Biomolecules Questions and Answers for Class 11 Students
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules (2025-26)
1. What step-by-step approach does the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 follow to explain the analysis of chemical composition in biomolecules?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 use a systematic, CBSE-recommended method for analyzing chemical composition.
- Tissue is ground and extracted using suitable solvents to obtain acid-soluble and acid-insoluble fractions.
- The acid-soluble fraction contains small biomolecules like amino acids and sugars, while the acid-insoluble fraction has macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
- Each category is examined further for the presence and types of biomolecules by chemical tests, chromatography, and spectroscopic analysis, ensuring clear identification aligned with CBSE 2025–26 exam methodology.
2. How does the NCERT Solutions for Biomolecules distinguish between primary and secondary metabolites?
According to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9, primary metabolites are molecules essential for normal growth and metabolism, such as amino acids, sugars, and nucleotides. Secondary metabolites include compounds like alkaloids and flavonoids that are not vital for basic survival but often provide ecological advantages, such as defense or signaling. Recognizing this distinction aids accurate textbook-based problem solving.
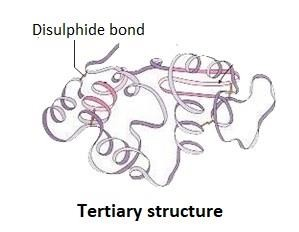
3. What is the recommended stepwise method to describe the tertiary structure of proteins in Class 11 NCERT Solutions?
NCERT Solutions recommend:
- First, depict the polypeptide chain’s linear (primary) order of amino acids, then the localized folding (secondary structure).
- Next, illustrate the comprehensive three-dimensional folding (tertiary structure), emphasizing bonds like hydrogen, ionic, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bridges.
- This specific folding determines protein functionality, essential for exam-based diagrammatic accuracy in CBSE 2025–26.
4. How should you explain the polymeric structure of biomacromolecules when using the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9?
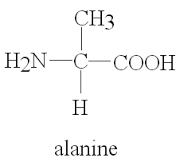
The NCERT Solutions define a polymeric structure as large molecules made up of repeating monomeric units linked by covalent bonds, such as peptide, glycosidic, or phosphodiester bonds. For example, proteins consist of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds; polysaccharides are formed by monosaccharides linked via glycosidic bonds.
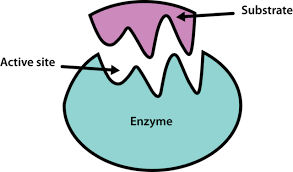
5. What are the correct steps for solving a question related to enzyme properties, as per the CBSE methodology in the NCERT Solutions?
Stepwise CBSE approach includes:
- Begin by defining enzymes as biological catalysts, usually proteins.
- List key properties such as substrate specificity, high efficiency, optimal temperature and pH, and sensitivity to inhibitors.
- Explain terms like active site and note features like denaturation under extreme conditions, matching official marking schemes.
6. Why is it crucial to follow the step-by-step methods outlined in NCERT Solutions when preparing for board exams?
Following the stepwise approach ensures clear presentation, logical flow, and coverage of all points as per CBSE marking schemes. This method reduces errors, helps score maximum marks, and ensures answers meet the length and depth expected in CBSE 2025–26 board exams.
7. How does the NCERT Solutions illustrate the application of biomolecules like enzymes in industry or medicine?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 highlight that enzymes are used in:
- Medicine (e.g., streptokinase for dissolving blood clots, insulin for diabetes management)
- Food processing (e.g., protease in cheese making, diastase in malting)
- Textile and leather industries (e.g., lipases for stain removal)
8. What would happen if the three-dimensional structure of an enzyme were lost, according to NCERT Solutions?
If the three-dimensional structure of an enzyme is lost (denaturation), its active site changes shape, preventing substrate binding. As a result, the enzyme becomes inactive and can no longer catalyze biological reactions, impacting cellular metabolism.
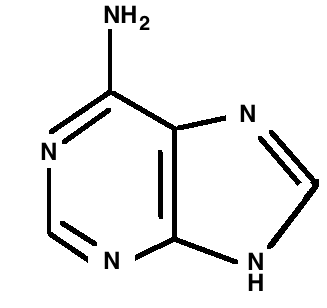
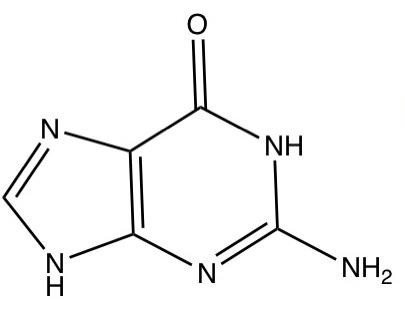
9. How does knowledge of biomolecules help explain vital physiological processes in humans as per the Class 11 NCERT Solutions?
Understanding biomolecules is key to explaining cell structure, energy production, genetic information flow, and responses to signals. This knowledge connects chemistry concepts with biological phenomena like metabolism and disease, as emphasized in the NCERT Solutions.
10. What are some common misconceptions students have when applying NCERT Solutions to Class 11 Biomolecules, and how can they be corrected?
Common errors include confusing primary and secondary metabolites, misunderstanding enzyme-substrate specificity, and mixing up covalent bonds in different macromolecules. The NCERT Solutions address these by providing clear definitions, examples, and stepwise explanations, strengthening conceptual clarity for CBSE 2025–26 board exams.
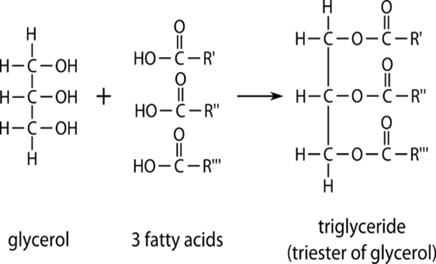
11. In solving Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 questions, how should you describe the composition of triglycerides for maximum marks?
NCERT Solutions recommend:
- State that a triglyceride consists of one glycerol molecule esterified with three fatty acids (which may be same or different).
- Emphasize they are primary energy storage molecules in living organisms.
- Differentiating between simple and mixed triglycerides adds detail as per marking scheme requirements.
12. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 ensure answers meet the expectations of CBSE examiners?
NCERT Solutions break down each question into logical, stepwise points, incorporate labeled diagrams where required, and provide concise explanations adhering to CBSE’s latest 2025–26 syllabus and marking schemes.
13. What are the key benefits of regularly practicing with NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules?
Regular use of NCERT Solutions offers:
- Improved conceptual understanding of biomolecules, enzymes, and their functions
- Practice in following CBSE-approved answer formats
- Increased confidence in diagram-based and descriptive questions
- Reduced exam anxiety through familiarity with expected question patterns for 2025–26
14. How can students leverage the detailed explanations in CBSE Class 11 NCERT Solutions to tackle high-order application questions on enzymes or nucleic acids?
By studying stepwise explanations and real-world examples given in NCERT Solutions, students can analyze case studies, predict outcomes of molecular changes, and apply fundamental principles to unfamiliar biological scenarios. This approach develops critical thinking as required for high-order thinking skill (HOTS) questions in CBSE exams.
15. What stepwise method should you follow to perform qualitative tests for proteins, fats, and starch as outlined in the NCERT Solutions?
The recommended steps are:
- For proteins: Use the xanthoproteic test (add nitric acid, heat – yellow color indicates proteins).
- For fats: Apply the emulsification test (mix with water and soap – persistent emulsion forms).
- For starch: Conduct the iodine test (blue-black color confirms starch presence).
- Ensure all procedures and observations are described according to CBSE’s expected format.