
What type of sugar molecule is present in DNA?
(A) D-3-deoxyribose
(B) D-ribose
(C) D-2-deoxyribose
(D) D-Glucopyranose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: DNA Is deoxyribonucleic acid. Hydrolysis of DNA gives sugar (Ribose), phosphoric acid and the heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen atoms called bases. In DNA, Oxygen is absent at position C-2 of the ribose sugar. RNA has D-ribose as sugar. Glucose has six carbon atoms and ribose has five carbon atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
-There are two types of nucleic acids; DNA and RNA
-DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is ribonucleic acid.
-Hydrolysis of DNA and RNA gives sugar (Ribose), phosphoric acid and a heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen atoms called bases.
-In DNA, oxygen is not present in C-2 of ribose sugar so the sugar part is called as 2-deoxyribose.
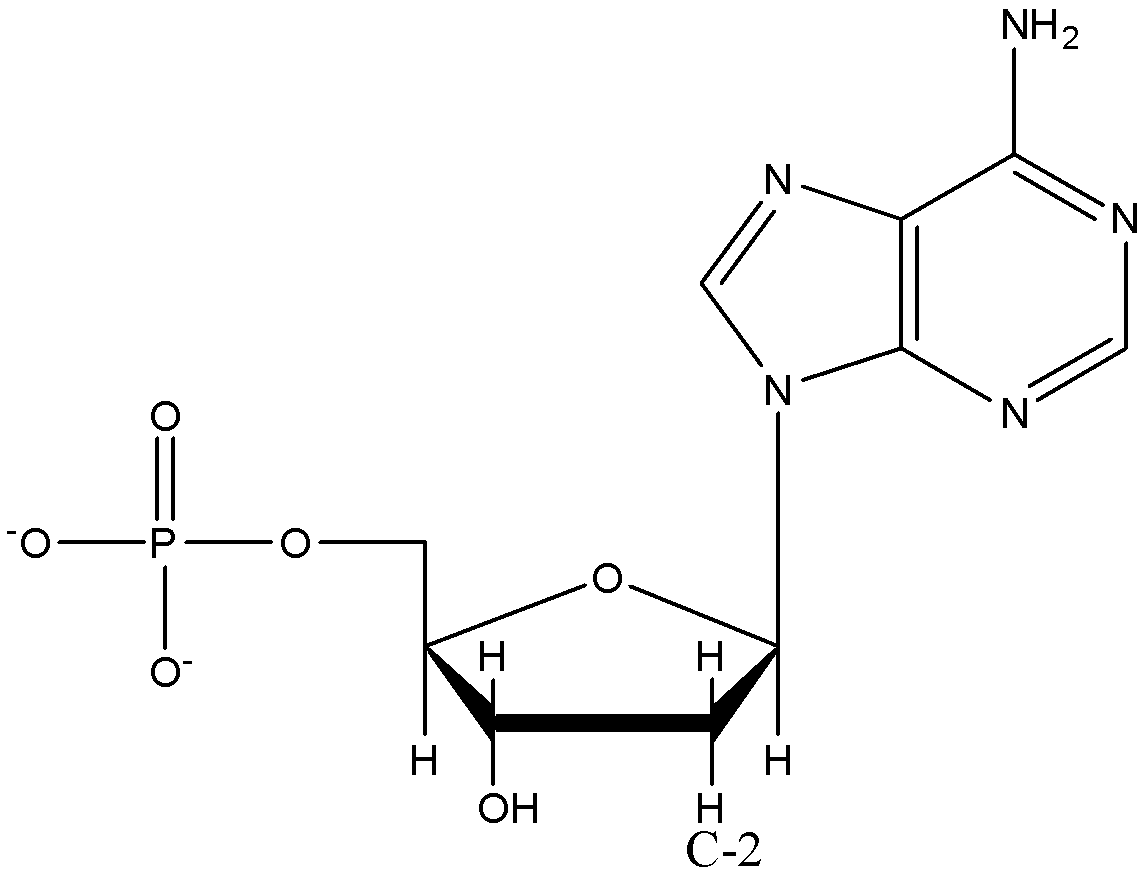
-In RNA, D-ribose is present as sugar.
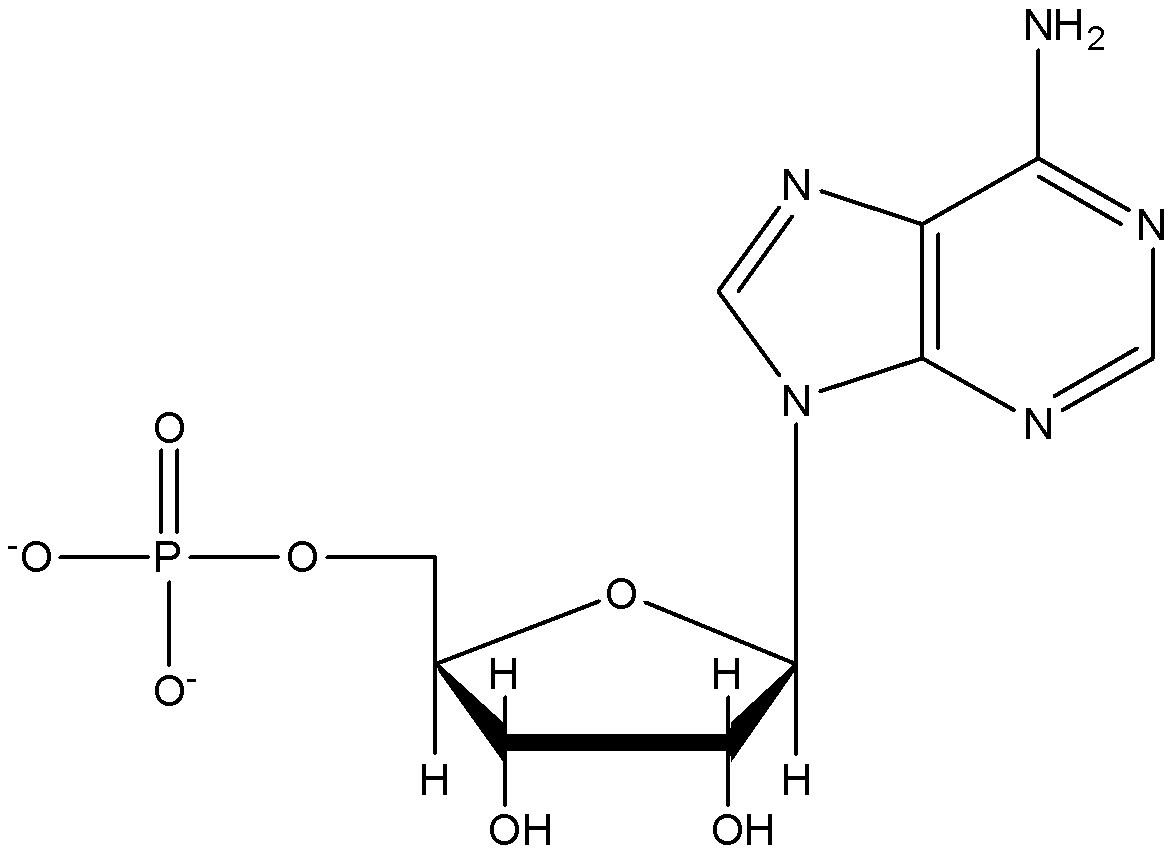
-Base is attached at position 1’ position of sugar which forms nucleoside and phosphoric acid is attached at position 5’ which forms nucleotide.
-Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms of the ribose sugar.

-Primary structure of DNA contains a sequence of nucleotides in the chain of nucleic acid.
-In secondary structure, two strands of nucleic acids are wound around each other to give double helix structure
-Two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds.
-These bases are complementary to each other because the hydrogen bonds are formed between a specific pair of bases.
The correct answer is option (C).
Note: DNA is a short form for deoxyribose nucleic acid. The backbone of DNA is built of alternating sugar and phosphate units. Ribose is a monosaccharide and has five carbon atoms. Glucose is hexose and contains six carbon atoms. The base is attached at position 1’ position of sugar which forms nucleoside and when phosphoric acid is attached at position 5’ which forms nucleotide. nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’ and 3’ carbon atom of the ribose sugar.
Complete step by step solution:
-There are two types of nucleic acids; DNA and RNA
-DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is ribonucleic acid.
-Hydrolysis of DNA and RNA gives sugar (Ribose), phosphoric acid and a heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen atoms called bases.
-In DNA, oxygen is not present in C-2 of ribose sugar so the sugar part is called as 2-deoxyribose.

-In RNA, D-ribose is present as sugar.

-Base is attached at position 1’ position of sugar which forms nucleoside and phosphoric acid is attached at position 5’ which forms nucleotide.
-Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms of the ribose sugar.

-Primary structure of DNA contains a sequence of nucleotides in the chain of nucleic acid.
-In secondary structure, two strands of nucleic acids are wound around each other to give double helix structure
-Two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds.
-These bases are complementary to each other because the hydrogen bonds are formed between a specific pair of bases.
The correct answer is option (C).
Note: DNA is a short form for deoxyribose nucleic acid. The backbone of DNA is built of alternating sugar and phosphate units. Ribose is a monosaccharide and has five carbon atoms. Glucose is hexose and contains six carbon atoms. The base is attached at position 1’ position of sugar which forms nucleoside and when phosphoric acid is attached at position 5’ which forms nucleotide. nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’ and 3’ carbon atom of the ribose sugar.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




