
Which site of an enzyme is called an allosteric site?
A) Which binds to the cell wall
B) Where drugs bind to an enzyme
C) Which is not the active site, where some drugs bind to an enzyme
D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: the drug binds with the enzyme. The substrate and the drug which are also known as inhibitors have an affinity to bind to the active site present on the enzyme. In the non –competitive inhibition the drug does not bind at the active site. But it binds to the allosteric site. This changes the shape and conformation of the enzyme and reduces the affinity of the substrate towards the enzyme.
Complete step by step answer:
Drugs interact with the macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acid. These macromolecules are known to perform different functions in the body. The enzymes carry out various functions in the body.
The main role of the drugs is to either increase or decrease the role of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The inhibition of enzymes is a common role in drug action. Many drugs show their effect by modifying the function of enzymes. The enzyme inhibitors can block the binding site and prevent the binding of the substrate or can inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
The drug inhibits the attachment of the substrate on the active site of the enzyme in the following two ways:
(I)Competitive inhibition:
The substrate and inhibitor cannot bind to the enzyme at the same time. This usually results from the inhibitor having an affinity for the active site of the enzyme where the substrate also binds. Therefore, the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the approach to the enzyme’s active site. Such drugs are called competitive inhibitors.
(II)Non-Competitive inhibition:
In non-competitive inhibition drugs, do not bind to the active site but bind to the different sites of the enzyme called the allosteric site. This binding of the inhibitor allosteric site changes the shape and conformation of the active site so that the affinity of the substrate for the active site is reduced.
It may be noted that if the bond formed between the enzyme and the inhibitor is a strong covalent bond, therefore, cannot be broken easily then the enzymes get blocked permanently. The body then degrades the enzyme-inhibitor complex and synthesis of new enzymes.
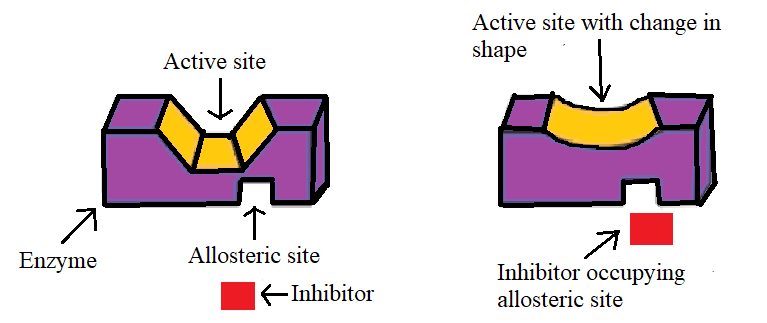
Thus from the non-competitive inhibition of drugs across the enzyme we get that allosteric sites are not active but the drug binds to this inactive site. This results in the binding of the drug to the enzyme.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The two important main functions of the enzymes are:
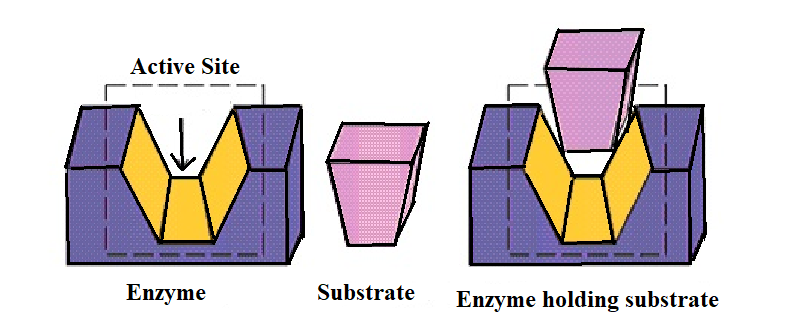
1) The first function of the enzyme is to hold the substrate for a chemical reaction. The substrate is held in the active site of the enzyme in such a position that it can be readily and effectively attacked by the reagent which can be a drug.
2) The second main function of the enzyme is to provide the functional group which will attack the substrate and carry out the chemical reaction.
Note:(1) The protein which performs the role of the biological catalyst in the biological system is called the enzyme.
(2) The enzyme acts on the lock and key principle.
(3)there is one more drug enzyme attachment which is uncompetitive inhibition.
Complete step by step answer:
Drugs interact with the macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acid. These macromolecules are known to perform different functions in the body. The enzymes carry out various functions in the body.
The main role of the drugs is to either increase or decrease the role of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The inhibition of enzymes is a common role in drug action. Many drugs show their effect by modifying the function of enzymes. The enzyme inhibitors can block the binding site and prevent the binding of the substrate or can inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
The drug inhibits the attachment of the substrate on the active site of the enzyme in the following two ways:
(I)Competitive inhibition:
The substrate and inhibitor cannot bind to the enzyme at the same time. This usually results from the inhibitor having an affinity for the active site of the enzyme where the substrate also binds. Therefore, the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the approach to the enzyme’s active site. Such drugs are called competitive inhibitors.

(II)Non-Competitive inhibition:
In non-competitive inhibition drugs, do not bind to the active site but bind to the different sites of the enzyme called the allosteric site. This binding of the inhibitor allosteric site changes the shape and conformation of the active site so that the affinity of the substrate for the active site is reduced.
It may be noted that if the bond formed between the enzyme and the inhibitor is a strong covalent bond, therefore, cannot be broken easily then the enzymes get blocked permanently. The body then degrades the enzyme-inhibitor complex and synthesis of new enzymes.

Thus from the non-competitive inhibition of drugs across the enzyme we get that allosteric sites are not active but the drug binds to this inactive site. This results in the binding of the drug to the enzyme.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The two important main functions of the enzymes are:
1) The first function of the enzyme is to hold the substrate for a chemical reaction. The substrate is held in the active site of the enzyme in such a position that it can be readily and effectively attacked by the reagent which can be a drug.
2) The second main function of the enzyme is to provide the functional group which will attack the substrate and carry out the chemical reaction.
Note:(1) The protein which performs the role of the biological catalyst in the biological system is called the enzyme.
(2) The enzyme acts on the lock and key principle.
(3)there is one more drug enzyme attachment which is uncompetitive inhibition.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




