
Which of the following shapes of \[S{F_4}\] is more stable and why?
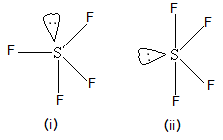
(A) (i) Lone pair at axial position is stable
(B) (ii) Lone pair at equatorial position is stable
(C) Both are equally stable due to lp-lp repulsion
(D) Both are unstable since \[S{F_4}\] has tetrahedral shape
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Repulsive forces between bond pairs and lone pairs have influence on the shapes of the molecules. Lone pair-lone pair repulsions are the most strong repulsions of these types of repulsions.
Complete step by step solution:
In both the shapes of \[S{F_4}\], we can say that the only difference is that lone pair is at axial position and in another shape, the lone pair of sulphur atoms is in equatorial position. So, let’s compare them two and their stability.
- In (i), lone pair is at axial position and hence, it has three fluorine atoms in the vicinity that give lone pair-bond pair repulsion. While in case of (ii), the lone pair of sulphur is having only two fluorine atoms in the vicinity and hence it will have two lone pair-bond pair repulsions with fluorine atoms.
- The rest of the repulsive factors are almost the same in both the molecules.
- So, based on this discussion, we can conclude that structure (ii) will be more stable because there is less repulsion for sulphur lone pair in comparison with structure (i).
Thus correct answer is (B) (ii) Lone pair at equatorial position is stable
Additional Information:
- If the atoms that are situated at a position that is in the plane that involves most number of atoms in that molecule, then the positions are called equatorial positions and axial positions are perpendicular to the equatorial ones.
Note: Do not consider that \[S{F_4}\] has a tetrahedral shape because it has 4 atoms binded with it, also take the lone pair of the central atom into consideration which also has higher repulsion towards other bond pairs. Do not consider that the amount of repulsion will be the same for all the compounds that have the same atoms; the arrangement of these atoms in space decides the repulsive factors.
Complete step by step solution:
In both the shapes of \[S{F_4}\], we can say that the only difference is that lone pair is at axial position and in another shape, the lone pair of sulphur atoms is in equatorial position. So, let’s compare them two and their stability.
- In (i), lone pair is at axial position and hence, it has three fluorine atoms in the vicinity that give lone pair-bond pair repulsion. While in case of (ii), the lone pair of sulphur is having only two fluorine atoms in the vicinity and hence it will have two lone pair-bond pair repulsions with fluorine atoms.
- The rest of the repulsive factors are almost the same in both the molecules.
- So, based on this discussion, we can conclude that structure (ii) will be more stable because there is less repulsion for sulphur lone pair in comparison with structure (i).
Thus correct answer is (B) (ii) Lone pair at equatorial position is stable
Additional Information:
- If the atoms that are situated at a position that is in the plane that involves most number of atoms in that molecule, then the positions are called equatorial positions and axial positions are perpendicular to the equatorial ones.
Note: Do not consider that \[S{F_4}\] has a tetrahedral shape because it has 4 atoms binded with it, also take the lone pair of the central atom into consideration which also has higher repulsion towards other bond pairs. Do not consider that the amount of repulsion will be the same for all the compounds that have the same atoms; the arrangement of these atoms in space decides the repulsive factors.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




