
How is the volume versus temperature graph for a sample of an ideal gas at constant pressure?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we should know about the relationship between volume and temperature. This relationship was given by Charles’ law. By using this law we can easily find out the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
> To answer this question, we should know about Charles’ law. We should know that Charles’ law is one of the gas laws which explain the relationship between volume and temperature of a gas. Charles’s law states that when pressure is held constant, the volume of a fixed amount of dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. It should be noted that, when we take two measurements in direct proportion then any change made in one of them affects the other through direct variation. Charles’ Law is expressed by the equation:
\[\begin{align}
& V\alpha T \\
& \dfrac{V1}{T1}=\dfrac{V2}{T2} \\
\end{align}\]
> From the above expression we should know that V1 and V2 are the Initial Volumes and Final Volume respectively. T1 refers to the Initial Temperature and T2 refers to the Final Temperature.
> We can understand this by taking one example, we should know that on heating up a fixed mass of gas, that is, increasing the temperature, the volume also increases. Similarly, on cooling, the volume of the gas decreases.
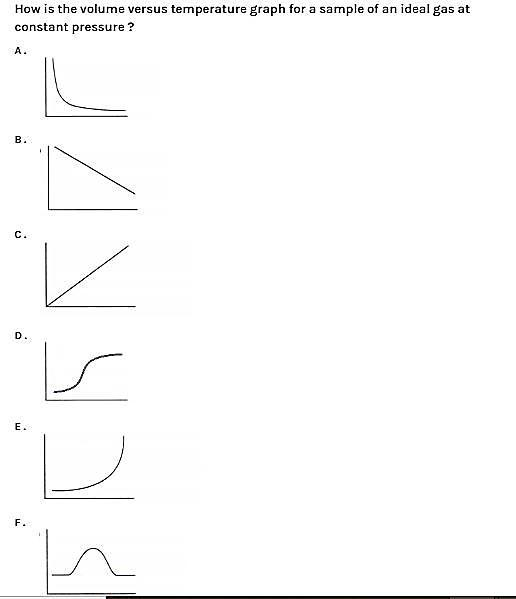
So, from this we can now say that option C is correct. In this graph we can say that it is a straight line because volume and temperature are directly proportional.
Note: It is important to discuss that the unit Kelvin is preferred for solving problems related to Charles Law, and not Celsius. Kelvin (T) is also known as the Absolute temperature scale. We should know about Charles' law application in real life. It has a wide range of applications. Helium balloons shrink in a cold environment. Second example is this : while jogging in winters, we face difficulty because our lung capacity decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
> To answer this question, we should know about Charles’ law. We should know that Charles’ law is one of the gas laws which explain the relationship between volume and temperature of a gas. Charles’s law states that when pressure is held constant, the volume of a fixed amount of dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. It should be noted that, when we take two measurements in direct proportion then any change made in one of them affects the other through direct variation. Charles’ Law is expressed by the equation:
\[\begin{align}
& V\alpha T \\
& \dfrac{V1}{T1}=\dfrac{V2}{T2} \\
\end{align}\]
> From the above expression we should know that V1 and V2 are the Initial Volumes and Final Volume respectively. T1 refers to the Initial Temperature and T2 refers to the Final Temperature.
> We can understand this by taking one example, we should know that on heating up a fixed mass of gas, that is, increasing the temperature, the volume also increases. Similarly, on cooling, the volume of the gas decreases.
So, from this we can now say that option C is correct. In this graph we can say that it is a straight line because volume and temperature are directly proportional.
Note: It is important to discuss that the unit Kelvin is preferred for solving problems related to Charles Law, and not Celsius. Kelvin (T) is also known as the Absolute temperature scale. We should know about Charles' law application in real life. It has a wide range of applications. Helium balloons shrink in a cold environment. Second example is this : while jogging in winters, we face difficulty because our lung capacity decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




