Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 8 Respiration and Circulation – Download Free PDF with Solution
Every organism has to respire to break down respiratory substrate and generate energy. This energy is then used at the cellular level to run various biochemical reactions and biological operations. It means that every cell needs a respiratory substrate to respire and respiratory substrates are delivered by the circulation system.
To understand these concepts of Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Respiration and Circulation, download the free solutions. Get the simplest explanation of these concepts and learn how the experts have answered the exercise questions to strengthen your foundation.
Access Maharashtra Board Solutions for Class XII Biology Chapter 8 Respiration and Circulation
Choose The Correct Alternatives From Those Given Below and Complete The Statements.
1. The muscular structure that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavity is ____
Pleura
Diaphragm
Trachea
Epithelium
Ans: Correct option - b. Diaphragm
Explanation: Diaphragm is the muscular structure that separates the thoracic cavity (lungs and heart) and the abdominal cavity (intestines, stomach, liver, etc).
2. What is the minimum number of plasma membranes that oxygen has to diffuse across to pass from air in the alveolus to hemoglobin inside an RBC?
Two
Three
Four
Five
Ans: Correct option- b. Three.
Explanation:
Alveolus has a squamous epithelium layer which lies on the basement membrane - alveolar membrane.
The capillary wall is made up of squamous epithelium, which lies on a thin basement membrane.
These three membranes, alveolar membrane, basement membrane and capillary wall together form a respiratory membrane.
3. ______ is a sound-producing organ,
Larynx
Pharynx
Tonsils
Trachea
Ans: Correct option - a. Larynx
Explanation: Larynx is the sound-producing organ, which is also known as the voice box; it contains the vocal cords which produce sound; it is also a part of the respiratory tract.
4. The maximum volume of gas that is inhaled during breathing in addition to T.V. is
Residual volume
I.R.V.
G.R.V.
Vital capacity
Ans: Correct option- b. I.R.V
Explanation: Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) is the maximum volume of air inhaled during breathing in addition to T.V. The amount of air inhaled is about 2000 to 3000ml.
5. Muscles contract when the external intercostal muscles contract
Internal abdominal
Jaw
Muscles in bronchial walls
Diaphragm
Ans: Correct option- d. Diaphragm
Explanation:
Diaphragm muscles contract when the external; intercostal muscles contract - so ribs and sternum move upward and downward. It shows an increase in thoracic volume and a decrease in the pressure of the thorax and the lungs.
This is an active process that transpires because of the pressure gradient which is formed between the lungs and the atmosphere during inspiration.
6. Movement of cytoplasm in a unicellular organism is called
Diffusion
Cyclosis
Circulation
Thrombosis
Ans: Correct option- b. Cyclosis
Explanation:
Cyclosis is a streaming movement of the cytoplasm shown by almost every organism.
In plants and animals, the movement of cytoplasm is within cells or called intracellular transport.
In flatworms, they do not have blood vessels, so body fluid moves around this extracellular transport.
7. Which of the following animals do not have closed circulation?
Earthworm
Rabbit
Butterfly
Shark
Ans: Correct option- c. Butterfly
Explanation: Butterfly has open circulation. In open blood circulation, the flood flows through the haemocoel.
8. Diapedesis is performed by
Erythrocytes
Thrombocytes
Adipocytes
Leucocytes
Ans: Correct option- d. Leucocytes
Explanation: Leukocytes or White blood cells(WBCs) have amoeboid movement by which they can move out of the capillary. This process is called diapedesis.
9. Pacemaker of heart is
SA node
AV node
His bundle
Purkinje fibres
Ans: Correct option- a. SA node
Explanation:
SA node (Sino-atrial node or sinus node)
It is called a natural pacemaker of the heart.
It is a part of conduction (nodal) tissue, which is a specialised cardiac musculature distributed in the heart.
10. Which of the following is without a nucleus?
Red blood corpuscle
Neutrophil
Basophil
Lymphocyte
Ans: Correct option- a. Red blood corpuscles
Explanation: Mature Red blood cells(RBCs) or erythrocytes do not have a nucleus or any other cell membrane-bound organelles.
11. Cockroach shows which kind of circulatory system?
Open
Closed
Lymphatic
Double
Ans. Correct option- a. Open
Explanation: Cockroaches have open blood circulation. In open blood circulation, the flood flows through the haemocoel.
12. Diapedesis can be seen in–cell
RBC
WBC
Platelet
Neuron
Ans. Correct option- b. WBC
Explanation: White blood cells(WBCs) have amoeboid movement by which they can move out of the capillary. This process is called diapedesis.
13. The opening of inferior vena cava is guarded by
bicuspid valve
tricuspid valve
Eustachian valve
Thebesian valve
Ans. Correct option- c. Eustachian valve
Explanation: Eustachian valve guards the opening of inferior vena cava or postcaval.
14. ___________ wave in ECG represents atrial depolarization.
P
QRS complex
Q
T
Ans. Correct option- a. P
Explanation: P-wave represents atrial depolarisation. It is a small deflection from the baseline of the graph.
15. The fluid seen in the intercellular spaces in Human is _________
blood
lymph
interstitial fluid
Water
Ans. Correct option- c. Interstitial fluid
Explanation: Interstitial fluid is found in spaces around the cells in humans.
Match the Respiratory Surface to The Organism in Which it is Found.
Respiratory surface | Organism |
Plasma membrane | Insect |
Lungs | Salamander |
External gills | Bird |
Internal Gills | Amoeba |
Trachea | Fish |
Ans:
Respiratory surface | Organism | Explanation |
Plasma membrane | Amoeba | Amoeba is a single-celled organism and is amoeboid in nature,respiration is aerobic through the cell surface. |
Lungs | Bird | Birds respire through lungs |
External gills | Salamander | Salamanders can respire through gills, lungs, skin, and the membranes of mouth and throat. |
Internal Gills | Fish | Fishes respire through gills. These tissues are present on either side of their head. |
Trachea | Insect | Insects respire through trachea, and the respiration in insects is called direct respiration. |
Very Short-Answer Questions.
1. Why does trachea have ‘C’ shaped rings of cartilage?
Ans: Trachea refers to the lower respiratory system. It is also known as windpipe, which is about 10 to 12cm in length. It is supported by ‘C’ shaped by 12 to 20 rings of cartilage (tracheal cartilage) to prevent its disintegration.
2. Why is respiration in an insect called direct respiration?
Ans: In insects, the respiration is direct as there is no role of the circulatory system in the respiration process as insects do not carry oxygen through blood but directly via the network of tubes (tracheal tubes) to the entire body.
3. Why is gas exchange very rapid at the alveolar level?
Ans: Alveolus is a single layer of squamous epithelium present inside lungs. They are elastic. The gas exchange is very rapid at the alveolar level because about 700 million alveoli provide a surface area for gasses.
4. Name the organ which prevents the following the entry of food into the trachea while eating.
Ans: Epiglottis prevents the entry of food into the trachea. It is a cartilage present on the top of the larynx. This prevents food from entering the windpipe (trachea).
Short Answer Questions.
1. Why is it advantageous to breathe through the nose than through the mouth?
Ans: Breathing through the nose is more advantageous than breathing through the mouth because it filters the air inhaled by you from the atmosphere.
When you breathe through your nose, the air going in from atmosphere to your lungs passes through three regions present inside your both right and left nasal chambers, i.e.,
Vestibule: it is an adjacent part of the nostrils. It has hair for filtering the air inhaled by trapping the dust particles.
Respiratory Part (Conditioner): the centre thin part is for warming and moistening the air.
Olfactory or Sensory Chamber: its function is for detection of smell.
2. Identify the incorrect statement and correct it.
A respiratory surface area should have a large surface area.
A respiratory surface area should be kept dry.
A respiratory surface area should be thin, maybe 1mm or less.
Ans: Wrong statement - b. A respiratory surface area should be kept dry.
Correct statement - a respiratory surface area should be moist.
Explanation - a respiratory surface should be moist so the gases inhales should dissolve and diffuse across the cell membranes.
3. Given below are the characteristics of some modified respiratory movement. Identify them.
a. Spasmodic contraction of muscles of expiration and forceful expulsion of air through nose and mouth.
Ans. Sneezing
b. An inspiration followed by many short convulsive expiration accompanied by facial expression.
Ans: Laughing and crying
4. Write a note on blood plasma.
Ans: Blood consists only 55% of plasma, <1% of leukocytes and platelets, and about 45% of erythrocytes as shown in figure.
Blood plasma is a yellow liquid part of blood in which all blood cells (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets) are suspended. Plasma contains 90% - water, proteins - 7 to 8%, inorganic salts - 1% and others - 1 to 2%.
Blood plasma carries the nutrients, hormones, and proteins to the body parts and the removal of waste products of the cells from the body.
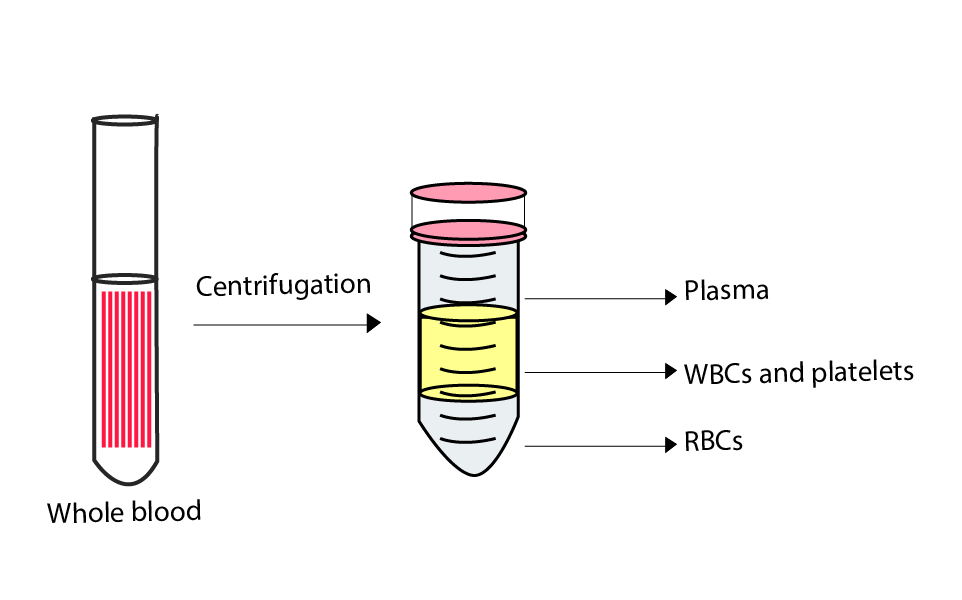
Constituents of Blood
5. Explain blood clotting in short.
Ans: Blood clotting or coagulation is the process that results in hemostasis, i.e. it stops bleeding when a blood vessel is injured.
When there is an injury or cut, the damaged tissue releases tissue thromboplastin and a damaged blood vessel releases a prothrombin activator.
Tissue thromboplastin converts prothrombin activator to thrombin (insoluble) with the help of enzyme thrombokinase.
Thrombin converts fibrinogen (insoluble) to fibrin threads, which form meshwork or clot on an injury or cut.
6. Describe pericardium.
Ans: The Pericardium is a double-walled sac that encloses the heart, the pericardial fluid and the roots of the great vessels, and is situated within the middle of the mediastinum.
The pericardium has two layers: one made of fibrous tissue and the other made of serous tissue.
Its function is to lubricate the heart to reduce friction.
7. Describe valves of the human heart.
Ans: Valves are present between chambers and the major arteries and veins of the heart to prevent any backflow of blood into the heart.
Types of valves present inside a human heart are:
In the right atrium: when the inferior vena cava brings the blood from the lower parts of the body to the heart, to prevent the backflow of the blood we require a valve which is the Eustachian valve.
The coronary sinus brings deoxygenated blood from the heart to the right atrium and to prevent backflow. Thebesian valve is present.
Tricuspid valve is a valve present on the right side of the heart between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
Bicuspid valve is present on the left side of the heart between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Semilunar valve or pulmonary valve is present in the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood.
Aortic valve is present on the aorta.
8. What is the role of papillary muscles and chordae tendineae in the human heart?
Ans: Papillary muscles are present inside ventricles and are attached to the atrioventricular valves via chordae tendineae, their role is to hold or pull the valves downward so it does not open in the opposite direction when and stop the backflow of blood from ventricles to atria when the ventricles contract.
9. Explain in brief the factors affecting blood pressure.
Ans: The pressure on the wall of blood vessels exerted by blood is called blood pressure. Our bodies work very hard to keep blood pressure at a stable level.
Factors that affect Blood Pressure are:
Blood Volume (Quantity): an increase in blood volume would increase blood pressure and vice versa. Regulated by the kidneys and influenced by salt.
Cardiac Output: if we increase cardiac output, the blood pressure increases.
Vessel Diameter: decrease in vessel diameter, and the blood pressure increases.
Vessel Elasticity: if we decrease elasticity, the blood pressure increases.
Vessel Viscosity (Thickness of Blood): increase in viscosity of blood, increases blood pressure.
Total Vessel Length: increase in total vessel length, increases blood pressure.
Give Scientific Reasons.
1. Closed circulation is more efficient than open circulation.
Ans: In the open circulatory system, the blood flows out of the blood vessels and in the closed circulatory system, blood flows inside arteries and veins by which the blood does not mix with other body fluids and transports blood to every part of the body.
2. The human heart is called myogenic and auto-rhythmic.
Ans: The SA node is present in the right auricle of the heat. This SA node generates an impulse which passes through Purkinje fibres by which the heart beats. As the impulse is generated by the heart itself, by which the heart beats so, the heart is called myogenic and auto rhythmic.
3. The person who has undergone a heart transplant needs a lifetime supply of immunosuppressants.
Ans: Immunosuppressant drugs are given to patients who undergo organ transplants, to reduce their body's immune activity and risk of rejection of transplant organs. As these patients are in constant threat of organ rejection in which their immune system may attack.
4. Arteries are thicker than veins.
Ans: Arteries are thicker than veins because of the blood pressure. Blood pressure drops as the blood gets farther from the heart. When the heart pumps, the blood pressure is highest in the aorta and lowest at the vena cava.
Blood pressure in the aorta is about 120/80 mm Hg and it drops as it goes through smaller arteries and by the end of arterioles.
Capillary beds' pulse pressure begins at about 35mm Hg and drops to 15mm Hg by the end of capillaries and continues to drop as it goes through venules and veins.
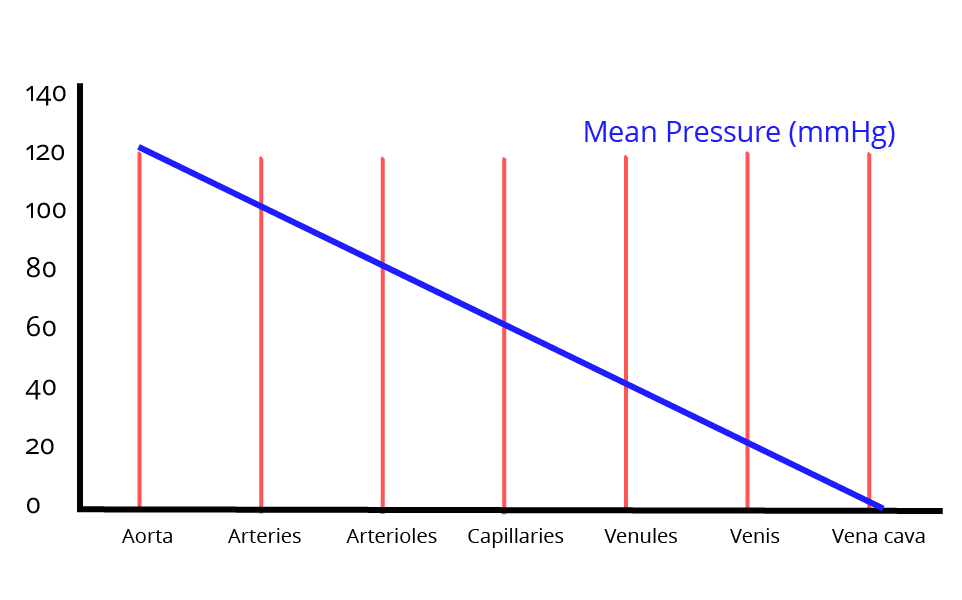
Graph of Blood Pressure
5. The left ventricle is thicker than all other chambers of the heart.
Ans: The human heart has four chambers, of which the upper two chambers are the Atrium and the lower two chambers are ventricles.
Ventricles are larger than the atria but narrow as they approach the apex. They function by collecting the blood that flows into them from the atria and then contracts.
As the left ventricle contracts it pumps blood to all the body parts at a higher pressure and to withstand that high pressure, the left ventricle is thick.
Distinguish Between
1. Open and Closed Circulation.
Ans.:
Open Circulation | Closed Circulation |
In the open circulatory system, it pumps blood directly into the body's cavities. | In the closed circulatory system, the blood is going to be contained within a vessel. |
In an open circulatory system, organisms are going to have blood-like fluid., which is a combination of blood and interstitial fluid. | In the closed circulatory system, we have blood, which is separated from the interstitial fluid |
The contraction of the heart is going to push blood from one cavity to another. | The contraction of the heart is going to move blood from a larger vessel into a smaller vessel. |
2. Artery and Vein.
Ans:
Artery | Vein |
Arteries move away from one cavity to another. | Veins go back to the heart. |
Arteries carry oxygenated blood except for the pulmonary artery, which goes away from the heart but it goes to the lungs to get oxygenated. | Veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the pulmonary vein, which carries oxygenated blood which is then pumped by heart to all body parts. |
Arteries have thick walls | Veins have thin walls compared with arteries. |
Arteries are brighter, like red | Veins are darker, almost purple. |
Blood pressure is higher in arteries. | Blood pressure in veins is low. |
3. Blood and Lymph.
Ans:
Blood | Lymph |
Blood colour is red, as blood has red blood cells. | Lymph fluid is colourless, due to the absence of red blood cells. |
Lymphocytes in blood are less. | Lymphocytes in lymph are more. |
Blood carries more nutrients and oxygen. | Lymph carries a less amount of nutrients and oxygen amount is also low. |
Blood has platelets which carry fibrinogen so blood has a fibrinogen in large amounts. | Lymph has a smaller amount of fibrinogen. |
4. Blood Capillary and Lymph Capillary.
Ans:
Blood Capillary | Lymph Capillary |
Blood capillaries carry blood and transport it. | Lymph capillaries carry lymph fluid and transport it. |
Blood capillaries are narrow. | Lymph capillaries are wider. |
Blood capillaries carry blood and so we can observe blood capillaries easily. | Lymph capillaries carry lymph fluid, which is colourless, and so it is difficult to observe lymph capillaries. |
5. Intrinsic and extrinsic process of clotting.
Ans:
Intrinsic clotting | Extrinsic clotting |
Internal trauma activates the intrinsic clotting pathway. | External trauma activates the extrinsic clotting pathway. |
Factors involved in the intrinsic clotting pathway are VIII, IX, XI, and XII. | Factors involved in extrinsic clotting pathway are VII. |
Intrinsic pathway is slow. | Extrinsic pathway is fast. |
The initiation of blood clotting at an injury starts within 15-20 seconds. | The initiation of blood clotting at an injury starts within 2-6 minutes. |
Long Answer Questions.
1. Smita was working in a garage with the doors closed and the automobile's engine running. After some time, she felt breathless and fainted. What would be the reason? How can she be treated?
Ans: Smita was working at a garage with all doors shut and an automobile engine running, which released carbon monoxide and did not come out of the garage, which suffocated her and so she felt breathless and fainted.
Carbon monoxide is dangerous for the human body and, if not treated, can be fatal.
To treat her and remove carbon monoxide from her body, we administer pure oxygen.
This will remove carbon monoxide from her hemoglobin.
2. Shreyas went to a garden on a wintry morning. When he came back, he found it difficult to breathe and started wheezing. What could be the possible condition and how can he be treated?
Ans: Shreyas showed symptoms like difficulty in breathing and wheezing sound. These are symptoms of asthma.
Asthma is a major noncommunicable disease that can affect anyone of any age. There are some other common symptoms of asthma, i.e. chest tightness or pain, trouble sleeping, coughing, etc.
Asthma can be treated by using inhalers which helps patients in breathing.
3. Why can you feel a pulse when you keep a finger on the wrist or neck but not when you keep them in a vein?
Ans: We can feel a pulse when you keep a finger on the wrist or neck but not when you keep them in a vein because as we know, the blood pressure is higher in arteries and lower in the veins, which weaker pulse in veins and so is not detectable.
When the heart pumps, the blood pressure is highest in the aorta and lowest at the vena cava.
Blood pressure in the aorta is about 120/80 mm Hg and it drops as it goes through smaller arteries and by the end of arterioles.
Capillary beds' pulse pressure begins at about 35mm Hg and drops to 15 mm Hg by the end of capillaries and continues to drop as it goes through venules and veins.
4. A man’s pulse rate is 68 and cardiac output is 5500 cm3. Find the stroke volume.
Ans: We have to find stroke volume (SV) with given,
Cardiac output (CO) = 5500cm3
Pulse rate (HR) = 68
Stroke volume (SV) = x
So, the formula to be applied is cardiac output = heart rate X stroke volume
CO = HR X SV
5500 = 68 X (x)
5500 ፥ 68 = (x)
x = 80.8 ≈ 81cm3
Therefore, the stroke volume is 81 cm3 with a pulse rate 8 and cardiac output 5500 cm3.
5. Which blood vessel of the heart will have the maximum content of oxygen and why?
Ans. Veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the pulmonary vein, which carries oxygenated blood from lungs which is then pumped by heart to all body parts. The oxygenated blood from the lungs which just got filtered, the oxygen level in this blood is high and the pulmonary vein which carries this oxygenated blood from lungs to heart has the maximum content of oxygen.
6. If the duration of the atrial systole is 0.1 sec and that of complete diastole is 0.4 sec, then how does one cardiac cycle complete in 0.8 sec?
Ans: Cardiac cycle is the cycle of the beginning of one heartbeat to the next heartbeat. As we all know, that heart beats 72 times per minute, so there are 72 cardiac cycles per minute. Cardiac cycle is a sum of atrial systole, ventricular systole and complete diastole. Duration of atrial systole is 0.1 sec, ventricular systole is 0.3 sec, and complete diastole is 0.4 sec and sum of all cardiac cycles is 0.8 sec.
7. How is blood kept moving in the large veins of the legs?
Ans: When the body moves the blood moves from veins, there is a rhythmic movement of smooth muscles in vessels (veins) of valves and the action of skeletal muscles takes place.
Veins carry deoxygenated blood and the flow of blood is against gravity (legs) and it prevents backward flow of blood by one-way valves.
So the Blood flows only in one direction in the large veins of the legs.
8. Describe the histological structure of artery, vein, and capillary.
Ans: Arteries: tubular cells which carry oxygenated blood and all nutrients to the body. As blood passes from the arteries (starting in the aorta to small arteries) the luminal diameter decreases.
We Categorize them into 3 Types: large elastic artery, medium muscular arteries, arterioles.
The following figure shows each artery has 3 primary layers:
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica adventitia
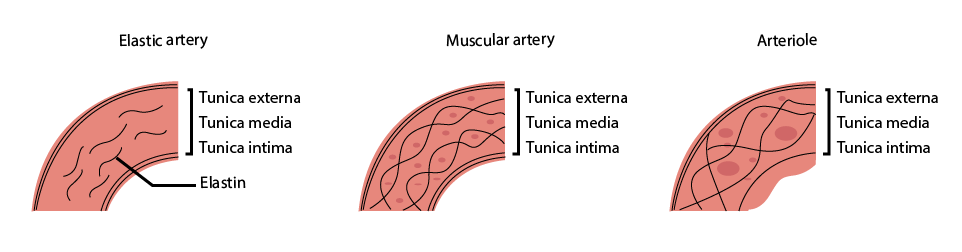
Layers of Arteriole
Veins: tubular cells which transport deoxygenated blood and waste from the capillary bed to the heart.
We Categorize them into 3 Types: small veins, medium veins and large veins.
The following figure shows each vein has 3 primary layers:
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica adventitia

Layers of Veins
Capillaries: Blood flows from the arteriole and goes to the capillary bed, they have a network like structure. Blood flows through these capillaries, supplying cells with all the interstitial fluid with all the nutrients, and collecting all the waste from the interstitial and returning to heart.
There are 3 Primary Types of Capillaries: continuous capillaries, fenestrated capillaries, and sinusoid or discontinuous capillaries.
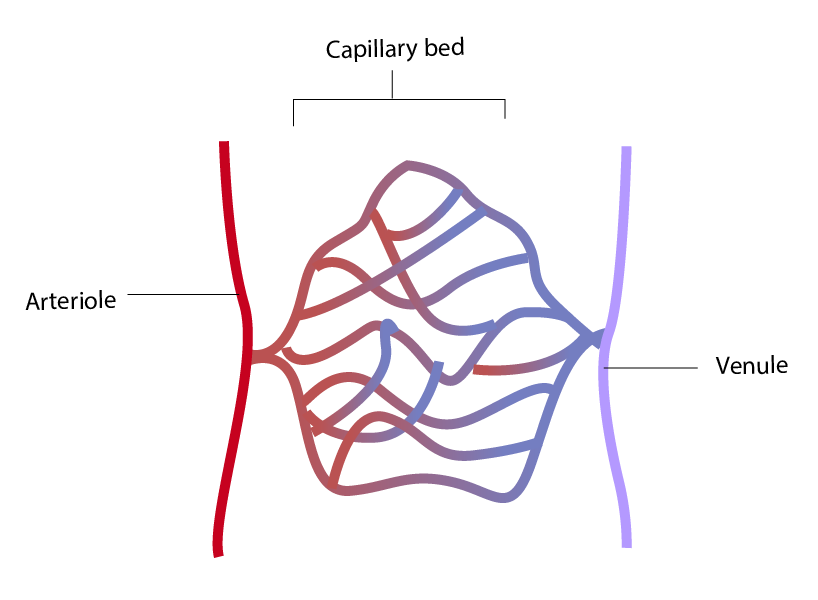
Capillary Bed
9. What is blood pressure? How is it measured? Explain factors affecting blood pressure.
Ans: Blood pressure is the pressure on the wall of blood vessels exerted by blood is called blood pressure. Our bodies work very hard to keep blood pressure at a stable level.
The five key players for maintaining the blood pressure are arterioles, baroreceptors, medulla oblongata, hormones/adrenal medulla and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
The instrument sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure. When we measure the patient's blood pressure, we are looking at the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure.
Systolic pressure (top number) = 120 mm Hg.
Diastolic pressure (lower number) = 80 mm Hg.
Factors that Affect Blood Pressure are:
Blood Volume (Quantity): an increase in blood volume would increase blood pressure and vice versa. Regulated by the kidneys and influenced by salt.
Cardiac Output: if we increase cardiac output, the blood pressure increases.
Vessel Diameter: decrease in vessel diameter, and the blood pressure increases.
Vessel Elasticity: if we decrease elasticity, the blood pressure increases.
Vessel Viscosity (Thickness of Blood): increase in viscosity of blood, increases blood pressure.
Total Vessel Length: increase in total vessel length, increases blood pressure.
10. Describe human blood and give its functions.
Ans: Blood is composed of specialized cells that circulate in an extracellular fluid called plasma. These three cells are:
Red Blood Cells / Erythrocytes: carry oxygen from our lungs to other parts of the body through blood.
White Blood Cells / Leukocytes: or WBCs circulate within our bloodstream. They are part of the immune system and attack pathogens cells or foreign bodies which enter our body.
Platelets / Thrombocytes: platelets' main function is to stop the bleeding by coagulation process on the wound or cut.
Plasma comprises about:
92% water
7% proteins
1% other solutes
The total blood volume of an adult is 6 L. leukocytes and thrombocytes only comprise about 1% of blood volume and plasma is the largest portion of the blood is about 55% and hematocrit (HTC) is the percent of packers red blood cells in blood, volume of hematocrit is between 30% to 40% in males and 35% to 45% in females.
Importance of Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Respiration and Circulation
Respiration is one of the crucial chapters of the Class 12 Biology syllabus of the Maharashtra Board. In this chapter, students will learn how a cell respires in the presence or absence of oxygen. A substrate is burned from a higher carbon number to a lower one to produce energy.
This energy is then used at the cellular level to perform various cytological functions. At a macro level, these cytological functions cumulatively result in the functions of a tissue or an organ.
This chapter will also explain how gaseous exchange occurs in different animals. The exchange of gasses is mandatory and it is done with the help of the circulation system. You will find the concepts explained well in the Respiration and Circulation Class 12 Solutions.
The complex respiratory system of human beings has also been explained in this chapter. You will learn how the organs are segmented into different parts for performing this function. These segments will take part in the mechanism of respiration and aid an organism to exchange glasses.
Benefits of Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 8 Respiration and Circulation
To understand the crucial concepts, refer to the Respiration and Circulation Class 12 Solutions. You will find an easy explanation of the concepts of this chapter. It will make your preparation easier and faster.
There is no need to make concise notes when the experts have done them for you. Instead, jump to solve the Respiration and Circulation Class 12 questions and answer and check your preparation level. Find out where you need to focus more and make your preparation stronger.
You can keep the files stored on your computer and refer to them anytime you want. Make your study sessions more fruitful and clarify doubts on your own. There is no need to waste time when you can resolve queries faster and proceed with the completion of the syllabus.
Find out how the experts have framed the answers to the exercise questions in the Respiration and Circulation Class 12 MCQ PDF. Learn how they have incorporated the concepts to formulate accurate answers.
Download Respiration and Circulation Class 12 Exercise Solutions PDF
Get the free PDF of Respiration and Circulation Solutions PDF download and complete your preparation for this chapter. Make it your ideal study partner and find out the best explanations of all the questions in the exercises of this chapter. Understand the concepts related to respiration and circulation and their relationship better to score well in the exams.
FAQs on Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 8 Respiration and Circulation
1. What is respiration?
The process of the exchange of gases in the respiratory system is called respiration. At the cellular level, it is the process where a respiratory substrate is broken down to generate energy.
2. Where does the exchange of gases occur in human beings?
The exchange of gases occurs in the lungs. The inhaled air passes oxygen to the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is passed to the inhaled air from the bloodstream.
3. Which animal performs cloacal respiration?
Turtles perform cloacal respiration when they get underwater. These animals have an extra pair of air bladders connected to the cloaca.
4. How do fishes breathe?
Fishes use external gills to breathe underwater. The exchange of gases takes place in the gills.
5. How do microorganisms breathe?
They perform the exchange of gases through their cell walls and/or cell membranes.























