
Which compound does not give HVZ reaction?
(A) ${ CH }_{ 3 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ COOH }$
(B) 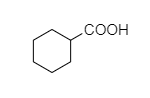
(C) 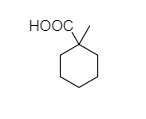
(D) 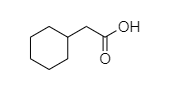
Answer
530.2k+ views
Hint: HVZ stands for Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction. The HVZ reaction is halogenation of carboxylic acids at alpha carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
> This reaction is generally carried out by treating carboxylic acids with halogen in the presence of red phosphorus and then works up with water.
> Those compounds which have alpha hydrogen show HVZ reaction while those which do not have alpha hydrogen do not show HVZ reaction.
- In this ${ CH }_{ 3 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ COOH }$ compound, alpha and beta hydrogen are present. That’s why butanoic acid shows a Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
- In cyclohexyl carboxylic acid, alpha hydrogen is present as shown below,
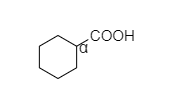
So, this compound also shows the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
- In 1-methylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, there is no alpha hydrogen present as the carbon is attached to 4 different bonds. So, this compound does not show the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
- In 2-cyclohexyl acetic acid, alpha hydrogen is present as shown in the figure;
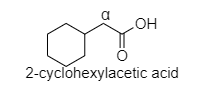
Hence, this compound shows the HVZ reaction. The correct option is C.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that this reaction is specific for the replacement of alpha-hydrogens and not beta- hydrogens.
Complete step by step solution:
> This reaction is generally carried out by treating carboxylic acids with halogen in the presence of red phosphorus and then works up with water.
> Those compounds which have alpha hydrogen show HVZ reaction while those which do not have alpha hydrogen do not show HVZ reaction.
- In this ${ CH }_{ 3 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ CH }_{ 2 }-{ COOH }$ compound, alpha and beta hydrogen are present. That’s why butanoic acid shows a Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
- In cyclohexyl carboxylic acid, alpha hydrogen is present as shown below,

So, this compound also shows the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
- In 1-methylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, there is no alpha hydrogen present as the carbon is attached to 4 different bonds. So, this compound does not show the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction.
- In 2-cyclohexyl acetic acid, alpha hydrogen is present as shown in the figure;

Hence, this compound shows the HVZ reaction. The correct option is C.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that this reaction is specific for the replacement of alpha-hydrogens and not beta- hydrogens.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




