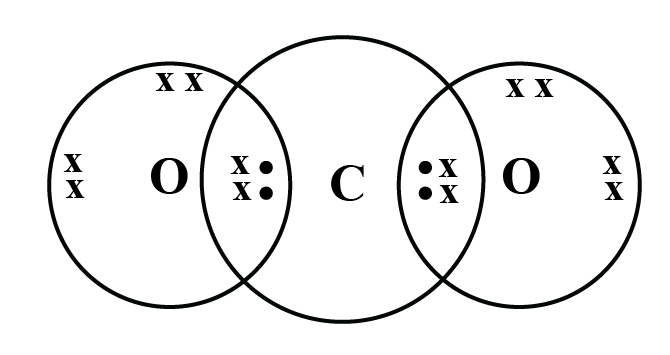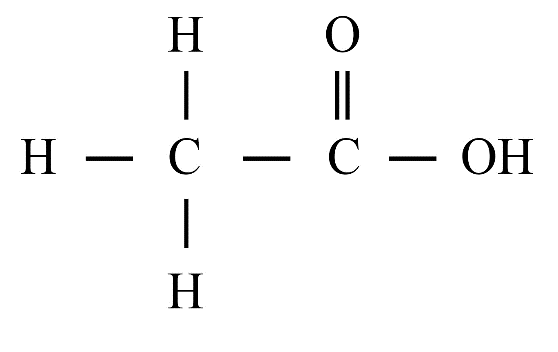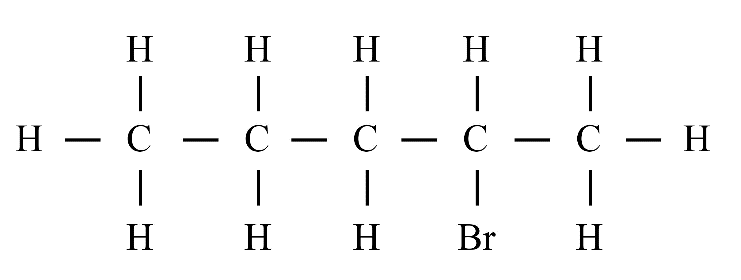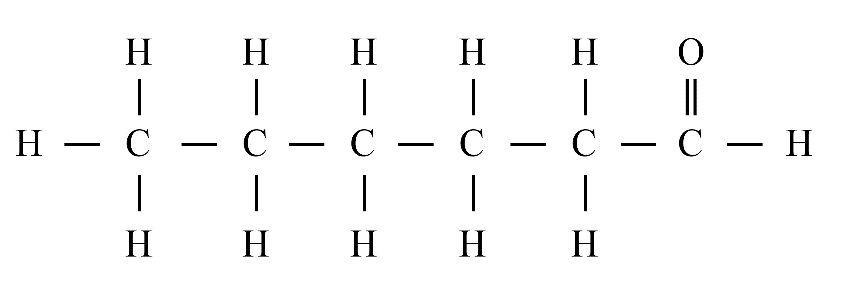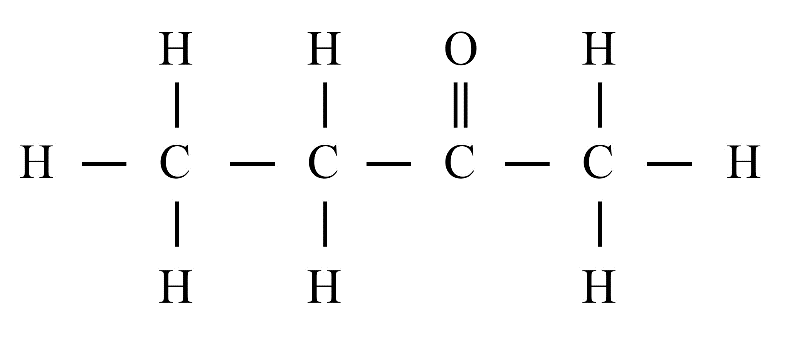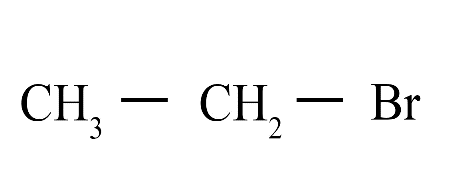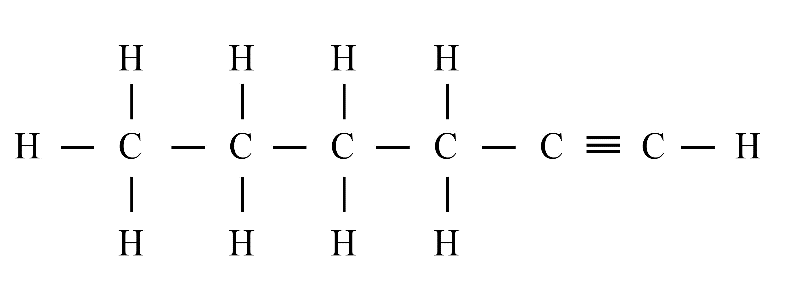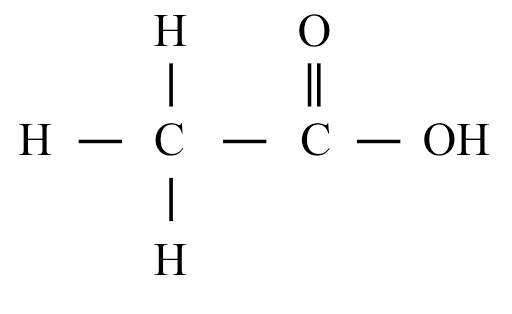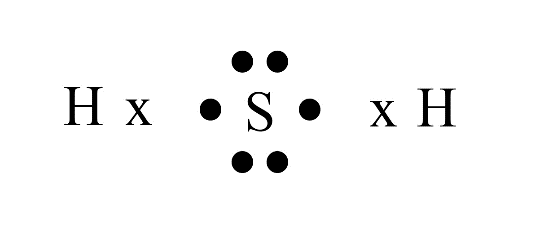Carbon And Its Compounds Class 10 Questions And Answers
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds (2025-26)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds (2025-26)
1. Why does carbon form covalent bonds?
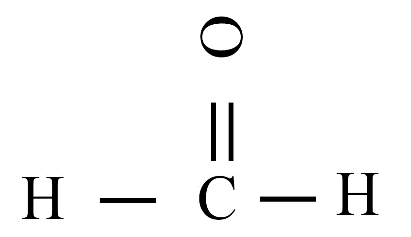
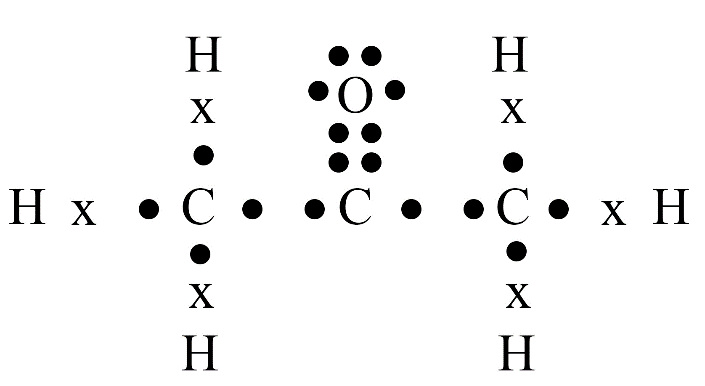
Carbon has four valence electrons. It cannot gain or lose four electrons to achieve a stable configuration due to high energy needs. Instead, it shares its valence electrons with other atoms to form stable covalent bonds, satisfying the octet rule.
2. What makes carbon a versatile element?
Carbon's versatility is due to two key properties: tetravalency (valency of four) and catenation (the ability to form long chains, branches, and rings with other carbon atoms). This allows it to form a vast number of stable organic compounds.
3. Where can I find all Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 questions and answers?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 are available on Vedantu. They provide detailed, step-by-step answers for all in-text and chapter-end exercise questions, ensuring a thorough understanding of all concepts and preparing you for exams.
4. What are isomers?
Isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula but have different structural arrangements. For instance, butane (C₄H₁₀) exists as n-butane (a straight chain) and isobutane (a branched chain), which have different physical properties.
5. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 help with homework?
These solutions provide clear and accurate answers for every question in the textbook. Students can use them to verify their own work, understand complex topics like nomenclature, and complete their homework correctly and efficiently, building a strong conceptual foundation.
6. What is a homologous series?
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds with the same functional group and similar chemical properties. Each successive member in the series differs by a –CH₂ group. Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are common examples.
7. Can I get the Class 10 Science Chapter 4 question answers in a PDF?
Yes, you can easily access a Free PDF download for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 question answers. This allows for convenient offline access to all solutions, making it easy to study and revise anytime, anywhere without an internet connection.
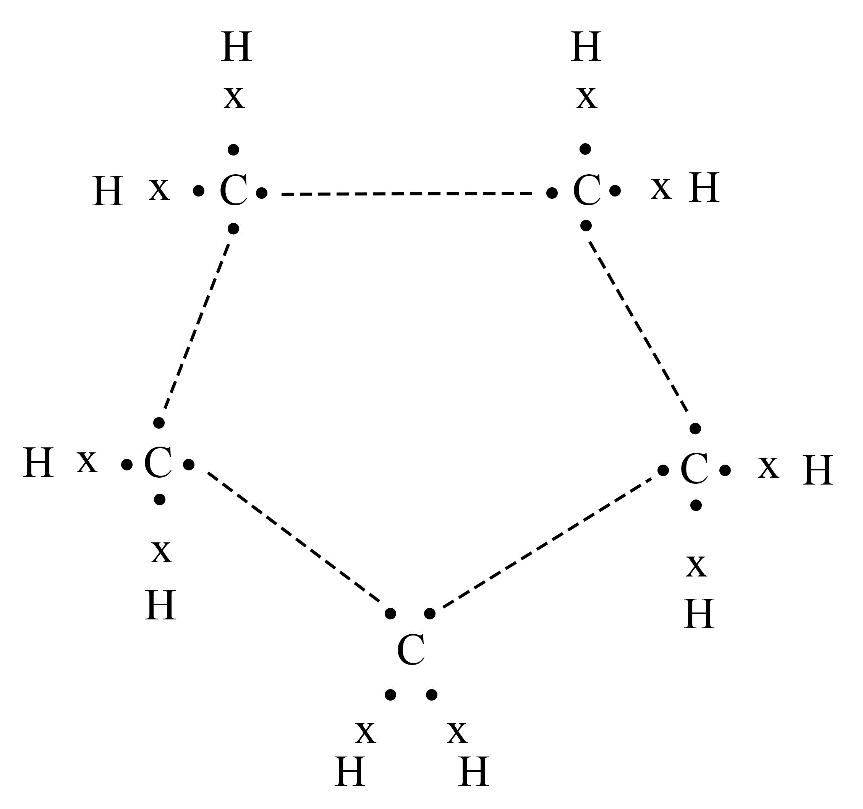
8. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?
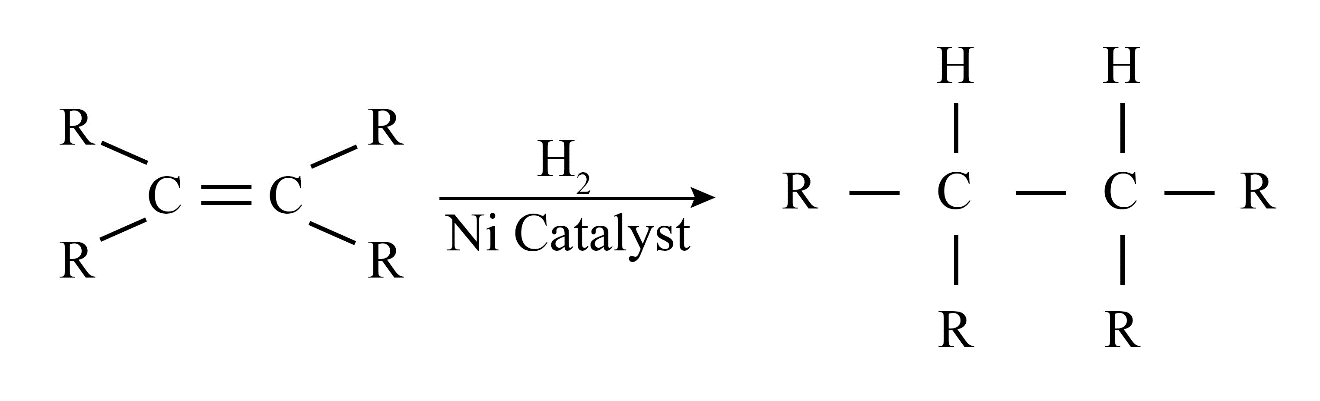
Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) contain only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes and alkynes) contain at least one double or triple covalent bond between carbon atoms, making them more reactive than saturated ones.
9. What is included in the Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 NCERT PDF solutions?
The solutions PDF covers answers to all questions from the NCERT textbook, including in-text and exercise problems. Vedantu's solutions explain chemical reactions, nomenclature, and reasoning questions step-by-step, following the CBSE marking scheme.
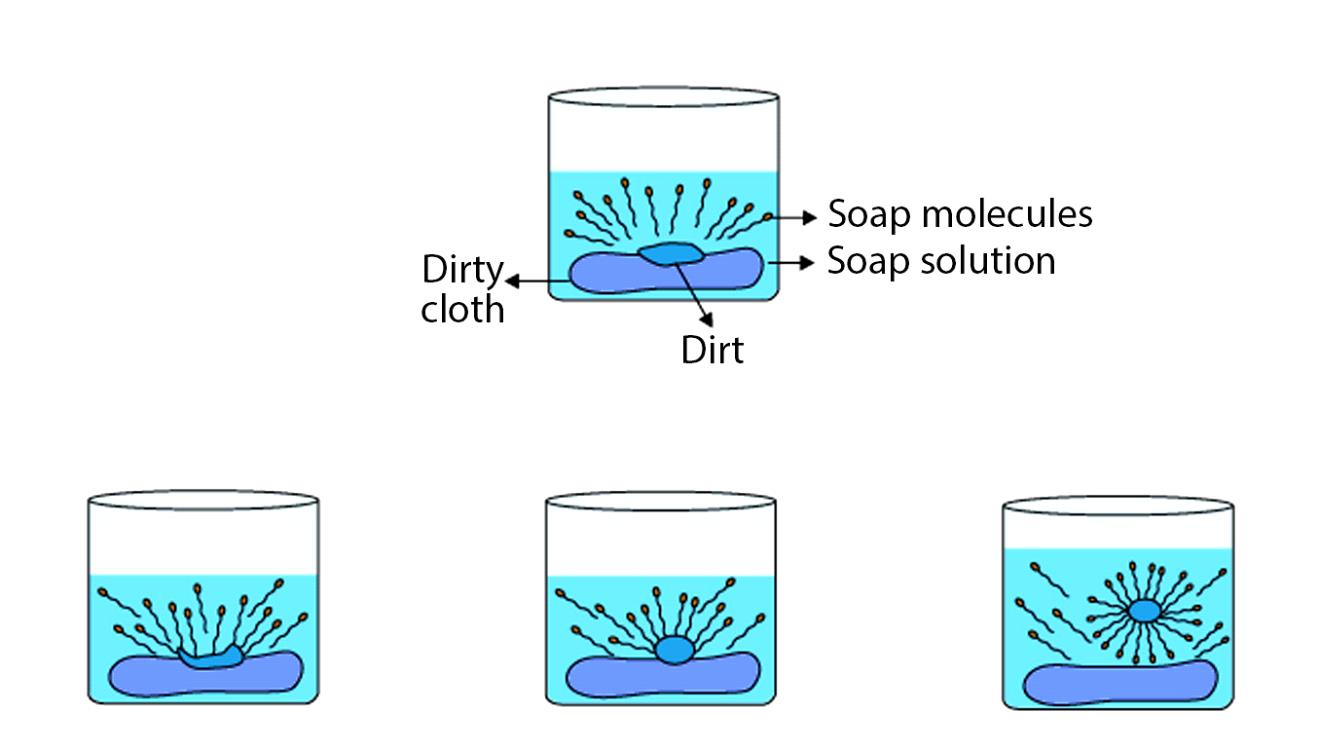
10. How does a soap molecule clean dirt?
A soap molecule has a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and a hydrophobic (oil-attracting) tail. The tails trap oily dirt in clusters called micelles. The hydrophilic heads face outwards, allowing the entire micelle to be washed away with water.
11. What are the main allotropes of carbon?
The main crystalline allotropes of carbon are diamond, graphite, and buckminsterfullerene. Diamond is extremely hard, graphite is a soft conductor of electricity, and buckminsterfullerene is a molecule made of 60 carbon atoms arranged in a spherical shape.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video