on a surface over any given $foo{t^2}$or ${m^2}$. That says light intensity can be written in terms of lumens per square foot (foot candles) or lumens per square meter (lux).
If we formulize it then we get
$I = \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light }}}}{{{\text{area }}}}$
$\Rightarrow I= \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light}}}}{{4\pi {r^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow I= \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light}}}}{{\dfrac{4}{3} \times \pi {r^2}}}$
In both the cases we can clearly see that light is proportional to the inverse of ${r^2}$ which means the square of distance. I think Up to now it's all clear. So, we can say that $I\varpropto\dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}}$.
In the given question we have to find a place between them such that the illuminance on one of its faces is four times that on another face. Let’s solve it. Let’s take the required distance at a $x{\text{ m}}$ from the first object. So, now we can compare at this point due to two sources.
\[{E_2} = 4{E_1}.{\text{ }}If{\text{ }}x{\text{ is distance from 1st source}},\]
Here ${E_1} = {\text{ intensity of light of 1st source}}$ and ${E_2} = {\text{ intensity of light of 2nd source}}$.
\[\dfrac{I}{{{{(1.2 - x)}^2}}} = \dfrac{I}{{4{x^2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{1.2 - x}} = \dfrac{2}{x}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3x = 2.4\]
\[\therefore x = 0.8\,m\]
Hence our answer is $0.8\,m$.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Note: As the distance increases, the light intensity decreases. If the light source moves farther away, the light spreads over to more areas. Light is proportional to the inverse of ${r^2}$ which means the square of distance.
Formula used:
The expression of intensity of wave is,
$I = \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light }}}}{{{\text{area }}}}$
\[{E_2} = 4{E_1}.{\text{ }}If{\text{ }}x{\text{ is distance from 1st source}},\]
Here ${E_1} = {\text{ intensity of light of 1st source}}$ and ${E_2} = {\text{ intensity of light of 2nd source}}$
Complete step by step solution:
First make a diagram for proper visualization

light intensity and distance are inversely proportional with each other. as the distance increases, the light intensity decreases. if the light source moves farther away, the light spreads over to more area. So light decreases in specific proportion with distance of light. Up to this all we say is general observation. Now let’s check this out scientifically. how light propagates through a medium. Let’s see it with a picture.

So now we can easily observe how light is really propagated. But it is a 2D view in 3D it obviously looks like a sphere. Now come to the point : what is the intensity of light? Intensity of light means the amount of light (lumens) falling on a surface over any given $foo{t^2}$or ${m^2}$. That says light intensity can be written in terms of lumens per square foot (foot candles) or lumens per square meter (lux).
If we formulize it then we get
$I = \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light }}}}{{{\text{area }}}}$
$\Rightarrow I= \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light}}}}{{4\pi {r^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow I= \dfrac{{{\text{amount of light}}}}{{\dfrac{4}{3} \times \pi {r^2}}}$
In both the cases we can clearly see that light is proportional to the inverse of ${r^2}$ which means the square of distance. I think Up to now it's all clear. So, we can say that $I\varpropto\dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}}$.
In the given question we have to find a place between them such that the illuminance on one of its faces is four times that on another face. Let’s solve it. Let’s take the required distance at a $x{\text{ m}}$ from the first object. So, now we can compare at this point due to two sources.
\[{E_2} = 4{E_1}.{\text{ }}If{\text{ }}x{\text{ is distance from 1st source}},\]
Here ${E_1} = {\text{ intensity of light of 1st source}}$ and ${E_2} = {\text{ intensity of light of 2nd source}}$.
\[\dfrac{I}{{{{(1.2 - x)}^2}}} = \dfrac{I}{{4{x^2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{1.2 - x}} = \dfrac{2}{x}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3x = 2.4\]
\[\therefore x = 0.8\,m\]
Hence our answer is $0.8\,m$.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Note: As the distance increases, the light intensity decreases. If the light source moves farther away, the light spreads over to more areas. Light is proportional to the inverse of ${r^2}$ which means the square of distance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




