
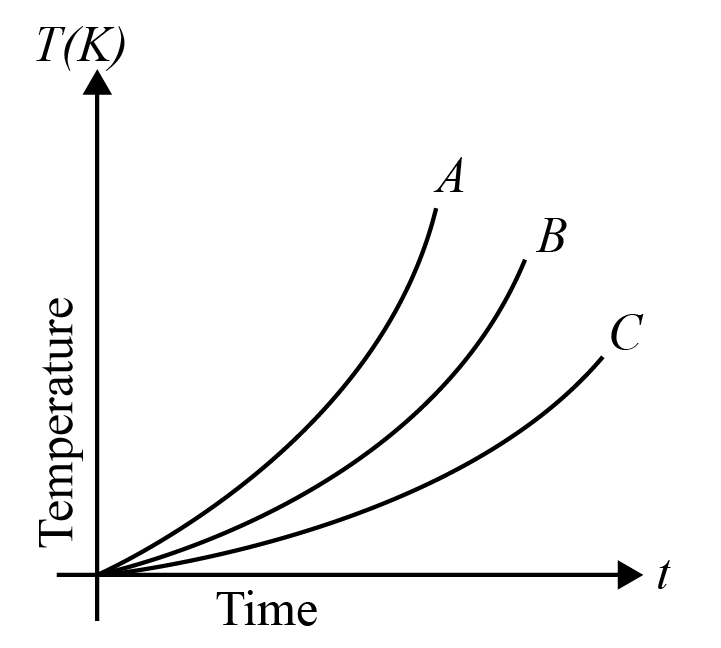
Which of the substances A, B or C has the highest specific heat? The temperature vs time graph is shown.
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) All have similar Specific heat
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint The given graph represents 3 substances A, B , and C on their behavioral characteristics due to change in temperature. Specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required by the substance to raise the overall temperature of the substance by one degree. Apply this concept to justify your answer.
Complete Step By Step Solution
Specific heat of any substance is defined as the quantity of heat required to increase the temperature of the substance by one degree. It is also given as the ratio of heat capacity of the substance that is heated to the mass of the substance. According to this relation, we can see that specific heat is inversely proportional to the mass of the substance. But, in our given graph, the masses of the substances aren’t mentioned.
But from the same relation we can see that specific heat is directly proportional to the change in temperature of the substance. The substance which gets heated more or under application of heat for a longer period of time, is expected to have a greater specific heat quotient.
In our graph, A undergoes heating under high temperature but for rather a short period of time. Hence, its heating capacity is quite lesser than the rest of the given substances. Body B undergoes heating for a greater period of time than that of substance A, but lesser than C. Thus, body C is said to be having greater specific heat than the other substances.
Thus, Option (c) is the right answer.
Note
Specific heat of water is higher than any other substance or medium. Water plays a vital role in regulating the temperature of any substance. The specific heat quotient of water per gram is much higher than the specific heat of a metal.
Complete Step By Step Solution
Specific heat of any substance is defined as the quantity of heat required to increase the temperature of the substance by one degree. It is also given as the ratio of heat capacity of the substance that is heated to the mass of the substance. According to this relation, we can see that specific heat is inversely proportional to the mass of the substance. But, in our given graph, the masses of the substances aren’t mentioned.
But from the same relation we can see that specific heat is directly proportional to the change in temperature of the substance. The substance which gets heated more or under application of heat for a longer period of time, is expected to have a greater specific heat quotient.
In our graph, A undergoes heating under high temperature but for rather a short period of time. Hence, its heating capacity is quite lesser than the rest of the given substances. Body B undergoes heating for a greater period of time than that of substance A, but lesser than C. Thus, body C is said to be having greater specific heat than the other substances.
Thus, Option (c) is the right answer.
Note
Specific heat of water is higher than any other substance or medium. Water plays a vital role in regulating the temperature of any substance. The specific heat quotient of water per gram is much higher than the specific heat of a metal.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




