
Which type of lens has negative power?
A) Convex lens
B) Concave lens
C) Both A and B
D) None
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Reciprocal of focal length is considered as power of a lens. To the numerical value of power we assign negative and positive signs as per sign convention. If the image resolves on the right side of the principal axis, the power is positive and if the image resolves on the left side of the principal axis, the power is positive.
Formula used:
${P_L} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where ${P_L}$ is the power of the lens.
$f$ is the focal length
Complete step by step answer:
Power of a lens is the ability to deviate the path of rays of light passing through it. If the lens converges the rays, power is positive and if the lens diverges the rays, the power is negative.
The converging and diverging abilities of both types of lenses is shown below,
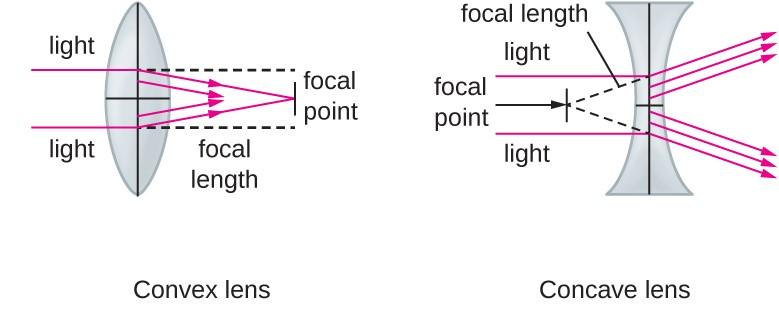
So we can now have an idea that a convex lens has positive power and a concave lens has negative power.
So, The correct answer is (B), concave lens.
Additional Information:
We can also solve this question by considering the sign convention of geometric optics.
By sign convention, any distance measured from the principal of the lens in the left direction is negative and any distance measured from the right of the length is positive.
For a convex lens, focal length $(f)$ is positive and for a concave lens, the value of $f$ is negative.
So by assigning signs to focal length in the power formula $({P_L} = \dfrac{1}{f})$ we get negative value for concave lens and positive value for convex lens.
Note: Never mix up sign conventions in optics, because examiners tend to put the same numerical options with different signs to confuse a student. Quick trick is, anything up or right from the principal is positive and anything left or down from the principal is negative.
Formula used:
${P_L} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where ${P_L}$ is the power of the lens.
$f$ is the focal length
Complete step by step answer:
Power of a lens is the ability to deviate the path of rays of light passing through it. If the lens converges the rays, power is positive and if the lens diverges the rays, the power is negative.
The converging and diverging abilities of both types of lenses is shown below,

So we can now have an idea that a convex lens has positive power and a concave lens has negative power.
So, The correct answer is (B), concave lens.
Additional Information:
We can also solve this question by considering the sign convention of geometric optics.
By sign convention, any distance measured from the principal of the lens in the left direction is negative and any distance measured from the right of the length is positive.
For a convex lens, focal length $(f)$ is positive and for a concave lens, the value of $f$ is negative.
So by assigning signs to focal length in the power formula $({P_L} = \dfrac{1}{f})$ we get negative value for concave lens and positive value for convex lens.
Note: Never mix up sign conventions in optics, because examiners tend to put the same numerical options with different signs to confuse a student. Quick trick is, anything up or right from the principal is positive and anything left or down from the principal is negative.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




