
Which of the following molecules are polar as well as planar?
A) $BFCLBr$
B) ${B_3}{N_3}{H_6}$
C) $Cl{F_3}$
D) ${H_2}C = C = C = C{F_2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To determine the shape of molecules, we must be acquainted with the Lewis electron dot structure. Although this theory does not actually determine the shapes of molecules, it is a step applied prior to VSEPR theory which actually determines molecular geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine the molecules that are polar as well as planar.
First of all molecular geometry is 3D arrangement of atoms or molecules around a central atom which is helpful in determining polarity. The Lewis dot structure helps us predict the bond pairs and the lone pairs. After that, we apply the valence-shell-electron-pair-repulsion (VSEPR) theory which states that electron pairs (both lone pair and bond pair) repel each other.
After the 3D representation of the molecule using VSEPR rules, if molecules have symmetry around the central atom, bond dipole cancels each other and molecule is nonpolar. And if the molecule is asymmetric, the dipole moment doesn’t cancel out. Thus, the molecules are polar.
We draw the 3D structure of the molecules given –
A) $BFClBr$
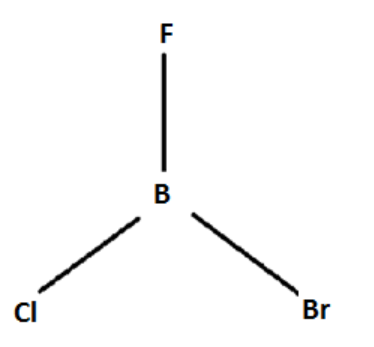
$s{p^2}$ , Trigonal planar polar
B) ${B_3}{N_6}{H_6}$
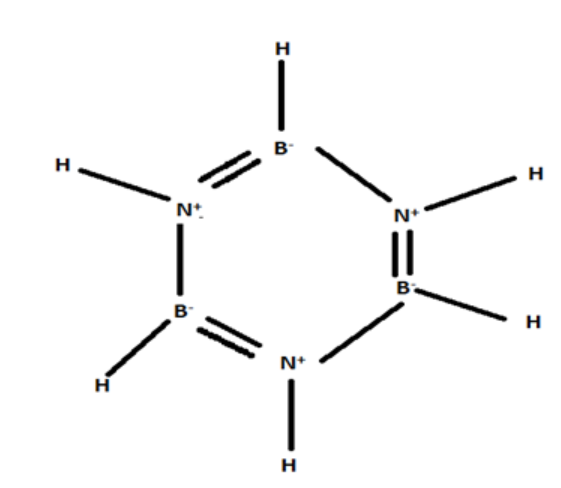
Planar, Non-polar
C) $Cl{F_3}$
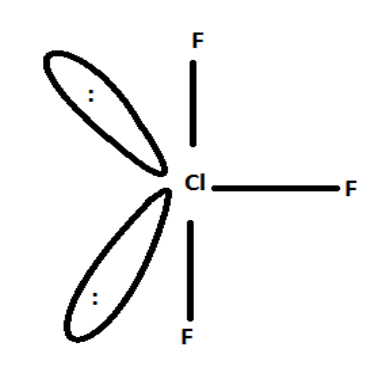
Planar, Polar
D) ${H_2}C = C = C = C{F_2}$

Planar, Polar
Option (A), (C), (D) are correct.
Note:
The general idea of the student that the compound in which the central atom has $sp/s{p^2}$ hybridization is planar might not work in analyzing allenes (in option (D)). So, a general simple rule that students should follow is – The molecule will not be planar if there is an $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon or two $s{p^2}/sp$ hybridized atoms separated by odd number of double bonds while others are planar.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine the molecules that are polar as well as planar.
First of all molecular geometry is 3D arrangement of atoms or molecules around a central atom which is helpful in determining polarity. The Lewis dot structure helps us predict the bond pairs and the lone pairs. After that, we apply the valence-shell-electron-pair-repulsion (VSEPR) theory which states that electron pairs (both lone pair and bond pair) repel each other.
After the 3D representation of the molecule using VSEPR rules, if molecules have symmetry around the central atom, bond dipole cancels each other and molecule is nonpolar. And if the molecule is asymmetric, the dipole moment doesn’t cancel out. Thus, the molecules are polar.
We draw the 3D structure of the molecules given –
A) $BFClBr$

$s{p^2}$ , Trigonal planar polar
B) ${B_3}{N_6}{H_6}$

Planar, Non-polar
C) $Cl{F_3}$

Planar, Polar
D) ${H_2}C = C = C = C{F_2}$

Planar, Polar
Option (A), (C), (D) are correct.
Note:
The general idea of the student that the compound in which the central atom has $sp/s{p^2}$ hybridization is planar might not work in analyzing allenes (in option (D)). So, a general simple rule that students should follow is – The molecule will not be planar if there is an $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon or two $s{p^2}/sp$ hybridized atoms separated by odd number of double bonds while others are planar.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




