Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 10 Human Health and Diseases – Download Free PDF with Solution
The overall health of a human being is defined by being physically and mentally well. The absence of disease does not make a human healthy. Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 teaches students what human health means and how it can be maintained. It will also explain what diseases mean.
To understand the concepts and principles of Human Health and Diseases, refer to the notes and solutions prepared by the experts. Get the simplest explanation of these concepts and learn how the experts have answered the exercise questions accurately.
Access Maharashtra Board Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Human Health and Diseases
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is NOT caused by unsterilized needles?
Elephantiasis
AIDS
Malaria
Hepatitis B
Ans: Correct option- a. Elephantiasis
Explanation: Elephantiasis is a rare disease or condition caused by mosquitoes and we also know it as lymphatic filariasis. Most common in tropical and subtropical areas. It is called elephantiasis because in this condition the affected person's body arms, legs, and sex organs swell up and skin becomes thick like an elephant’s skin.
2. Opium derivative is ..............
Codeine
Caffeine
Heroin
Psilocybin
Ans: Correct option- c. Heroin
Explanation: Heroin is an addictive analgesic brown or white powder derived from the plant opium poppy. It is used by drug addicts to get the euphoria effect. The heroin is an illegal drug which if smoked or inhaled through the nose and most people inject themselves which can easily cause the drug overdose which can lead to death.
3. The stimulant present in tea is .............
tannin
cocaine
caffeine
Crack
Ans: Correct option- c. Caffeine
Explanation: The stimulant present in tea is caffeine which is a natural chemical which also has side effects if taken for a long time and overdosed. It may cause insomnia, nervousness, nausea, restlessness, anxiety, chest pain and other side effects.
4. Which of the following is caused by smoking?
Liver cirrhosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Emphysema
Malaria
Ans: Correct option- c. Emphysema
Explanation: Smoking causes Emphysema, and it damages the alveoli. The common symptom of this condition is the person has shortness of breath or difficulty breathing while doing some heavy work.
5. An antibody is ...............
molecule that binds specifically an antigen
WBC which invades bacteria
secretion of mammalian RBC
cellular component of blood
Ans: Correct option- a. Molecule that binds specifically an antigen
Explanation: Antibodies is a molecule that binds specifically an antigen. It is a protein made by our immune system to fight off foreign bodies which enter our body called antigen.
6. The antiviral proteins released by a virus-infected cell are called ............
histamines
interferons
pyrogens
Allergens
Ans: Correct option- b. Interferons
Explanation: Interferons are signaling proteins and are part of our natural defense system. Our immune system releases them in the presence of viruses and so they are called antiviral factors.
7. Both B-cells and T-cells are derived from ....................
lymph nodes
thymus glands
liver
stem cells in bone marrow
Ans: Correct option- d. Stem cells in bone marrow
Explanation: Both B-cell and T-cell are derived from stem cells of bone marrow but T-cells mature in thymus glands. These white are blood cells which are part of adaptive immune response. B-cells or B lymphocytes make antibodies, whereas T- cells destroy all infected or cancerous cells.
8. Which of the following diseases can be contracted by droplet infection?
Malaria
Chicken pox
Pneumonia
Rabies
Ans: Correct option- c. Pneumonia
Explanation: Pneumonia is an infection caused by bacterial or viral infection which causes lung inflammation. We may get infected by bacteria, fungi and viruses. The most common bacteria which causes pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). The common cause of viral pneumonia is the influenza virus.
9. The Confirmatory test used for detecting HIV infection is .................
ELISA
Western blot
Widal test
Eastern blot
Ans: Correct option- a. ELISA
Explanation: Confirmatory test used for detecting HIV infection is ELISA. The full form of ELISA is Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. There are four types of ELISA: direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive.
10. Elephantiasis is caused by ............
W. bancrofti
P. vivax
Bedbug
Elephant
Ans: Correct option- a. W. bancrofti
Explanation: A parasite worms-nematodes cause Filariasis/Elephantiasis they are threadlike in structure. Wuchereria bancrofti causes Lymphatic filariasis, a type of filariasis. It affects arms, legs, breasts, scrotum, etc.
11. Innate immunity is provided by ...........
phagocytes
antibody
T- Lymphocytes
B- Lymphocytes
Ans: Correct option- a. Phagocytes
Explanation: Innate immunity means inborn/congenital is the type of immunity present by birth in every human. It can fight various acute infections on its own. There are some important components of innate immunity which fight against pathogens. They are physical barriers, physiological barriers, and cellular barriers. Neutrophils (motile) provide the innate immunity which are phagocytic cells.
Very Short-Answer Questions
1. What is the source of cocaine?
Ans: Cocaine is an alkaloid and is derived from the coca plant its scientific name is Erythroxylum coca. This is a mind-expanding drug which increases your dopamine level and causes hallucinations, paranoia, extreme happiness, and irritability.
2. Name one disease caused by smoking?
Ans: Smoking causes many diseases like cancer, heart disease, lung disease, emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It increases the risk of TB. The most common disease caused by smoking is lung cancer.
Cancer is the abnormal growth of cells. There are various reasons a person can get cancer: they are chemicals, radiation, viruses, oncogenes, and addictions to drugs, smoking, tobacco, and alcohol.
3. Which cells stimulate B-cells to form Antibodies?
Ans: Antigens and helper T-cells stimulate B-cells or B lymphocytes. They make glycoproteins called antibodies which circulate in our blood and lymph. These free antibodies have functions: Agglutination, opsonization and neutralization.
4. What does the abbreviation AIDS stand For?
Ans: The abbreviation AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A single-stranded RNA retrovirus causes AIDS also known as human-immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It weakens your immune system causing lethal opportunistic diseases. ADIS was first founded in the USA in 1981 and 1986 in Tamil Nadu, India.
5. Name the causative agent of typhoid Fever?
Ans: Typhoid fever is an infection of the intestine and is caused by the gram-negative bacteria Salmonella typhi.
Symptoms of typhoid fever are high fever, nausea, fatigue, headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Food and water-borne diseases, and poor hygiene habits may cause typhoid fever.
6. What is the Rh factor?
Ans: Rh factor was first discovered on the surface of red blood cells of the Rhesus monkey in 1940 by Landsteiner and Wiener. It is also called the D antigen. An antigenic protein is present on the surface of the red blood cells of human-beings.
Those who have Rh factor (D antigen) are Rh positive and those who do not have Rh factor are Rh negative.
7. What is schizont?
Ans: In malaria when cells formed during asexual reproduction by fission (schizogony) are called merozoites. The trophozoite matures into schizonts and when the rupture it releases merozoites.
8. Name the addictive component found in Tobacco.
Ans: The addictive component found in tobacco is nicotine. Smoking tobacco causes many diseases but the most common is lung cancer which damages your lungs. Smoking causes Emphysema, and it damages the alveoli. The common symptom of this condition is the person has shortness of breath or difficulty breathing while doing some heavy work.
9. Name the pathogen causing Malaria.
Ans: Malaria is a vector-borne disease which spreads through mosquito bites. It is caused by the pathogen Plasmodium species: P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. falciparum. P. falciparum causes a more fatal illness than the other species.
10. Name the vector of Filariasis.
Ans: Nematodes Parasites, which spread from person to person via mosquito bite, cause filariasis/Elephantiasis. Wuchereria bancrofti causes Lymphatic filariasis, a type of filariasis. It affects arms, legs, breasts, scrotum, etc. Most common in tropical and subtropical areas. It is called elephantiasis because in this condition the affected person's body arms, legs and sex organs swell up and skin becomes thick like an elephant’s skin.
11. Give the name of the causative agent of Ringworm.
Ans: Ringworm is the fungal infection of the skin caused by a fungal species of genera Trichophyton and Microsporum. Infected skin shows the following symptoms:
Enlarged red ring
Appearance of dry and scaly lesions
Onychomycosis (infection to nails)
Athlete’s foot
12. Define health.
Ans: Health is not only an absence of disease or physical fitness. According to the WHO, an individual has a complete state of physical, mental and social well-being called health. Having a strong immune system which protects our body from various foreign bodies and infectious agents daily.
For good health and a strong immune system we should maintain hygiene, eat a healthy balanced diet, do physical exercises/yoga and drink clean water, etc.
Short-Answer Questions:
1. What are acquired diseases?
Ans: Acquired diseases are the ones which a person gets at some point in life. They are not by birth or inherited from their mother. Pathogenic infections, aging and climatic changes cause acquired diseases.
For example AIDS, Salmonella infection, influenza, malaria, cancer and other infectious diseases are all acquired diseases.
2. Differentiate between antigen and Antibody.
Ans:
Antigen | Antibody |
Antigen triggers the immune system to produce antibodies. | Antibodies recognize antigen and bind to it to attack it. |
They are proteins but can be polysaccharides, lipids or nucleic acids. | They are proteins. |
It has an epitope site where antibodies bind to antigen. | It has a para-tope site where antigen binds to antibody |
Antigen structure is variable; it depends on the type of pathogen. | Antibody is Y-shaped. |
3. Name the infective stage of Plasmodium. Give any two symptoms of malaria.
Ans: The infective stage of Plasmodium is when the sporozoites enter the human body through mosquito bite of a female Anopheles.
Malaria is a vector-borne disease which spreads through mosquito bites. It is caused by the pathogen Plasmodium species: P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. falciparum. P. falciparum causes a more fatal illness than the other species.
Malaria shows following symptoms:
Fever, chills, and headache
Arthralgia (joint pain)
Anemia
4. Explain the mode of infection and cause of elephantiasis.
Ans: The mode of infection of filariasis/elephantiasis is through the mosquito bite of Wuchereria bancrofti larvae is transmitted to the human body through female Culex mosquitoes.
The larvae infiltrate through skin and go through the molting process twice and settle in the lymphatic system.
Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Brugia timori are worm-nematodes which spread from person to person via mosquito bite causing Filariasis/Elephantiasis. Filariasis subtypes: Lymphatic Filariasis, Subcutaneous Filariasis, Serous (abdominal) cavity Filariasis.
5. Why is smoking a bad habit?
Ans: Smoking causes many diseases like cancer, heart disease, lung disease, emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It increases the risk of TB. The most common disease caused by smoking is lung cancer.
Cancer is the abnormal growth of cells. There are various reasons a person can get cancer: chemicals, radiation, viruses, oncogenes, and addictions to drugs, smoking, tobacco, and alcohol.
6. What do the abbreviations AIIMS and CMIS denote?
Ans: AIIMS - All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
CMIS - Cell-Mediated Immune System. T-lymphocytes form cell-mediated immune systems and antibodies do not take part in cell-mediated immune systems. CMIS activates phagocytes and releases cytokines to attack antigens.
7. What is a carcinogen? Name one chemical carcinogen with its target Tissue.
Ans: Carcinogens: cancer-causing agents or factors are called carcinogens. There are various factors responsible for causing cancer, they are:
Chemicals: nicotine, caffeine, polycyclic hydrocarbons, etc.
Radiations: X-rays, gamma rays, UV rays, cosmic rays.
Viruses called viral oncogenes and oncogenes.
Addictions: smoking, alcohol and drugs.
8. Distinguish between active immunity and passive immunity.
Ans:
Active Immunity | Passive Immunity |
Active immunity is also called adaptive immunity; we develop it after antigenic stimulus. | Passive immunity the body cells do not take part actively in making passive immunity. |
Active immunity lives for a longer time. | Passive immunity lives for a short time. |
Natural acquired active immunity: is developed when a person gets infected by a pathogen and our body makes natural immunity by producing antibodies for the infection/pathogens. | Naturally acquired passive immunity: is transferred from mother to baby during pregnancy in the uterus and after pregnancy while breastfeeding period. |
Artificially acquired active immunity: in this the antibodies are formed after vaccination. Example: Polio vaccine and BCG vaccine | Artificially acquired passive immunity: the previously made antibodies in humans and animals a serum from those humans and animals is used. |
Short-Answer Questions
1. Differentiate between B-cells and T-cells.
Ans:
B-cells | T-cells |
B-cells or B-lymphocytes are produced in bone marrow and mature in bone marrow. | T-cells or T-lymphocytes are produced in bone marrow as well but they do not mature in bone marrow. They mature in thymus glands. |
B-cells have two types: plasma cells and memory cells. | T-cells have three types: T-cells or T-lymphocytes, Cytotoxic T-cells and suppressor T-cells. |
B-cell with antibodies. | T-cell with TCR- T-cell receptor. |
2. What are the symptoms of malaria? How does malaria spread?
Ans: Malaria shows following symptoms:
Fever, chills, and headache
Arthralgia (joint pain), anemia
Haemoglobinuria, hepatomegaly
Retinal damage
Cerebral malaria
Malaria is a vector-borne disease which spreads through a bite of a female Anopheles mosquito. It is caused by the pathogen Plasmodium species: P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. falciparum. P. falciparum causes a more fatal illness than the other species.
3. Write a short note on AIDS.
Ans: AIDS-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. They reported the first case of AIDS in 1981. Syndrome means a group of diseases.
The causative agent of AIDS is HIV-human immunodeficiency virus, which is a retrovirus. It has a single-stranded RNA with reverse transcriptase gene.
AIDS can be transmitted by:
Sexual contact with infected person
Using infected needles
Transfusion of contaminated or infected blood
From an infected mother to a newborn child through placenta.
AIDS takes time to cause infection in a person and symptoms may also vary from 5 to 10 years. A ELISA-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method does a diagnosis of AIDS.
ADIS can be treated by giving the infected person antiretroviral drugs to prolong the lifespan of the person, as AIDS has no cure.
4. Give the symptoms of cancer.
Ans: Cancer is the abnormal growth of cells. Cancer-causing agents or factors are called carcinogens. There are various reasons a person can get cancer: chemicals, radiation, viruses, oncogenes, addictions to drugs, smoking, tobacco, and alcohol.
Symptoms of cancer are as follows:
fatigue
lump under skin (breast cancer: lump in breasts)
difficulty in swallowing
breathing problem
indigestion problems
joint pains, muscle pains
fever or night sweats
skin problems
5. Write a note on antigens on blood cells.
Ans: Antigens are present on the surface of blood cells. There are different blood group systems like ABO, Rh, Duffy, Kidd, Lewis, P, MNS, Bombay blood group, etc.
ABO blood group.
In the 1900s Karl Landsteiner discovered the ABO blood group he noticed humans have two types of antigens or agglutinogens present on the surface of red blood cells; antigen A and antigen B and related antibodies or agglutinins in serum antibody 'a' and antibody 'b'.
In ABO blood group systems we observe the type of blood group of an individual by the presence or absence of antigens A and B and then the blood group is classified into A, B, AB, and O.
6. Write a note on antigens-antibody Complex.
Ans: The study of antigen-antibody interaction is called serology.
The antibody is Y- shaped. It has two regions Fab (variable) and Fc (constant in every antibody).
The antigen can be a single protein/protein conjugate lipid and so on.
Antigen when entering the body triggers the immune response which then leads to the secretion of antibodies, and they produce antibodies matching the structure of the antigen.
Interaction between antigen-antibodies occurs between the Fab region of the antibody, it is the attachment region of an antigen with this section.
7. What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as a safeguard against infectious diseases?
Ans: The various public health measures against infectious diseases are:
Vaccination up-to-date.
Wash your hands regularly and before eating as well.
Do not touch your face or eyes frequently and especially with dirty hands.
Practice safe sex to avoid STDs, AIDS, and HIV.
Ventilate your home and your working space.
When you sneeze or cough covers your face.
Use a clean washroom, try to avoid using public and unhygienic washrooms.
Keep a sanitizer with yourself.
Keep intimate sanitizing products with yourself.
8. How does the transmission of each of the following diseases take place?
a. Amoebiasis
Ans: It is also called Amoebic dysentery which is caused by the protist parasite Entamoeba histolytica, it causes diarrhea in the human body and affects 10 - 15% of the population.
Life Cycle of Entamoeba Histolytica:
The food contaminated by the cyst of Entamoeba histolytica when consumed by a person causes amebiasis. The cyst of Entamoeba histolytica is non-motile i.e. it cannot move.
When the cyst enters our body via the mouth, it travels through the gastrointestinal tract.
When Entamoeba histolytica enters the mouth, it is in a cyst (non-motile) form but when it passes the stomach, this cyst forms 8 trophozoites (motile).
These trophozoites then enter the intestine, and it reproduces by binary fission. It reproduces in our colon and also forms cyst (non-motile) which then passes out of our body via feces.
This stool of an infected person contains a cyst of Entamoeba histolytica which can contaminate food or drinks and the cycle continues.
b. Malaria
Ans: Plasmodium vivax is a parasitic protozoan that causes malaria in humans.
The life cycle of Plasmodium vivax: this parasite has two life cycles, one asexual, which happens in the human body, and another sexual reproduction which happens inside the gut of the female Anopheles mosquito.
The vector female Anopheles mosquito bite carries it to healthy humans. The mosquito bite inserts sporozoites of Plasmodium vivax in healthy humans.
These sporozoites enter the bloodstream, it first targets the liver cells and reproduces asexually.
When sporozoites enter the liver cells, it becomes a spherical shape with a dominant nucleus. At this stage, it is called Schizont and goes through asexual reproduction called Schizogony and forms crypto merozoites/Cryptozoic.
After leaving one liver cell the trophozoites enter another liver cell and the cycle continues. These cryptozoites form merozoites called meta crypto merozoites.
These merozoites are of two types: macro meta crypto merozoites (trophozoites) which attack other liver cells and micro meta crypto merozoites which attack erythrocytes/RBCs.
When trophozoites enter RBC it develops and forms an amoeboid structure and it forms schizont. These cells go through schizogony (asexual reproduction) forming lots of merozoites inside RBC which creates pressure on RBC and rupture RBC cell and merozoites are released in the bloodstream and attack another RBC.
The merozoites reproduce sexually forming gametes macrogametocyte (female) and microgametocyte (male). But this sexual reproduction of merozoites takes place in the gut of the female Anopheles mosquito when it sucks the blood from an infected human.
These gametocytes enter the gut of the mosquito the sexual reproduction takes place by syngamy and forms a zygote (non-motile).
This zygote forms a motile structure ookinete. This ookinete crosses the stomach wall of the mosquito by lytic enzyme and goes inside the stomach wall and changes its form to a cyst-like structure called an oocyst.
The oocyst forms sporozoites which enter the salivary gland of the mosquito and when this mosquito bites another healthy human these sporozoites can enter the human body and infect them.
c. Ascariasis
Ans: Ascaris lumbricoides/roundworm causes ascariasis disease in the human body.
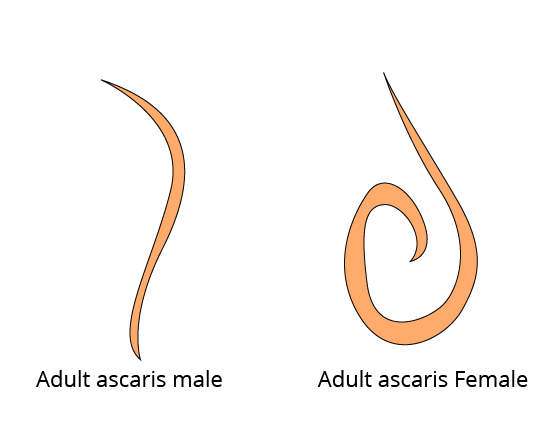
Ascaris
The Life Cycle of Ascaris Lumbricoides/Roundworm:
The eggs of Ascaris get inside our bodies when we consume contaminated food or drinks. The fertilized eggs of Ascaris can be present on vegetables or other foods.
The eggs have Rhabditiform larva in them; it goes inside our body through the GI tract and goes to the small intestine. In the small intestine, this larva comes out of the egg.
After 4th molting it becomes adult Ascaris. This adult Ascaris male and female travel to the large intestine and form eggs which will then come out of the human body through feces and to soil where these eggs get their 1st molting.
d. Pneumonia
Ans: Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs. Various pathogens can cause it.
Viruses: influenza virus, adenovirus, parainfluenza virus or Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Fungi: Pneumocystis jiroveci and Pneumocystis carinii.
Symptoms of pneumonia are:
Cough
High fever
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Loss of appetite
Fatigue
Headaches
Vomiting
Joint pain and muscle pain
Pneumonia spreads from person to person through direct contact by droplets released by an infected person while sneezing or coughing, by using shared clothes and utensils.
Treatment of pneumonia is given antibiotics and to prevent pneumonia vaccination is provided for both adults and children. Vaccines against Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
9. What measure would you take to prevent water-borne diseases?
Ans: Measures to prevent water-borne diseases are:
Drink purified water.
Boil water for at least 1-2 minutes before drinking.
Wash all your water storage containers, and bottles regularly.
Wash vegetables with lukewarm water with salt in it.
Eating cooked food.
When traveling, drink bottled water.
Clean places where water collects.
10. Write a short note on typhoid.
Ans: The gram-negative bacteria Salmonella typhi causes typhoid. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) causes the pathogenicity present on the surface of bacteria.
Salmonella Typhi
Symptoms of typhoid are:
High fever
Abdominal pain
Constipation
Diarrhea
Skin rashes
Anorexia
Nausea
Fatigue
Headache
Typhoid can spread through contaminated food, it is food and waterborne disease. Houseflies and cockroaches which feed on fecal matter pass bacteria on food. It can also spread through droplets if an infected person sneezes or coughs around you.
Typhoid can be diagnosed by a Widal test and can be treated by giving antibiotics to an infected person.
Match The Following
Column 1 | Column 2 |
AIDS | Antibody production |
Lysozyme | Activation of B-cells |
B-cells | Immunoglobulin |
T-helper cells | Tears |
Antibody | Immunodeficiency |
Ans:
Column 1 | Column 2 | Explanation |
AIDS | Immunodeficiency | AIDS-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. They reported the first case of AIDS in 1981. Syndrome means a group of diseases. The causative agent of AIDS is HIV-human immunodeficiency virus, which is a retrovirus. |
Lysozyme | Tears | A natural enzyme present in humans tears, saliva, and milk. It acts as an antimicrobial agent by removing the peptidoglycan layer of bacteria which leads to death. |
B-cells | Antibody production | B-cells or B-lymphocytes are produced in bone marrow and mature in bone marrow. |
T-helper cells | Activation of B-cells | T-helper cells stimulate the B-cells and B-cells then produce antibodies. |
Antibody | Immunoglobulin | Antibodies recognize antigen and bind to it to attack it. The antibody is Y- shaped. It has two regions Fab (variable) and Fc (constant in every antibody). |
Long Answer Questions
1. Describe the structure of antibodies.
Ans: Antibodies are also called Immunoglobulins (Ig). Antibody is Y-shaped protein molecules made up of different polypeptide chains. Antibodies recognize antigen and bind to it to attack it.
Antibodies consist of the heavy chain (H) ; it is the constant region and the light chain (L) has both constant and variable regions.
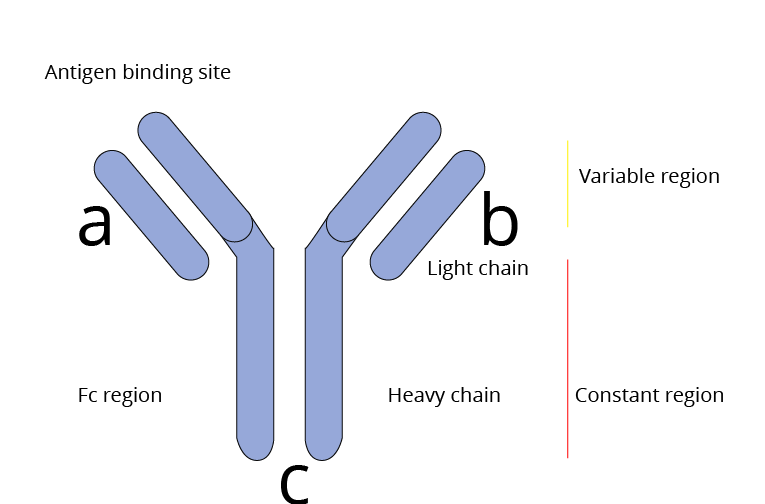
Antibody
Antigen-binding site is in the light chain region Interaction between antigen-antibody occurs between the Fab region of the antibody and the Fc region which binds to the immune cell receptors is in the heavy chain region.
The antibody can be a single molecule such as IgD, IgE. or IgG.
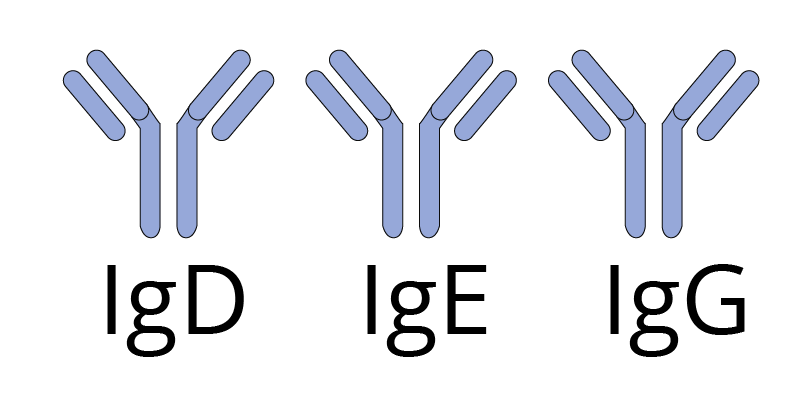
Single Molecule of Antibody
They can be a couple of molecules like IgA or a cluster of five antibody IgM.
2. Write a note on Vaccination.
Ans: Vaccination is the administration of inactivated pathogens of a particular pathogenic disease which provides immunity against disease or infection. It is a type of artificially acquired active immunity. Vaccination develops immunity against the disease without having a disease. It is a primary prevention measure to be taken to avoid infection.
3. What is cancer? Differentiate between benign tumor and malignant tumor. Name the main five types of cancer.
Ans: Cancer is the abnormal growth of cells. Cancer-causing agents or factors are called carcinogens. There are various factors responsible for causing cancer, they are:
Chemicals: nicotine, caffeine, polycyclic hydrocarbons, etc.
Radiations: X-rays, gamma rays, UV rays, cosmic rays.
Viruses called viral oncogenes and oncogenes.
Addictions: smoking, alcohol and drugs.
Symptoms of cancer are as follows: fatigue, lump under skin (breast cancer: lump in breasts), difficulty in swallowing, breathing problem, indigestion problems, joint pains, muscle pains, fever or night sweats, skin problems, and etc.
There are two types of tumors:
Benign or Non Malignant Tumor: this type of tumor is large, and it grows slowly but it does not spread to other parts of the body.
Malignant tumor or cancer: the growth of this tumor is rapid, and it spreads in other parts of the body.
The five main types of cancer are:
Carcinoma: the cancer that emerges from the epithelial lining of body organs is called carcinoma. Examples are breast cancer, lung cancer, skin cancer, etc.
Sarcoma: the cancer that emerges from the connective tissue is called sarcoma. Examples are bone tumors, muscle tumors, etc.
Lymphoma: the cancer that emerges from the lymphatic tissue is called lymphoma.
Leukemia: it is a type of blood cancer of white blood cells or leukocytes.
Adenocarcinoma: the cancer that emerges in the thyroid is called adenocarcinoma pituitary adrenal and other glandular tissues.
4. Describe the different types of immunity.
Ans: The immune system in our body provides immunity against infections, diseases and foreign invaders like microorganisms, allergy-causing agents, etc.
White blood cells (WBCs) are an essential part of the immune system. They are also called the immune cells of our body. Lymphocytes are a type of WBC which produces proteins called antibodies which bind and attack the foreign invaders which enter our body called antigens.
The Types of Immunity are:
Innate Immunity: the term itself means inborn/congenital is the type of immunity present by birth in every human. It can fight various acute infections on its own. There are important components of innate immunity which help them to perform tasks. They are physical barriers, physiological barriers, and cellular barriers.
Acquired Immunity: it is a type of immunity developed along a lifetime. There are two types of Acquired immunity: active and passive immunity.
Active Immunity: Active immunity is also called adaptive immunity; we develop it after antigenic stimulus. Active immunity lives for a longer time. Types of active immunity are:
Natural Acquired Active Immunity: is developed when a person gets infected by a pathogen and our body makes natural immunity by producing antibodies for the infection/pathogens.
Artificially acquired active immunity: in this they form the antibodies after vaccination.
Example: Polio vaccine and BCG vaccine.
Passive Immunity: the body cells do not take part actively in making passive immunity. Passive immunity lives for a short time. Types of passive immunity are:
Naturally acquired passive immunity: is transferred from mother to baby during pregnancy in the uterus and after pregnancy while breastfeeding period.
Artificially acquired passive immunity: the previously made antibodies in humans and animals a serum from those humans and animals is used.
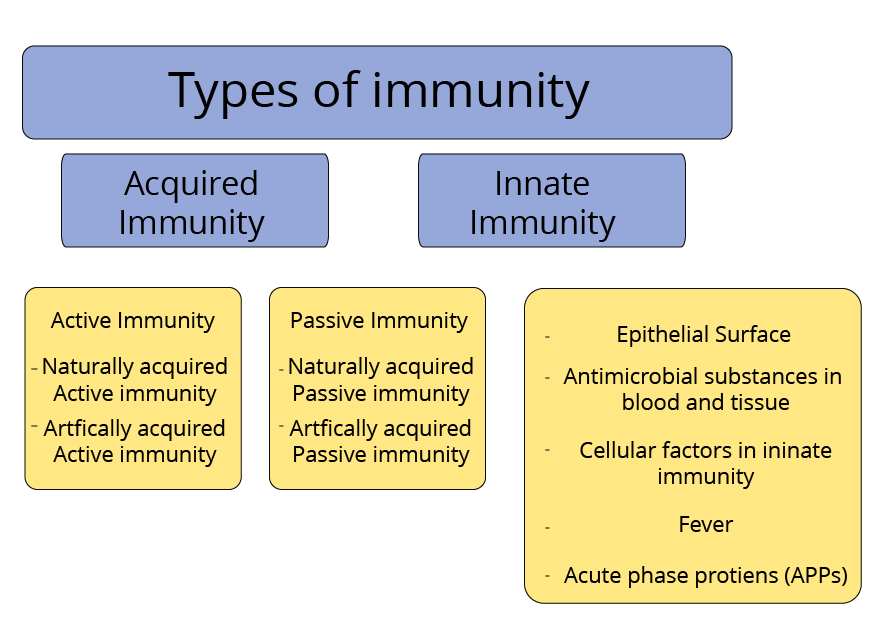
Types of Immunity
5. Describe the ill–effects of alcoholism on Health.
Ans: Alcohol is a powerful chemical. Drinking alcohol daily may leave you dehydrated, headache, digestion problems, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and can lead to alcohol poisoning.
Other risks of drinking alcohol excessively or getting addicted to alcohol on a daily basis affect addicted people's behavior:
They can get into accidents and injure themselves or others.
They become violent and antisocial behavior
Can have unsafe sex which can cause STDs.
Other long-term health problems alcohol addicted people have are: high blood pressure, liver cancer mouth cancer, breast cancer, depression, dementia, infertility, sexual problems, stroke, pancreatitis, etc.
6. In your view, what motivates the youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be avoided?
Ans: Addiction is the constant use of drugs, smoking and drinking alcohol. The addicted person may get various physical, physiological and psychological dysfunctions in the body.
Alcohol is a powerful chemical. Drinking alcohol daily may leave you dehydrated, headache, digestion problems, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea and can lead to alcohol poisoning.
Other long-term health problems alcohol addicted people have are: high blood pressure, liver cancer mouth cancer, breast cancer, depression, dementia, infertility, sexual problems, stroke, pancreatitis, etc.
Smoking causes many diseases like cancer, heart disease, lung disease, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. It increases the risk of TB. The most common disease caused by smoking is lung cancer.
Doing drugs like opioids, cocaine is an alkaloid and is derived from the coca plant. These are mind-expanding drugs which increase your dopamine level and cause hallucinations, paranoia, extreme happiness, and irritability.
These addictions tempt youngsters due to peer pressure, to get relieved from depression and other personal stress, and some may do it for fun and excitement.
To avoid such addictions, they should go for counsellings, or to a therapist where they can talk about their personal life problems and can be sent to a rehabilitation center.
7. Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Ans: Addiction is the constant use of drugs, smoking and drinking alcohol. The addicted person may get various physical, physiological and psychological dysfunctions in the body.
Addictions like smoking, drinking and doing drugs friends can influence you to do such things.
These addictions tempt youngsters due to peer pressure, to get relieved from depression and other personal stress, and some may do it for fun and excitement.
To avoid such addictions, they should go for counsellings, or to a therapist where they can talk about their personal life problems and can be sent to a rehabilitation center.
Importance of Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 10 Human Health and Diseases
This chapter describes what human health is and what its different aspects are. Back in the day, we used to consider that human health means the absence of any disease. The definition has changed and the mental condition of a person is now considered one of its crucial factors.
The health of an organism is defined by its functional efficiency. It is influenced by many factors. It also explains that an organism is healthy when it can avoid diseases and shows good physiological functions.
The chapter also explains what immunity is and how it determines the health of a person. The immunity of an individual is the power to resist infection caused by various pathogens. It also determines whether a person is immunized from various diseases.
This chapter will explain how different white blood cells of our circulatory system maintain immunity. The functions and mechanism of protection of our immunity will be explained. Students will also study the structure and functions of antibodies.
To understand these concepts, you can download and refer to the Human Health and Disease Class 12 notes. Get a simpler explanation of these fundamental concepts and get assistance to prepare this chapter.
Benefits of Human Health and Disease Class 12 PDF Notes
As mentioned earlier, these notes are prepared by experts. They have focused on the standard of the Maharashtra Board and simplified the concepts for your understanding.
These notes can be used as references to resolve doubts. You will not have to wait anymore and can proceed with the preparation of this chapter.
Learn from the Human Health and Disease Class 12 questions and answers PDF how the experts have formulated them. Find out how the experts have skillfully used the concepts to answer these questions accurately.
Reduce your preparation time by using the simplified version of this chapter. You can easily memorize and recall the concepts and answer questions faster during the board exams.
Download Human Health and Disease Class 12 Notes PDF
Perform the Human Health and Disease Class 12 PDF download Maharashtra Board today and complete your study material for this chapter. You can follow the answering patterns developed by the experts keeping the Maharashtra Board protocols in mind. Understand the concepts related to health and diseases better and score more in the exams.
FAQs on Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 10 Human Health and Diseases - PDF
1. What are pathogens?
Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms. They enter humans and consider them hosts. They start multiplying using the various biological nutrients available resulting in the development of various symptoms. Example: Plasmodium is an amoeba that causes malaria.
2. What is a vector?
A vector is an animal that carries pathogens. Vectors are responsible for the contamination of pathogens. Sometimes, an immune human can also act as a vector. Example: Anopheles mosquitoes act as the vector of malarial parasites.
3. Why is mental and social well-being considered in the definition of health?
Social and mental well-being determines how a person stays in society. It determines his mental status. It is directly linked to the physical well-being of that person.
4. What is the immune system?
A complex system of cells, tissues, and organs along with the biochemical substances created by them to defend us from diseases is called the immune system.
5. What protects us from pathogens?
The pathogens in our system are destroyed by the white blood cells present in the circulatory system.























