
What is meant by phase angle?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here, we have to understand the meaning of the term phase angle. In basic Physics, phase angle is used in terms of firstly, wave motion and secondly, for describing alternating current and voltage. We will discuss in terms of both the concepts. Basically, it represents angular shifts or displacements corresponding to two points having the same value along the y-axis.
Complete step by step solution:
Graphically understanding, phase angle is the angular displacement of a point on a sinusoidal wave from a reference point or time. Both waves and alternating quantities are expressed in the form of waves. So, the term is used in both ways.
In electrical quantities, alternating current as voltage are expressed as sinusoids. In waves, amplitude, velocity and acceleration of particles have alternating values and hence are expressed as sinusoids.
In an electrical circuit, we can recognize angle between resistive current and total current on phasor diagram as current phase angle(Φ)
The difference in two quantities have the same frequency and two corresponding points attain maximum value or zero value at two different instants, then the angle between two alternating quantities is called difference of phase angles. Below is the explanation of phase angle in terms of waves.
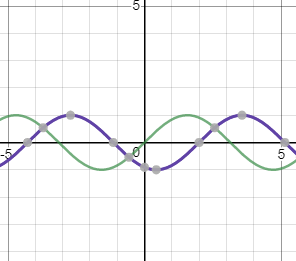
ΔΦ represents phase difference
For the purple graph, ΔΦ is the phase angle.
Note: Phase angle for any quantitative angle can be defined as the angle at the instant at which it attains zero value measured taking origin as reference. It can also be defined as the angle between total current and resistive current in an electrical circuit. If the phase angle in any phasor diagram is counter clockwise, it is taken as positive and negative for clockwise direction.
Complete step by step solution:
Graphically understanding, phase angle is the angular displacement of a point on a sinusoidal wave from a reference point or time. Both waves and alternating quantities are expressed in the form of waves. So, the term is used in both ways.
In electrical quantities, alternating current as voltage are expressed as sinusoids. In waves, amplitude, velocity and acceleration of particles have alternating values and hence are expressed as sinusoids.
In an electrical circuit, we can recognize angle between resistive current and total current on phasor diagram as current phase angle(Φ)

The difference in two quantities have the same frequency and two corresponding points attain maximum value or zero value at two different instants, then the angle between two alternating quantities is called difference of phase angles. Below is the explanation of phase angle in terms of waves.

ΔΦ represents phase difference
For the purple graph, ΔΦ is the phase angle.
Note: Phase angle for any quantitative angle can be defined as the angle at the instant at which it attains zero value measured taking origin as reference. It can also be defined as the angle between total current and resistive current in an electrical circuit. If the phase angle in any phasor diagram is counter clockwise, it is taken as positive and negative for clockwise direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




