
Vector Algebra - Exercise-wise Questions and Answers For Class 12 Maths - Free PDF Download
In NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra, you’ll discover what vectors are and how they work in real life—like understanding movement, force, and direction. This chapter explains vector addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and both dot and cross products, with simple examples so you don’t get confused between vectors and scalars.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentIf you ever feel lost with direction cosines or vector operations, Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions make these tricky concepts straightforward. You can download easy-to-understand PDFs and practice at your own pace. Don't forget to check out the Class 12 Maths syllabus for a clear overview.
Use these solutions for quick revision and doubt-solving—it’s a great way to feel more confident before exams. This chapter carries 7 marks in your CBSE exam, so mastering it can really boost your score.
Access Exercise Wise NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 Maths Class 12



Exercises Under NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
Vectors Class 12 NCERT Solutions introduces students to the concept of vectors and their algebraic operations. It covers topics such as scalar and vector products, triple products, and their applications in geometry and physics.
The chapter is divided into four exercises and one miscellaneous exercise. Here is a brief summary of each exercise:
Exercise 10.1: This exercise has ten questions that ask students to find the direction cosines of a given vector and vice versa.
Exercise 10.2: This exercise has eleven questions that ask students to find the magnitude and direction of a given vector, as well as to perform vector operations such as addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication.
Exercise 10.3: This exercise has seven questions that ask students to find the scalar and vector products of two given vectors.
Exercise 10.4: This exercise has six questions that ask students to find the scalar and vector triple products of given vectors.
Miscellaneous Exercise: This exercise has six questions that ask students to apply the concepts of vector algebra to solve problems in geometry and physics.
Overall, this chapter is essential for students who want to pursue higher education in Mathematics and Physics. It provides a solid foundation for students to understand the concepts of vectors and their applications in real-world problems.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 – Vector Algebra
Exercise 10.1
1. Represent graphically a displacement of $40\;{\text{km}},{30^\circ }$ east of north.
Ans:
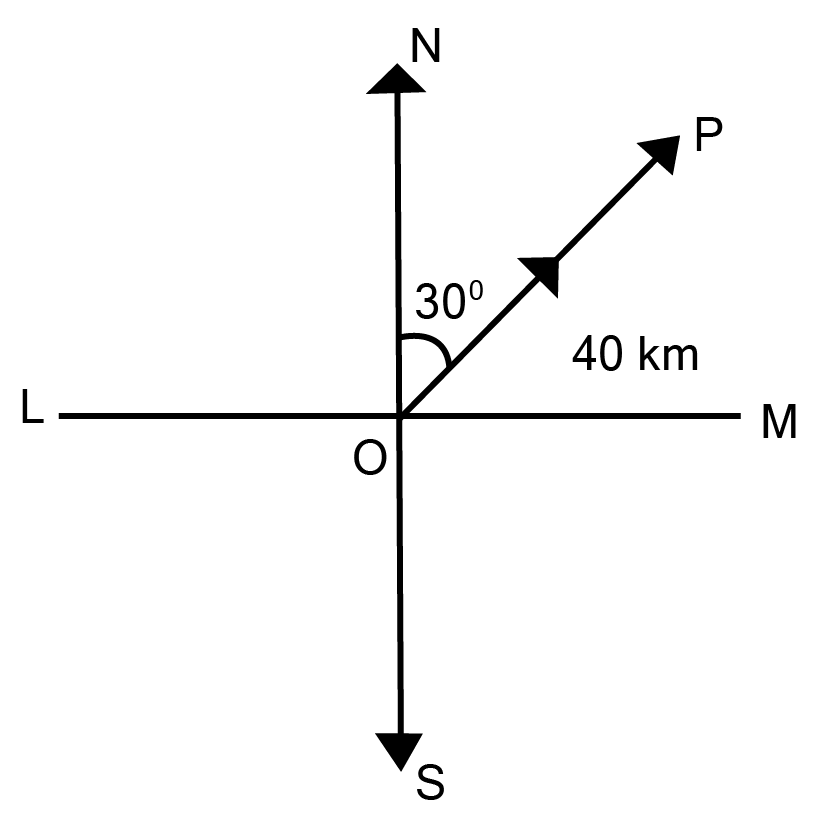
Here, the vector OP is representing the displacement of $40\;{\text{km}},{30^\circ }$ in East of North direction.
2. Classify the following measures as scalars and vectors.
i. $10\;{\text{kg}}$
Ans: $10\;{\text{kg}}$is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude not direction.
ii. 2 meters north-west
Ans: 2 meters north-west is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude as well as direction.
iii. ${40^\circ }$
Ans: ${40^\circ }$ is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude, not direction.
iv. $40$ watt
Ans: 40 watts is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude, not direction.
v. ${10^{ - 19}}$coulomb
Ans: ${10^{ - 19}}$Coulomb is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude not direction.
vi. $20\;{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}$
Ans: $20\;{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}$ is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude as well as direction.
3. Classify the following as scalar and vector quantities:-
i. Time period
Ans: Time period is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude.
ii. distance
Ans: Distance is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude.
iii. force
Ans: Force is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude as well as direction.
iv. velocity
Ans: Velocity is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude as well as direction.
v. work done
Ans: Work done is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude.
4. In Figure, identify the following vectors.
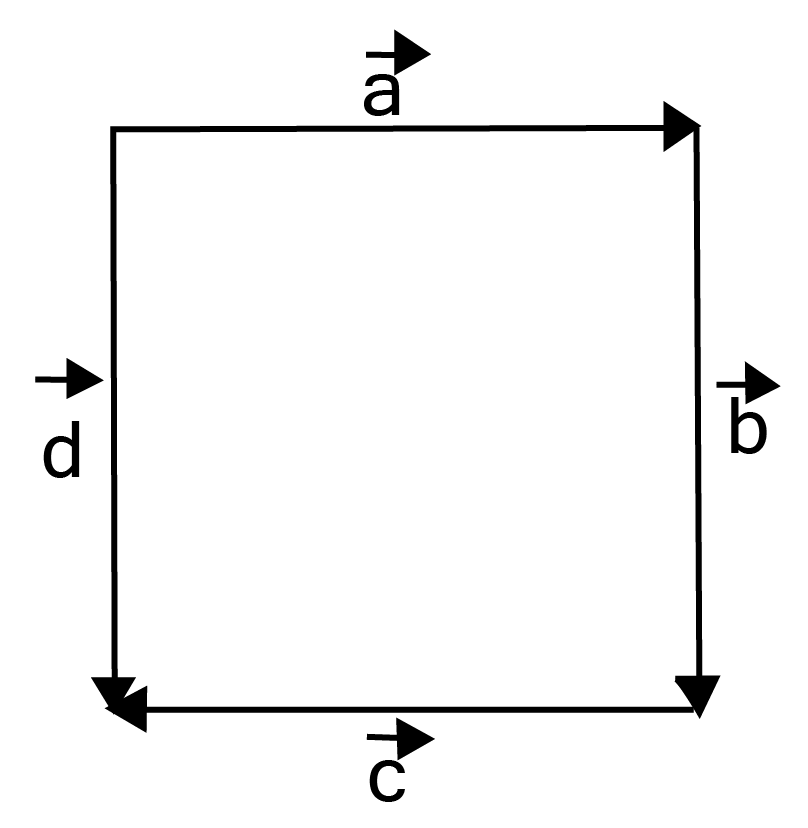
i. Co-initial
Ans: Vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec d$ are co-initial.
ii. Equal
Ans: Vectors $\vec b$ and $\vec d$ are equal.
iii. Collinear but not equal
Ans: Vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec c$ are collinear but not equal.
5. Answer the following as true or false.
i.$\vec a$ and $ - \vec a$ and are collinear.
Ans: True
ii. Two collinear vectors are always equal in magnitude.
Ans: False
iii. Two vectors having same magnitude are collinear.
Ans: False
iv. Two collinear vectors having the same magnitude are equal.
Ans: False
Exercise 10.2
1. Compute the magnitude of the following vectors:-
$\vec a = \hat i + \hat j + \hat k\;;\;\vec b = 2\hat i - 7\hat j - 3\hat k\;;\;\vec c = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\hat i + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\hat j - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\hat k$
Ans: $|\vec a| = \sqrt {{{(1)}^2} + {{(1)}^2} + {{(1)}^2}} = \sqrt 3 $
$|\vec b| = \sqrt {{{(2)}^2} + {{( - 7)}^2} + {{( - 3)}^2}} $
$ = \sqrt {4 + 49 + 9} $
$ = \sqrt {62} $
$|\vec c| = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)}^2}} $
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{1}{3}} = 1$
2. Write two different vectors having the same magnitude.
Ans: $\vec a = (\hat i - 2\hat j + 3\hat k)$ and $\vec b = (2\hat i + \hat j - 3\hat k)$.
$|\vec a| = \sqrt {{1^2} + {{( - 2)}^2} + {3^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 4 + 9} = \sqrt {14} $
$|\vec b| = \sqrt {{2^2} + {1^2} + {{( - 3)}^2}} = \sqrt {4 + 1 + 9} = \sqrt {14} $
But $\vec a \ne \vec b$
3. Write two different vectors having same direction.
Ans: $\vec p = (\hat i + \hat j + \hat k)$ and $\vec q = (2\hat i + 2\hat j + 2\hat k)$.
The Direction Cosines of $\vec p$ are $a = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{1^2} + {1^2} + {1^2}} }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},b = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{1^2} + {1^2} + {1^2}} }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},c = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{1^2} + {1^2} + {1^2}} }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
The Direction Cosines of $\vec q$ are$a = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {2^2} + {2^2}} }} = \dfrac{2}{{2\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},b = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {2^2} + {2^2}} }} = \dfrac{2}{{2\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},c = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {2^2} + {2^2}} }} = \dfrac{2}{{2\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
The Direction Cosines of $\vec p$ and $\vec q$ are equal but $\vec p \ne \vec q$.
4. Find the values of x and y so that the vectors $2\hat i + 3\hat j$ and $x\hat i + y\hat j$ are equal.
Ans: $2\hat i + 3\hat j = x\hat i + y\hat j \Rightarrow x = 2,y = 3$
5. Find the scalar and vector components of the vector with initial point $(2,1)$ and terminal point $( - 5,7)$.
Ans: Let the points be ${\text{P}}(2,1)$ and ${\text{Q}}( - 5,7)$
$\overrightarrow {PQ} = ( - 5 - 2)\hat i + (7 - 1)\hat j$
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {PQ} = - 7\hat i + 6\hat j$
So, scalar components of required vector are $ - 7$ and 6 and the vector components are $ - 7\hat i$ and $6\hat j$.
6. Find the sum of the vectors $\vec a = \hat i - 2\hat j + \hat k\;,\;\vec b = - 2\hat i + 4\hat j + 5\hat k$ and $\vec c = \hat i - 6\hat j - 7\hat k$.
Ans: $\vec a + \vec b + \vec c = (1 - 2 + 1)\hat i + ( - 2 + 4 - 6)\hat j + (1 + 5 - 7)\hat k{\text{ }} = 0\hat i - 4\hat j - 1\hat k{\text{ }} = - \;4\hat j - \hat k{\text{ }}$
7. Find the unit vector in the direction of the vector $\vec a = \hat i + \hat j + 2\hat k$.
Ans: $|\vec a| = \sqrt {{1^2} + {1^2} + {2^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 1 + 4} = \sqrt 6 $
$\therefore \hat a = \dfrac{{\vec a}}{{|\vec a|}} = \dfrac{{\hat i + \hat j + 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt 6 }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }}\hat i + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 6 }}\hat j + \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 6 }}\hat k$
8. Find the unit vector in the direction of vector $\overrightarrow {PQ} $, where ${\text{P}}$ and ${\text{Q}}$ are the points $(1,2,3)$ and $(4,5,6)$, respectively.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {PQ} = (4 - 1)\hat i + (5 - 2)\hat j + (6 - 3)k = 3\hat i + 3\hat j + 3k$
$|\overrightarrow {PQ} | = \sqrt {{3^2} + {3^2} + {3^2}} = \sqrt {9 + 9 + 9} = \sqrt {27} = 3\sqrt 3 $
So, unit vector $ = \dfrac{{\overrightarrow {PQ} }}{{|\overrightarrow {PQ} |}} = \dfrac{{3\hat i + 3\hat j + 3\hat k}}{{3\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\hat i + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\hat j + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\hat k$
9. For given vectors, $\vec a = 2\hat i - \hat j + 2\hat k$ and $\vec b = - \hat i + \hat j - \hat k$, find the unit vector in the direction of the vector $\vec a + \vec b$.
Ans: $\vec a + \vec b = (2 - 1)\hat i + ( - 1 + 1)\hat j + (2 - 1)\hat k = 1\hat i + 0\hat j + 1\hat k = \hat i + \hat k$
$|\vec a + \vec b| = \sqrt {{1^2} + {1^2}} = \sqrt 2 $
So, unit vector $ = \dfrac{{(\vec a + \vec b)}}{{|\vec a + \vec b|}} = \dfrac{{\hat i + \hat k}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\hat i + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\hat k$
10. Find a vector in the direction of vector $5\hat i - \hat j + 2\hat k$ which has magnitude 8 units.
Ans: $\vec a = 5\hat i - \hat j + 2\hat k$
$|\vec a| = \sqrt {{5^2} + {{( - 1)}^2} + {2^2}} = \sqrt {25 + 1 + 4} = \sqrt {30} $
$\therefore \hat a = \dfrac{{\vec a}}{{|\vec a|}} = \dfrac{{5\hat i - \hat j + 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {30} }}$
So, a vector in direction of $5\hat i - \hat j + 2\hat k$ with magnitude 8 units is:$8\hat a = 8\left( {\dfrac{{5\hat i - \hat j + 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {30} }}} \right) = \dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt {30} }}\hat i - \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt {30} }}\hat j + \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt {30} }}\hat k$
11. Show that the vectors $2\hat i - 3\hat j + 4\hat k$ and $ - 4\hat i + 6\hat j - 8\hat k$ are collinear.
Ans: $\vec a = 2\hat i - 3\hat j + 4\hat k$ and $\vec b = - 4\hat i + 6\hat j - 8\hat k$
$\vec b = - 4\hat i + 6\hat j - 8\hat k = - 2(2\hat i - 3\hat j + 4\hat k) = - 2\vec a$
$\therefore \vec b = \lambda \vec a,\;\;\lambda = - 2$
So, the given vectors are collinear.
12. Find the direction cosines of the vector $\hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k$.
Ans: $\vec a = \hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k$.
$|\vec a| = \sqrt {{1^2} + {2^2} + {3^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 4 + 9} = \sqrt {14} $
So, the Direction cosines of $\vec a$ are $\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {14} }},\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {14} }},\dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {14} }}} \right)$
13. Find the direction cosines of the vector joining the points ${\text{A}}(1,2, - 3)$ and ${\text{B}}( - 1, - 2,1)$ directed from A to b.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = ( - 1 - 1)\hat i + ( - 2 - 2)\hat j + \{ 1 - ( - 3)\} \hat k$
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = - 2\hat i - 4\hat j + 4\hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} | = \sqrt {{{( - 2)}^2} + {{( - 4)}^2} + {4^2}} = \sqrt {4 + 16 + 16} = \sqrt {36} = 6$
So, the Direction cosines of $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} $ are $\left( { - \dfrac{2}{6}, - \dfrac{4}{6},\dfrac{4}{6}} \right) = \left( { - \dfrac{1}{3}, - \dfrac{2}{3},\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)$
14. Show that the vector $\hat i + \hat j + \hat k$ is equally inclined to the axes OX, OY and OZ .
Ans: $\vec a = \hat i + \hat j + \hat k$
$|\vec a| = \sqrt {{1^2} + {1^2} + {1^2}} = \sqrt 3 $
So, the Direction Cosines of $\vec a$ are $\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)$
$\cos \alpha = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\cos \beta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\cos \gamma = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
So, the vector is equally inclined to OX, OY, and ${\text{OZ}}$.
15. Find the position vector of a point ${\text{R}}$ which divides the line joining two points P and Q whose position vectors are $\hat i + 2\hat j - \hat k$ and $ - \hat i + \hat j + \hat k$ respectively, in the ratio 2 : 1 ,
i. Internally
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{OP}}} = \hat i + 2\hat j - \hat k$ and $\overrightarrow {{\text{OQ}}} = - \hat i + \hat j + \hat k$
The position vector of ${\text{R}}$ is $\overrightarrow {{\text{OR}}} = \dfrac{{2( - \hat i + \hat j + \hat k) + 1(\hat i + 2\hat j - \hat k)}}{{2 + 1}} = \dfrac{{( - 2\hat i + 2\hat j + 2\hat k) + (\hat i + 2\hat j - \hat k)}}{3}$
$ = \dfrac{{ - \;\hat i + 4\hat j + \hat k}}{3} = - \dfrac{1}{3}\hat i + \dfrac{4}{3}\hat j + \dfrac{1}{3}\hat k$
ii. Externally.
Ans: The position vector of $R$ is $\overrightarrow {{\text{OR}}} = \dfrac{{2( - \hat i + \hat j + \hat k) - 1(\hat i + 2\hat j - \hat k)}}{{2 - 1}} = ( - 2\hat i + 2\hat j + 2\hat k) - (\hat i + 2\hat j - \hat k)$
$ = - 3\hat i + 3\hat k$
16. Find the position vector of the mid point of the vector joining the points P(2,3,4) and Q(4,1,-2).
Ans: The position vector of $R$ is
$\overrightarrow {{\text{OR}}} = \dfrac{{(2\hat i + 3\hat j + 4\hat k) + (4\hat i + \hat j - 2\hat k)}}{2} = \dfrac{{(2 + 4)\hat i + (3 + 1)\hat j + (4 - 2)\hat k}}{2}$
$ = \dfrac{{6\hat i + 4\hat j + 2\hat k}}{2} = 3\hat i + 2\hat j + \hat k$
17. Show that the points ${\text{A}},{\text{B}}$ and ${\text{C}}$ with position vectors, $\vec a = 3\hat i - 4\hat j - 4\hat k\;,\;\vec b = 2\hat i - \hat j + \hat k$ and $\vec c = \hat i - 3\hat j - 5\hat k$, respectively form the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Ans:
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = \vec b - \vec a = (2 - 3)\hat i + ( - 1 + 4)\hat j + (1 + 4)\hat k = - \hat i + 3\hat j + 5\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = \vec c - \vec b = (1 - 2)\hat i + ( - 3 + 1)\hat j + ( - 5 - 1)\hat k = - \hat i + 2\hat j - 6\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec a - \vec c = (3 - 1)\hat i + ( - 4 + 3)\hat j + ( - 4 + 5)\hat k = 2\hat i - \hat j + \hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} {|^2} = {( - 1)^2} + {3^2} + {5^2} = 1 + 9 + 25 = 35$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} {|^2} = {( - 1)^2} + {( - 2)^2} + {( - 6)^2} = 1 + 4 + 36 = 41$
$|\overrightarrow {CA} {|^2} = {2^2} + {( - 1)^2} + {1^2} = 4 + 1 + 1 = 6$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} {|^2} + |\overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} {|^2} = 35 + 6 = 41 = |\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} {|^2}$
So, ABC is a right angled triangle.
18. In triangle ABC, which of the following is not true?
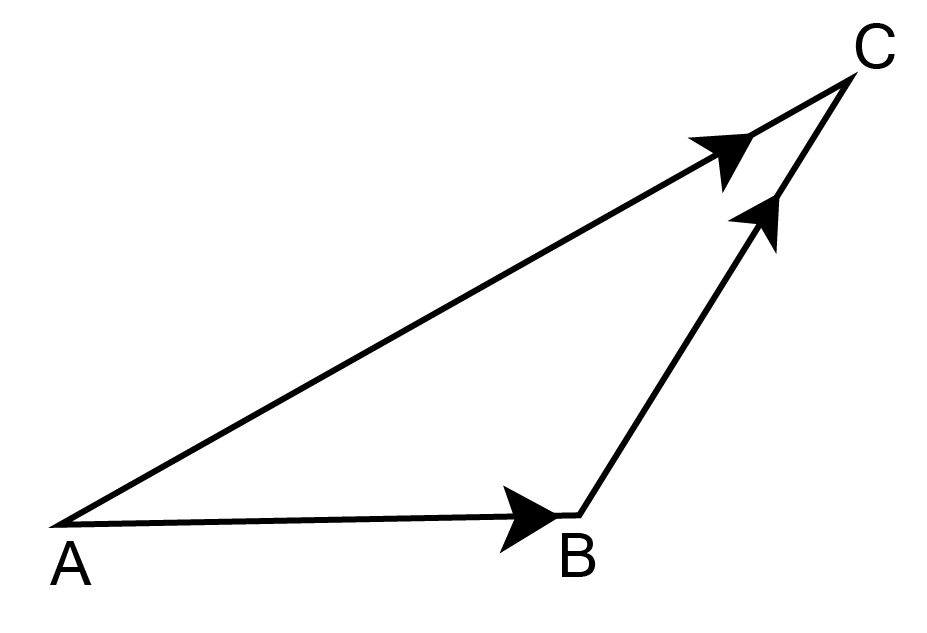
a. $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
b. $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} - \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = \vec 0$
c. $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} - \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
d. $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} - \overrightarrow {{\text{CB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
Ans:
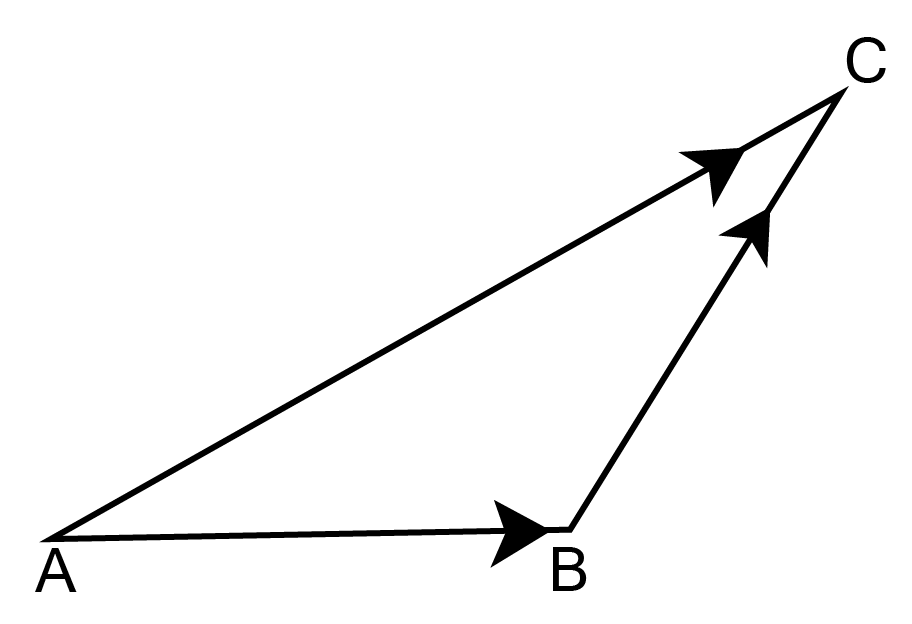
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = - \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} - \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = \vec 0$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} - \overrightarrow {{\text{CB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
If $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} - \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = \vec 0$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = \overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = - \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = \vec 0$
$ \Rightarrow 2\overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = \vec 0$
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = \vec 0$, which is not true.
So, the equation given in option ${\text{C}}$ is False.
Hence, the correct answer is ${\text{C}}$.
19. If $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ are two collinear vectors, then which of the following are incorrect?
a. $\vec b = \lambda \vec a$, for some scalar $\lambda $
b. $\vec a = \pm \vec b$
c. the respective components of $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ are proportional
d. both the vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ have same direction, but different magnitudes
Ans: If $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ are collinear vectors, they are parallel. $\vec b = \lambda \vec a($ scalar $\lambda )$
If $\lambda = \pm 1$, then $\vec a = \pm \vec b$
If $\vec a = {a_1}\hat i + {a_2}\hat j + {a_3}\hat k$ and $\vec b = {b_1}\hat i + {b_2}\hat j + {b_3}\hat k$,
$\vec b = \lambda \vec a \Rightarrow {b_1}\hat i + {b_2}\hat j + {b_3}\hat k = \lambda \left( {a\hat i + {a_2}\hat j + {a_3}\hat k} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {b_1}\hat i + {b_2}\hat j + {b_3}\hat k = \left( {\lambda {a_1}} \right)\hat i + \left( {\lambda {a_2}} \right)\hat j + \left( {\lambda {a_3}} \right)\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow {b_1} = \lambda {a_1},{b_2} = \lambda {a_2},{b_3} = \lambda {a_3}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b_1}}}{{{a_1}}} = \dfrac{{{b_2}}}{{{a_2}}} = \dfrac{{{b_3}}}{{{a_3}}} = \lambda $
Thus, respective components of $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ are proportional.
But, $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ may have different directions. So, option D is incorrect. The correct answer is ${\text{D}}$.
Exercise 10.3
1. Find the angle between two vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ with magnitudes $\sqrt 3 $ and 2, respectively having $\vec a \cdot \vec b = \sqrt 6 $
Ans: $|\vec a| = \sqrt 3 \;,\;|\vec b| = 2\;,\;\vec a\;.\;\vec b = \sqrt 6 $
$\therefore \sqrt 6 = \sqrt 3 \times 2 \times \cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{{\sqrt 6 }}{{\sqrt 3 \times 2}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$
2. Find the angle between the vectors $i - 2\hat j + 3\hat k$ and $3\hat i - 2\hat j + \hat k$.
Ans: $|\vec a| = \sqrt {{1^2} + {{( - 2)}^2} + {3^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 4 + 9} = \sqrt {14} $
$|\vec b| = \sqrt {{3^2} + {{( - 2)}^2} + {1^2}} = \sqrt {9 + 4 + 1} = \sqrt {14} $
$\vec a\;.\;\vec b = (i - 2\hat j + 3\hat k)(3\hat i - 2\hat j + \hat k)$
$ = 1.3 + ( - 2)( - 2) + 3.1$
$ = 3 + 4 + 3$
$ = 10$
$\therefore 10 = \sqrt {14} \sqrt {14} \cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{{10}}{{14}}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{5}{7}} \right)$
3. Find the projection of the vector $\hat i - \hat j$ on the vector $i + \hat j$.
Ans: $\vec a = \hat i - \hat j$ and $\vec b = \hat i + \hat j$
Projection of $\vec a$ on $\vec b$ is $\dfrac{1}{{\mid \vec b|}}(\vec a \cdot \vec b) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + 1} }}\{ 1.1 + ( - 1)(1)\} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}(1 - 1) = 0$
4. Find the projection of the vector $\hat i + 3\hat j + 7\hat k$ on the vector $7\hat i - \hat j + 8\hat k$.
Ans: $\vec a = \hat i + 3\hat j + 7\hat k$ and $\vec b = 7\hat i - \hat j + 8\hat k$
Projection of $\vec a$ on $\vec b$ is $\dfrac{1}{{|\vec b|}}(\vec a \cdot \vec b) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{7^2} + {{( - 1)}^2} + {8^2}} }}\{ 1(7) + 3( - 1) + 7(8)\} = \dfrac{{7 - 3 + 56}}{{\sqrt {49 + 1 + 64} }} = \dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt {114} }}$
5. Show that each of the given three vectors is a unit vector, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. $\dfrac{1}{7}(2\hat i + 3\hat j + 6\hat k)\;\;,\;\;\dfrac{1}{7}(3\hat i - 6\hat j + 2\hat k)\;\;,\;\;\dfrac{1}{7}(6\hat i + 2\hat j - 3\hat k)$
Ans: $\vec a = \dfrac{1}{7}(2\hat i + 3\hat j + 6\hat k) = \dfrac{2}{7}\hat i + \dfrac{3}{7}\hat j + \dfrac{6}{7}\hat k$,
$\vec b = \dfrac{1}{7}(3\bar i - 6\hat j + 2\hat k) = \dfrac{3}{7}\hat i - \dfrac{6}{7}\bar j + \dfrac{2}{7}\hat k$
$\vec c = \dfrac{1}{7}(6\hat i + 2\hat j - 3\hat k) = \dfrac{6}{7}\hat i + \dfrac{2}{7}\hat j - \dfrac{3}{7}\hat k$
$|\vec a| = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{7}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{6}{7}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{4}{{49}} + \dfrac{9}{{49}} + \dfrac{{36}}{{49}}} = 1$
$|\vec b| = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - \dfrac{6}{7}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{2}{7}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{9}{{49}} + \dfrac{{36}}{{49}} + \dfrac{4}{{49}}} = 1$
$|\vec c| = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{6}{7}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{2}{7}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - \dfrac{3}{7}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{36}}{{49}} + \dfrac{4}{{49}} + \dfrac{9}{{49}}} = 1$
So, each of the vectors is a unit vector.
$\vec a\;.\;\vec b = \dfrac{2}{7} \times \dfrac{3}{7} + \dfrac{3}{7} \times \left( {\dfrac{{ - 6}}{7}} \right) + \dfrac{6}{7} \times \dfrac{2}{7} = \dfrac{6}{{49}} - \dfrac{{18}}{{49}} + \dfrac{{12}}{{49}} = 0$
$\vec b \cdot \vec c = \dfrac{3}{7} \times \dfrac{6}{7} + \left( {\dfrac{{ - 6}}{7}} \right) \times \dfrac{2}{7} + \dfrac{2}{7} \times \left( {\dfrac{{ - 3}}{7}} \right) = \dfrac{{18}}{{49}} - \dfrac{{12}}{{49}} - \dfrac{6}{{49}} = 0$
$\vec c\;.\;\vec a = \dfrac{6}{7} \times \dfrac{2}{7} + \dfrac{2}{7} \times \dfrac{3}{7} + \left( {\dfrac{{ - 3}}{7}} \right) \times \dfrac{6}{7} = \dfrac{{12}}{{49}} + \dfrac{6}{{49}} - \dfrac{{18}}{{49}} = 0$
So, given vectors are mutually perpendicular to each other.
6. Find $|\vec a|$ and $|\vec b|$, if $(\vec a + \vec b) \cdot (\vec a - \vec b) = 8$ and $|\overrightarrow a |\; = \;8|\vec b|$.
Ans: $(\vec a + \vec b) \cdot (\vec a - \vec b) = 8$
$ \Rightarrow \vec a\vec a - \vec a\;.\;\vec b + \vec b \cdot \vec a - \vec b\vec b = 8$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a{|^2} - |\vec b{|^2} = 8$
$ \Rightarrow {(8|\vec b|)^2} - |\vec b{|^2} = 8$
$ \Rightarrow 64|\vec b{|^2} - |\vec b{|^2} = 8$
$ \Rightarrow 63|\vec b{|^2} = 8$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec b{|^2} = \dfrac{8}{{63}}$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec b| = \sqrt {\dfrac{8}{{63}}} $
$ \Rightarrow |\vec b| = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{{3\sqrt 7 }}$
$|\vec a| = 8|\vec b| = \dfrac{{8 \times 2\sqrt 2 }}{{3\sqrt 7 }} = \dfrac{{16\sqrt 2 }}{{3\sqrt 7 }}$
7. Evaluate the product $(3\vec a - 5\vec b) \cdot (2\vec a + 7\vec b)$
Ans: $(3\vec a - 5\vec b) \cdot (2\vec a + 7\vec b)$
$ = 3\vec a \cdot 2\vec a + 3\vec a.7\vec b - 5\vec b \cdot 2\vec a - 5\vec b \cdot 7\vec b$
$ = 6\vec a\vec a + 21\vec a\vec b - 10\vec a\vec b - 35\vec b\vec b$
$ = 6|\vec a{|^2} + 11\vec a\vec b - 35|\vec b{|^2}$
8. Find the magnitude of two vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec b$, having the same magnitude and such that the angle between them is ${60^\circ }$ and their scalar product is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
Ans: Let $\theta $ be angle between $\vec a$ and $\vec b$.
$|\vec a| = |\vec b|,\vec a\;.\;\vec b = \dfrac{1}{2}$, and $\theta = {60^\circ }$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2} = |\vec a|\vec b\mid \cos {60^\circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = |\vec a{|^2} \times \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a{|^2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a| = |\vec b| = 1$
9. Find $|\vec x|$, if for a unit vector $\vec a\;,\;(\vec x - \vec a) \cdot (\vec x + \vec a) = 12$
Ans: $(\vec x - \vec a) \cdot (\vec x + \vec a) = 12$
$ \Rightarrow \vec x \cdot \vec x + \vec x\vec a - \vec a\vec x - \vec a \cdot \vec a = 12$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec x{|^2} - |\vec a{|^2} = 12$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec x{|^2} - 1 = 12$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec x{|^2} = 13$
$\therefore |\vec x| = \sqrt {13} $
10. If $\vec a = 2\hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k,\vec b = - \hat i + 2\hat j + \hat k$ and $\vec c = 3\hat i + \hat j$ are such that $\vec a + \lambda \vec b$ is perpendicular to $\vec c$, then find the value of $\lambda $.
Ans: $\vec a + \lambda \vec b = (2\hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k) + \lambda ( - \hat i + 2\hat j + \dot k) = (2 - \lambda )\hat i + (2 + 2\lambda )\hat j + (3 + \lambda )\hat k$
$(\vec a + \lambda \vec b) \cdot \vec c = 0$
$ \Rightarrow [(2 + - )\hat i + (2 + 2\lambda )\hat j + (3 + \lambda )\hat k] \cdot (3\hat i + j) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 3(2 - \lambda ) + (2 + 2\lambda ) + 0(3 + \lambda ) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 3\lambda + 2 + 2\lambda = 0$
$ \Rightarrow - \lambda + 8 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 8$
11. Show that $|\vec a|\vec b + |\vec b|\vec a$ is perpendicular to $|\vec a|\vec b - |\vec b|\vec a$ , For any two nonzero vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec b$.
Ans: $(|\vec a|\vec b + |\vec b|\vec a) \cdot (|\vec a|\vec b - |\vec b|\vec a)$
$ = |\vec a{|^2}\vec b\vec b - |\vec a||\vec b|\vec b\vec a + |\overrightarrow b ||a|\vec a\vec b - |\vec b{|^2}\vec a \cdot \vec a$
$ = |\vec a{|^2}|\overrightarrow b {|^2} - |\overrightarrow b {|^2}|\overrightarrow a {|^2}\;\; = \;\;0$
12. If $\vec a \cdot \vec a = 0$ and $\vec a\vec b = 0$, then what can be concluded above the vector $\vec b$ ?
Ans: $\vec a \cdot \vec a = 0 \Rightarrow |\vec a{|^2} = 0 \Rightarrow |\vec a| = 0$
$\therefore \vec a$ is the zero vector. Thus, any vector $\vec b$ can satisfy $\vec a\;.\;\vec b = 0$.
13. If $\vec a,\vec b,\vec c$ are unit vectors such that $\vec a + \vec b + \vec c = 0$, find the value of $\vec a \cdot \vec b + \vec b \cdot \vec c + \vec c\;.\;\vec a$.
Ans: $|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c{|^2} = (\vec a + \vec b + \vec c) \cdot (\vec a + \vec b + \vec c) = |\vec a{|^2} + |\vec b{|^2} + |\vec c{|^2} + 2(\vec a\vec b + \vec b\vec c + \vec c \cdot \vec a)$
$ \Rightarrow 0 = 1 + 1 + 1 + 2(\vec a\vec b + \vec b \cdot \vec c + \vec c \cdot \vec a)$
$ \Rightarrow (\vec a\;.\;\vec b + \vec b \cdot \vec c + \vec c\;.\;\vec a) = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2}$
14. If either vector $\vec a = \vec 0$ or $\vec b = \vec 0$, then $\vec a \cdot \vec b = 0.$ But the converse need not be true. Justify your answer with an example.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {\text{a}} = 2\widehat {\text{i}} + 4\widehat {\text{j}} + 3\widehat {\text{k}}$ and $\overrightarrow b = 3\widehat {\text{i}} + 3\widehat {\text{j}} - 6\widehat {\text{k}}$
$\vec a \cdot \vec b = 2.3 + 4.3 + 3( - 6) = 6 + 12 - 18 = 0$
$|{\text{a}}| = \sqrt {{2^2} + {4^2} + {3^2}} = \sqrt {29} $
$\therefore \vec a \ne \vec 0$
$|\vec b| = \sqrt {{3^2} + {3^2} + {{( - 6)}^2}} = 54$
$\therefore \vec b \ne \bar 0$
So, it is clear from the above example that the converse of the given statement need not be true.
15. If the vertices ${\text{A}},{\text{B}},{\text{C}}$ of a triangle ${\text{ABC}}$ are $(1,2,3),( - 1,0,0),(0,1,2)$, respectively, then find $\angle {\text{ABC}}$. $[\angle {\text{ABC}}$ is the angle between the vectors $\overrightarrow {{\text{BA}}} $ and $\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} $ ]
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{BA}}} = \{ 1 - ( - 1)\hat i + (2 - 0)\hat j + (3 - 0)\hat k = 2\hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = \{ 0 - ( - 1)\} \hat i + (1 - 0)\hat j + (2 - 0)\hat k = \hat i + \hat j + 2\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BA}}} \cdot \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = (2\hat i + 2\hat \jmath + 3\hat k) \cdot (\hat i + \hat \jmath + 2\hat k) = 2 \times 1 + 2 \times 1 + 3 \times 2 = 2 + 2 + 6 = 10$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{BA}}} | = \sqrt {{2^2} + {2^2} + {3^2}} = \sqrt {4 + 4 + 9} = \sqrt {17} $
$|\overrightarrow {BC} | = \sqrt {1 + 1 + {2^2}} = \sqrt 6 $
$\therefore 10 = \sqrt {17} \times \sqrt 6 \cos (\angle {\text{ABC}})$
$ \Rightarrow \cos (\angle {\text{ABC}}) = \dfrac{{10}}{{\sqrt {17} \times \sqrt 6 }}$
$ \Rightarrow (\angle {\text{ABC}}) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{10}}{{\sqrt {102} }}} \right)$
16. Show that the points ${\text{A}}(1,2,7),\;{\text{B}}(2,6,3)$ and ${\text{C}}(3,10, - 1)$ are collinear.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = (2 - 1)\hat i + (6 - 2)\hat j + (3 - 7)\hat k = \hat i + 4\hat j - 4\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = (3 - 2)\hat i + (10 - 6)\hat \jmath + ( - 1 - 3)\hat k = \hat i + 4\hat j - 4\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} = (3 - 1)\hat i + (10 - 2)\hat j + ( - 1 - 7)\hat k = 2\hat i + 8\hat j - 8\hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {AB} | = \sqrt {{1^2} + {4^2} + {{( - 4)}^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 16 + 16} = \sqrt {33} $
$|\overrightarrow {BC} | = \sqrt {{1^2} + {4^2} + {{( - 4)}^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 16 + 16} = \sqrt {33} $
$|\overrightarrow {AC} | = \sqrt {{2^2} + {8^2} + {8^2}} = \sqrt {4 + 64 + 64} = 2\sqrt {33} $
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} | = |\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} | + |\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} |$
Hence, the given points are collinear.
17. Show that the vectors $2\hat i - \hat j + \hat k\;,\;\hat i - 3\hat j - 5\hat k$ and $3\hat i - 4\hat j - 4\hat k$ form the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{OA}}} = 2\hat i - \hat j + \hat k\;,\;\overrightarrow {{\text{OB}}} = \hat i - 3\hat j - 5\hat k\;,\;\overrightarrow {{\text{OC}}} = 3\hat i - 4\hat j - 4\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = (1 - 2)\hat i + ( - 3 + 1)\hat j + ( - 5 - 1)\hat k = - \hat i - 2\hat j - 6 \hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = (3 - 1)\hat i + ( - 4 + 3)\hat j + ( - 4 + 5)\hat k = 2\hat i - \hat j + \hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{CA}}} = (2 - 3)\hat i + ( - 1 + 4)\hat j + (1 + 4)\hat k = - \hat i + 3\hat j + 5\hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} | = \sqrt {{{( - 1)}^2} + {{( - 2)}^2} + {{( - 6)}^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 4 + 36} = \sqrt {41} $
$|\overrightarrow {BC} | = \sqrt {{2^2} + {{( - 1)}^2} + {1^2}} = \sqrt {4 + 1 + 1} = \sqrt 6 $
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} | = \sqrt {{{( - 1)}^2} + {3^2} + {5^2}} = \sqrt {1 + 9 + 25} = \sqrt {35} $
$\therefore |\overrightarrow {BC} {|^2} + |\overrightarrow {AC} {|^2} = 6 + 35 = 41 = |\overrightarrow {AB} {|^2}$
Hence, $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ is a right triangle.
18. If $\vec a$ is a nonzero vector of magnitude 'a' and $\lambda $ a nonzero scalar. then $\lambda \vec a$ is unit vector if
a. $\lambda = 1$
b. $\lambda = - 1$
c. $a = |\lambda |$
d. $a = \dfrac{1}{{|\lambda |}}$
Ans: $|\lambda \vec a| = 1$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a| = \dfrac{1}{{|\lambda |}}$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{1}{{|\lambda |}}$
Exercise 10.4
1. Find $|\vec a \times \vec b|$, if $\vec a = \hat i - 7\hat j + 7\hat k$ and $\vec b = 3\hat i - 2\hat j + 2\hat k$
Ans: We have, $\vec a = \hat i - 7\hat j + 7\hat k$ and $\vec b = 3\hat i - 2\hat j + 2\hat k$
$\vec a \times \vec b = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ 1&{ - 7}&7 \\ 3&{ - 2}&2 \end{array}} \right|$
$ = \hat i( - 14 + 14) - \hat j(2 - 21) + \hat k( - 2 + 21) = 19\hat j + 19\hat k$
$\therefore |\vec a \times \vec b| = \sqrt {{{(19)}^2} + {{(19)}^2}} = \sqrt {2 \times {{(19)}^2}} = 19\sqrt 2 $
2. Find a unit vector perpendicular to each of the vector $\vec a + \vec b$ and $\vec a - \vec b$, where $\vec a = 3\hat i + 2\hat j + 2\hat k$ and $\vec b = \hat i + 2\hat j - 2\hat k$.
Ans: $\vec a = 3\hat i + 2\hat j + 2\hat k$ and $\vec b = \hat i + 2\hat j - 2\hat k$
$\vec a + \vec b = 4\hat i + 4\hat j\;,\;\vec a - \vec b = 2\hat i + 4\hat k$
$(\vec a + \vec b) \times (\vec a - \vec b) = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ 4&4&0 \\ 2&0&4 \end{array}} \right| = \hat i(16) - \hat j(16) + \hat k( - 8) = 16\hat i - 16\hat j - 8\hat k$
$|(\vec a + \vec b) \times (\vec a - \vec b)| = \sqrt {{{16}^2} + {{( - 16)}^2} + {{( - 8)}^2}} $
$ = \sqrt {{2^2} \times {8^2} + {2^2} \times {8^2} + {8^2}} $
$ = 8\sqrt {{2^2} + {2^2} + 1} = 8\sqrt 9 = 8 \times 3 = 24$
So, the unit vector is $ = \pm \dfrac{{(\vec a + \vec b) \times (\vec a - \vec b)}}{{|(\vec a + \vec b) \times (\vec a - \vec b)\mid }} = \pm \dfrac{{16\hat i - 16\hat j - 8\hat k}}{{24}}$
$ = \pm \dfrac{{2\hat i - 2\hat j - \hat k}}{3} = \pm \dfrac{2}{3}\hat i \mp \dfrac{2}{3}\hat j \mp \dfrac{1}{3}\hat k$
3. If a unit vector $\vec a$ makes an angle $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ with $\hat i,\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ with $\hat j$ and an acute angle $\theta $ with $\hat k$, then find $\theta $ and hence, the components of $\vec a$
Ans: $\vec a = {a_1}\hat i + {a_2}\hat j + {a_3}\hat k$
$|\vec a|\; = 1$. $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{{{a_1}}}{{|\vec a|}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = {a_1}$
$\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4} = \dfrac{{{a_2}}}{{|\vec a|}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = {a_2}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{a_3}}}{{|\vec a|}}$
$ \Rightarrow {a_3} = \cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {a_1^2 + a_2^2 + a_3^2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2} + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{2} + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{4} + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - \dfrac{3}{4} = \dfrac{1}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
$\therefore {a_3} = \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So, $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$ and components of $\vec a$ are $\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
4. Show that $(\vec a - \vec b) \times (\vec a + \vec b) = 2(\vec a \times \vec b)$
Ans: $(\vec a - \vec b) \times (\vec a + \vec b)$
$ = (a - b) \times \vec a + (a - b) \times b$
$ = a \times \vec a - \vec b \times \vec d + a \times \vec b - \vec b \times \vec b$
$ = 0 + \vec a \times \vec b + \vec a \times \vec b - 0$
$ = 2\;(\vec a \times \vec b)$
5. Find $\lambda $ and $\mu $ if $(2\hat i + 6\hat j + 27\hat k) \times (\hat i + \lambda \hat j + \mu \hat k) = \vec 0$
Ans: $(2\hat i + 6\hat j + 27\hat k) \times (\hat i + \lambda \hat j + \mu \hat k) = \vec 0$
$ \Rightarrow \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ 2&6&{27} \\ 1&\lambda &\mu \end{array}} \right| = 0\hat i + 0\hat j + 0\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow \hat i(6\mu - 27\lambda ) - \hat j(2\mu - 27) + \hat k(2\lambda - 6) = 0\hat i + 0\hat j + 0\hat k$
$6\mu - 27\lambda = 0$
$2\mu - 27 = 0$
$2\lambda - 6 = 0$
$\lambda = 3$
$\mu = \dfrac{{27}}{2}$
6. Given that $\vec a\;.\;\vec b = 0$ and $\vec a \times \vec b = 0$. What can you conclude about $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ ?
Ans: $\vec a\;.\;\vec b = 0$
i. $|\vec a| = 0$ or $|\vec b| = 0$ or $\vec a \bot \vec b\quad ($ if $|\vec a| \ne 0$ and $|\vec b| \ne 0)$
$\vec a \times \vec b = 0$
ii. $|\overrightarrow a |\; = \;0\;{\text{or}}\;|\vec b|\; = \;0$ or (if $|\vec a| \ne 0$ and $|\vec b| \ne 0)$
But $\overrightarrow a $ and $\overrightarrow b $ cannot be parallel and perpendicular at same time.
So, $|\vec a| = 0$ or $|\vec b| = 0$
7. Let the vectors $\vec a,\vec b,\vec c$ given as ${a_1}\hat i + {a_2}\hat j + {a_3}\hat k\;,\;{b_1}\hat i + {b_2}\hat j + {b_3}\hat k\;,\;{c_1}\hat i + {c_2}\hat j + {c_3}\hat k$.
Then show that $ = \vec a \times (\vec b + \vec c) = \vec a \times \vec b + \vec a \times \vec c$
Ans: $(\vec b + \vec c) = \left( {{b_1} + {c_1}} \right)\hat i + \left( {{b_2} + {c_2}} \right)\hat j + \left( {{b_3} + {c_3}} \right)\hat k$
Now, $\vec a \times (\vec b + \vec c)\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ {{a_1}}&{{a_2}}&{{a_3}} \\ {{b_1} + {c_1}}&{{b_2} + {c_2}}&{{b_3} + {c_3}} \end{array}} \right|$
$ = i\left[ {{a_2}\left( {{b_3} + {c_3}} \right) - {a_3}\left( {{b_2} + {c_2}} \right)} \right] - \hat j\left[ {{a_1}\left( {{b_3} + {c_3}} \right) - {a_3}\left( {{b_1} + {c_i}} \right)} \right] + \hat k\left[ {{a_1}\left( {{b_2} + {c_2}} \right) - {a_2}\left( {{b_1} + {c_1}} \right)} \right]$
$ = i\left[ {{a_2}{b_3} + {a_2}{c_3} - {a_3}{b_2} - {a_3}{c_2}} \right] + \hat j\left[ { - {a_1}{b_3} - {a_1}{c_3} + {a_3}{b_1} + {a_3}{c_1}} \right] + \hat k\left[ {{a_1}{b_2} + {a_1}{c_2} - {a_2}{b_1} - {a_2}{c_i}} \right]$
$\vec a \times \vec b = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ {{a_1}}&{{a_2}}&{{a_3}} \\ {{b_1}}&{{b_2}}&{{b_3}} \end{array}} \right|$
$ = i\left[ {{a_2}{b_3} - {a_3}{b_2}} \right] + \hat j\left[ {{b_1}{a_3} - a{b_3}} \right] + \hat k\left[ {{a_1}{b_2} - {a_2}h} \right]$
$\vec a \times \vec c = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ {{a_1}}&{{a_2}}&{{a_3}} \\ {{c_1}}&{{c_2}}&{{c_3}} \end{array}} \right|$
$ = \hat i\left[ {{a_2}{c_3} - {a_3}{c_2}} \right] + \hat j\left[ {{a_3}{c_1} - {a_1}{c_3}} \right] + \hat k\left[ {a{b_2} - {a_2}b} \right]$
$\left. {(\vec a \times \vec b) + (\vec a \times \vec c) = \hat i\left[ {{a_2}{b_3} + {a_2}{c_3} - {a_3}{b_2} - {a_3}{c_2}} \right] + \hat j{{[{b_1}{a_3} + {a_3}{c_1} - {a_1}{b_3} - {a_i}\} }_3}} \right]$
$ + \hat k\left[ {a,b, + {a_1}c, - a,{b_1} - a,{c_1}} \right]$
$\vec a \times (\vec b + \vec c) = \vec a \times \vec b + \vec a \times \vec c$
Hence, proved.
8. If either $\vec a = 0$ or $b = 0$, then $\vec a \times b = 0$.Is the converse true? Justify your answer with an example.
Ans: Let $\vec a = 2\hat i + 3\hat j + 4\hat k\;,\;\vec b = 4\hat i + 6\hat j + 8\hat k\;,\;\vec a \times \vec b = \vec 0$
$\vec a \times \vec b = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ 2&3&4 \\ 4&6&8 \end{array}} \right| = \hat i(24 - 24) - \hat j(16 - 16) + \hat k(12 - 12) = 0\hat i + 0\hat j + 0\hat k$
$|\vec a| = \sqrt {{2^2} + {3^2} + {4^2}} = \sqrt {29} $
$\therefore \vec a \ne \vec 0$
$|\vec b| = \sqrt {{4^2} + {6^2} + {8^2}} = \sqrt {116} $
$\therefore \vec b \ne \vec 0$
Hence, the converse of the statement need not be true.
9. Find the area of the triangle with vertices A $(1,1,2)$, B $(2,3,5)$ and $C(1,5,5)$.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = (2 - 1)\hat i + (3 - 1)\hat j + (5 - 2)\hat k = \hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = (1 - 2)\hat i + (5 - 3)\hat j + (5 - 5)\hat k = - \hat i + 2\hat j$
Area $ = \dfrac{1}{2}|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} \times \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} |$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} \times \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ 1&2&3 \\ { - 1}&2&0 \end{array}} \right| = \hat i( - 6) - \hat j(3) + \hat k(2 + 2) = - 6\hat i - 3\hat j + 4\hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} \times \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} | = \sqrt {{{( - 6)}^2} + {{( - 3)}^2} + {4^2}} = \sqrt {36 + 9 + 16} = \sqrt {61} $
So, the area of $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ is $\dfrac{{\sqrt {61} }}{2}$ sq units.
10. Find the area of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are determined by the vector $\vec a = \hat i - \hat j + 3\hat k$ and $\overrightarrow {\text{b}} = 2\hat i - 7\hat j + \hat k$
Ans: $\vec a \times \overrightarrow {\text{b}} = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&{\hat k} \\ 1&{ - 1}&3 \\ 2&{ - 7}&1 \end{array}} \right| = \hat i( - 1 + 21) - \hat j(1 - 6) + \hat k( - 7 + 2) = 20\hat i + 5\hat j - 5\hat k$
$\therefore |\vec a \times \vec b| = \sqrt {{{20}^2} + {5^2} + {5^2}} = \sqrt {400 + 25 + 25} = 15\sqrt 2 $
So, area of parallelogram is $15\sqrt 2 $ sq units
11. Let the vectors $\vec a$ and $\overrightarrow {\text{b}} $ be such that $|\vec a| = 3$ and $|\vec b| = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{3}$, then $\vec a \times \overrightarrow {\text{b}} $ is a unit vector, if the angle between $\vec a$ and $\vec b$is:
a. $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
b. $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
c. $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
d. $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Ans:$|\vec a \times \vec b| = 1$
$ \Rightarrow ||a||\vec b|\sin \theta | = 1$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a||\overrightarrow {\text{b}} ||\sin \theta | = 1$
$ \Rightarrow 3 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{3} \times \sin \theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$
12. Area of a rectangle having vertices ${\text{A}},{\text{B}},{\text{C}}$, and ${\text{D}}$ with position vectors $ - \hat i + \dfrac{1}{2}\hat j + 4\hat k,\hat i + \dfrac{1}{2}\hat j + 4\hat k,\hat i - \dfrac{1}{2}\hat j + 4\hat k$ and $ - \hat i - \dfrac{1}{2}\hat j + 4\hat k$ respectively is
a. $\dfrac{1}{2}$
b. 1
c. 2
d. 4
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = (1 + 1)\hat i + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2} - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\hat j + (4 - 4)\hat k = 2\hat i$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = (1 - 1)\hat i + \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2} - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\hat j + (4 - 4)\hat k = - \hat j$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} \times \overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} | = \sqrt {{{( - 2)}^2}} = 2$
So, the area of the required rectangle is 2 square units.
Miscellaneous Exercise
1. Write down a unit vector in XY-plane, making an angle of ${30^\circ }$ with the positive direction of x axis.
Ans: Unit vector is $\vec r = \cos \theta \hat i + \sin \theta \hat j$, where $\theta $ is angle with positive ${\text{X}}$ axis. $\vec r = \cos {30^\circ }\hat i + \sin {30^\circ }\hat j = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\hat i + \dfrac{1}{2}\hat j$
2. Find the scalar components and magnitude of the vector joining the points ${\text{P}}\left( {{x_1},{y_1},{z_1}} \right)$ and ${\text{Q}}\left( {{x_2},{y_2},{z_2}} \right)$
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = \left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)\hat i + \left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)\hat j + \left( {{z_2} - {z_1}} \right)\hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} |\; = \;\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{z_2} - {z_1}} \right)}^2}} $
3. A girl walks 4 km towards west, then she walks 3 km in a direction ${30^\circ }$ east of north and stops. Determine the girl's displacement from her initial point of departure.
Ans:
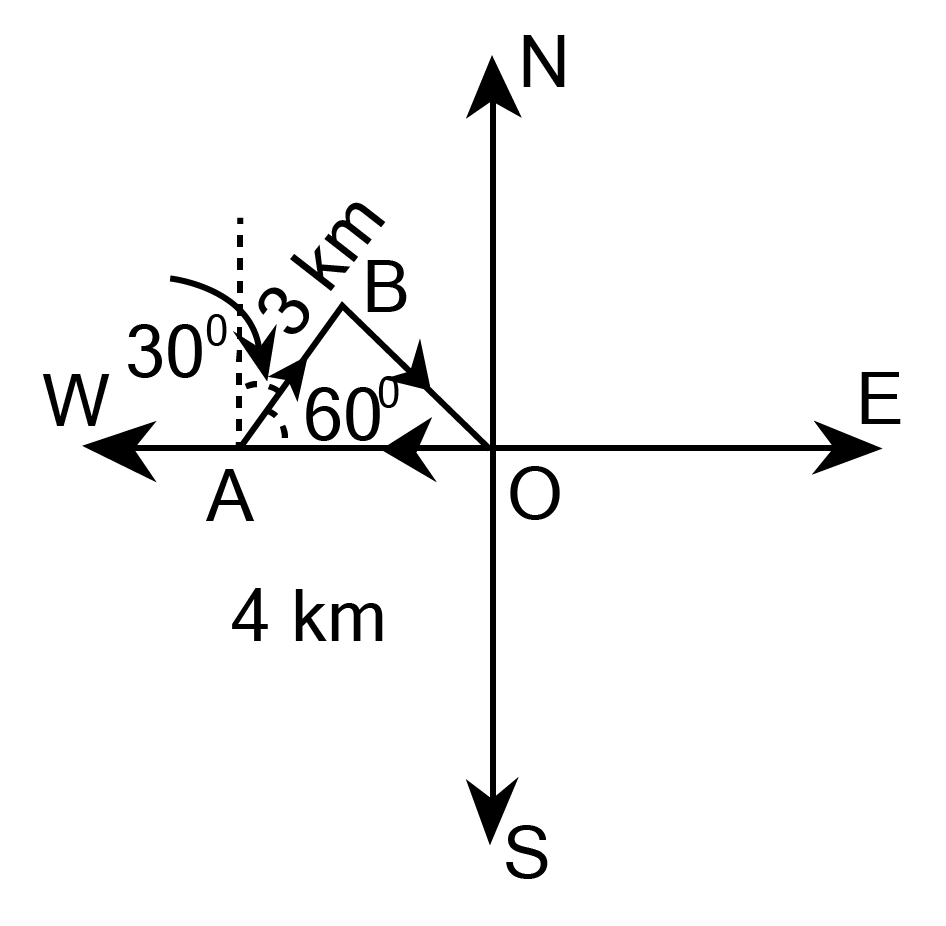
$\overrightarrow {{\text{OA}}} = - 4\hat i$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = \hat i|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} |\cos {60^\circ } + \hat j|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} |\sin {60^\circ }$
$ = \hat i3 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + \hat j3 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ = \dfrac{3}{2}\hat i + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{2}\hat j$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{OB}}} = \overrightarrow {{\text{OA}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} $
$ = ( - 4\hat i) + \left( {\dfrac{3}{2}\hat i + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{2}j} \right)$
$ = \left( { - 4 + \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)\hat i + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{2}\hat j$
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 8 + 3}}{9}} \right)\hat i + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{9}\hat j$
$ = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\vec i + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{2}\hat j$
4. If $\overrightarrow a = \vec b + \vec c$, then is it true that $|\overrightarrow a | = |\vec b| + |\vec c|$ ? Justify your answer.
Ans: $\operatorname{In} \Delta {\text{ABC}},\overrightarrow {\;CB} = \vec a,\;\overrightarrow {CA} = b,\;\overrightarrow {AB} = \vec c$
$\vec a = \vec b + \vec c$, by triangle law of addition for vectors.
$|\vec a|\; < \;|\vec b| + |\vec c|$, by triangle inequality law of lengths.
Hence, it's not true that $|\vec a| = |\vec b| + |\vec c|$
5. Find the value of $x$ for which $x(\hat i + \hat j + \hat k)$ unit vector.
Ans: $|x(\hat i + \hat j + \hat k)| = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{x^2} + {x^2} + {x^2}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {3{x^2}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 x = 1$
$ \Rightarrow x = \pm \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
6. Find a vector of magnitude 5 units, and parallel to the resultant of the vectors $\vec a = 2\hat i + 3\hat j - \hat k$ and $\vec b = \hat i - 2\hat j + \hat k$
Ans: $\vec c = \vec a + \vec b = (2 + 1)\hat i + (3 - 2)\hat j + ( - 1 + 1)\hat k = 3\hat i + \hat j$
$|\vec c| = \sqrt {{3^2} + {1^2}} = \sqrt {9 + 1} = \sqrt {10} $
$\therefore \hat c = \dfrac{{\vec c}}{{|\vec c|}} = \dfrac{{(3\hat i + \hat j)}}{{\sqrt {10} }}$
So, a vector of magnitude 5 and parallel to the resultant of $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ is $ \pm 5(\hat c) = \pm 5\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {10} }}(3\hat i + \hat j)} \right) = \pm \dfrac{{3\sqrt {10} }}{2}\hat i \pm \dfrac{{\sqrt {10} }}{2}\hat j$
7. If $\vec a = \hat i + \hat j + \hat k\;,\;\vec b = 2\hat i - \hat j + 3\hat k$ and $\vec c = \hat i - 2\hat j + \hat k$, find a unit vector parallel to the vector $2\vec a - \vec b + 3\vec c$.
Ans: $2\vec a - \vec b + 3\vec c = 2(\hat i + \hat j + \hat k) - (2\hat i - \hat j + 3\hat k) + 3(\hat i - 2\hat j + \hat k)$
$ = 2\hat i + 2\hat j + 2\hat k - 2\hat i + j - 3\vec k + 3\hat i - 6\hat j + 3\hat k$
$ = 3\hat i - 3\hat j + 2\hat k$
$|2\vec a - \vec b + 3c| = \sqrt {{3^2} + {{( - 3)}^2} + {2^2}} = \sqrt {9 + 9 + 4} = \sqrt {22} $
Thus ,required unit vector is $\dfrac{{2\vec a - \vec b + 3\vec c}}{{|2\vec a - \vec b + 3\vec c|}} = \dfrac{{3\hat i - 3\hat j + 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {22} }} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {22} }}\hat i - \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt {22} }}\hat j + \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {22} }}\hat k$
8. Show that the points ${\text{A}}(1, - 2, - 8),{\text{B}}(5,0, - 2)$ and ${\text{C}}(11,3,7)$ are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides Ac.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} = (5 - 1)\hat i + (0 + 2)\hat j + ( - 2 + 8)\hat k = 4\hat i + 2\hat j + 6\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} = (11 - 5)\hat i + (3 - 0)\hat j + (7 + 2)\hat k = 6\hat i + 3\hat j + 9\hat k$
$\overrightarrow {AC} = (11 - 1)\hat i + (3 + 2)\hat j + (7 + 8)\hat k = 10\hat i + 5\hat j + 15\hat k$
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} | = \sqrt {{4^2} + {2^2} + {6^2}} = \sqrt {16 + 4 + 36} = \sqrt {56} = 2\sqrt {14} $
$|\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} | = \sqrt {{6^2} + {3^2} + {9^2}} = \sqrt {36 + 9 + 81} = \sqrt {126} = 3\sqrt {14} $
$|\overrightarrow {AC} | = \sqrt {{{10}^2} + {5^2} + {{15}^2}} = \sqrt {100 + 25 + 225} = \sqrt {350} = 5\sqrt {14} $
$\therefore \;\;|\overrightarrow {{\text{AC}}} | = |\overrightarrow {{\text{AB}}} | + |\overrightarrow {{\text{BC}}} |$
So, the points are collinear.
Let B divide AC in ratio $\lambda :1$. $\overrightarrow {{\text{OB}}} = \dfrac{{\lambda \overrightarrow {{\text{OC}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{OA}}} }}{{(\lambda + 1)}}$
$ \Rightarrow 5\hat i - 2\hat k = \dfrac{{\lambda (11\hat i + 3\hat j + 7\hat k) + (\hat i - 2\hat j - 8\hat k)}}{{\lambda + 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow (\lambda + 1)(5\hat i - 2\hat k) = 11\lambda \hat i + 3\lambda \hat j + 7\lambda \hat k + \hat i - 2\hat j - 8\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow 5(\lambda + 1)\hat i - 2(\lambda + 1)\hat k = (11\lambda + 1)\hat i + (3\lambda - 2)\hat j + (7\lambda - 8)\hat k$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = \dfrac{2}{3}$
So, the required ratio is 2:3
9. Find the position vector of a point $R$ which divides the line joining two points $P$ and $Q$ whose position vectors are $(2\vec a + \vec b)$ and $(\vec a - 3\vec b)$ externally in the ratio 1: 2. Also, show that $P$ is the mid point of the line segment RQ.
Ans: $\overrightarrow {{\text{OP}}} = 2\vec a + \vec b,\overrightarrow {{\text{OQ}}} = \overrightarrow {\text{a}} - 3\overrightarrow {\text{b}} $
$\overrightarrow {OR} = \dfrac{{2(2\vec a + \vec b) - (\vec a - 3\vec b)}}{{2 - 1}} = \dfrac{{4\vec a + 2\vec b - \vec a - 3\vec b}}{1} = 3\vec a + 5\vec b$
So, the position vector of ${\text{R}}$ is $3\overrightarrow {\text{a}} + 5\overrightarrow {\text{b}} $
Position vector of midpoint of ${\text{RQ}} = \dfrac{{\overrightarrow {{\text{OQ}}} + \overrightarrow {{\text{OR}}} }}{2}$
$ = \dfrac{{(a\sqrt 6 ) + (3\vec a + 5\bar b)}}{2}$
$ = 2\vec a + \vec b$
$ = \overrightarrow {OP} $
Thus, ${\text{P}}$ is midpoint of line segment ${\text{RQ}}$
10. The two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are $2\hat i - 4\hat j + 5\hat k$ and $\hat i - 2\hat j - 3\hat k$. Find the unit vector parallel to its diagonal. Also, find its area.
Ans: Diagonal of a parallelogram is $\vec a + \vec b$
$\vec a + \vec b = (2 + 1)\hat i + ( - 4 - 2)\hat j + (5 - 3)\hat k = 3\hat i - 6\hat j + 2\hat k$
So, the unit vector parallel to diagonal is $\dfrac{{\vec a + \vec b}}{{|\vec a + \vec b|}} = \dfrac{{3\hat i - 6\hat j + 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {{3^2} + {{( - 6)}^2} + {2^2}} }} = \dfrac{{3\hat i - 6\hat j + 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {9 + 36 + 4} }} = \dfrac{{3\hat i - 6\hat j + 2\hat k}}{7} = \dfrac{3}{7}\hat i - \dfrac{6}{7}\hat j + \dfrac{2}{7}\hat k$
$\vec a \times \vec b = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{r}} {\hat i}&{\hat j}&k \\ 2&{ - 4}&3 \\ 1&{ - 2}&{ - 3} \end{array}} \right|$
$ = \hat i(12 + 10) - \hat j( - 6 - 5) + \bar k( - 4 + 4)$
$ = 22\hat i + 11\hat j$
$ = 11(2\hat i + \hat j)$
$\therefore |\vec a \times \vec b| = 11\sqrt {{2^2} + {1^2}} = 11\sqrt 5 $
So, area of parallelogram is $11\sqrt 5 $ sq units
11. Show that the direction cosines of a vector equally inclined to the axes OX, OY and OZ are $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
Ans: Let a vector be equally inclined to ${\text{OX}},{\text{OY}}$, and ${\text{OZ}}$ at an angle $\alpha $.
So, the Direction Cosines of the vector are $\cos \alpha ,\cos \alpha $and $\cos \alpha $.
${\cos ^2}\alpha + {\cos ^2}\alpha + {\cos ^2}\alpha = 1$
$ \Rightarrow 3{\cos ^2}\alpha = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \alpha = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
So, the DCs of the vector are $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }},\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
12. Let $\vec a = \hat i + 4\hat j + 2\hat k$ and $\vec b = 3\hat i - 2\hat j + 7\hat k$ and $\vec c = 2\hat i - \hat j + 4\hat k$. Find a vector $\vec d$ which is
perpendicular to both $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ and $\vec c \cdot \vec d = 15$
Ans: $\vec d = {d_1}\hat i + {d_2}\hat \jmath + {d_3}\hat k$
$\vec d\;.\;\vec a = 0 \Rightarrow {d_1} + 4{d_2} + 2{d_3} = 0$
$\vec d\;.\;\vec b = 0 \Rightarrow 3{d_1} - 2{d_2} + 7{d_3} = 0$
$\vec c \cdot \vec d = 15 \Rightarrow 2{d_1} - {d_2} + 4{d_3} = 15$
Solving these equations, we get ${d_1} = \dfrac{{160}}{3},{d_2} = - \dfrac{5}{3},{d_3} = - \dfrac{{70}}{3}$
$\therefore \vec d = \dfrac{{160}}{3}\hat i + \dfrac{5}{3}\widehat j + \dfrac{{70}}{3}\hat k = \dfrac{1}{3}(160\hat i + 5\hat j + 70\hat k)$
13. The scalar product of the vector $\hat i + \hat j + \hat k$ with a unit vector along the sum of vectors $2\hat i + 4\hat j - 5\hat k$ änd $\lambda \hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k$ is equal to one. Find the value of $\lambda $.
Ans: $(2\hat i + 4\hat j - 5\hat k) + (\lambda \hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k) = (2 + \lambda )\hat i + 6\hat j - 2\hat k$
So, unit vector along $(2\hat i + 4\hat j - 5\hat k) + (\lambda \hat i + 2\hat j + 3\hat k)$ is $\left( {\dfrac{{(2 + \lambda )\hat i + 6\hat j - 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {{\lambda ^2} + 4\lambda + 44} }}} \right)$
$(\hat i + \hat j + \hat k) \cdot \left( {\dfrac{{(2 + \lambda )\hat i + 6\hat j - 2\hat k}}{{\sqrt {{\lambda ^2} + 4\lambda + 44} }}} \right) = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{(2 + \lambda ) + 6 - 2}}{{\sqrt {{\lambda ^2} + 4\lambda + 44} }} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{\lambda ^2} + 4\lambda + 44} = \lambda + 6$
$ \Rightarrow {\lambda ^2} + 4\lambda + 44 = {(\lambda + 6)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\lambda ^2} + 4\lambda + 44 = {\lambda ^2} + 12\lambda + 36$
$ \Rightarrow 8\lambda = 8$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 1$
14. If $\vec a,\vec b,\vec c$ are mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitudes, show that the vector $\vec a + \vec b + \vec c$ is equally inclined to $\vec a\;,\;\vec b$ and $\vec c$.
Ans: $\vec a\;.\;\vec b = \vec b\;.\;\vec c = \vec c\;.\;\vec a = 0$
$|\vec a| = |\vec b| = |\vec c|$
Let $\vec a + \vec b + \vec c$ be inclined to $\vec a,\vec b,\vec c$ at angles ${\theta _1},{\theta _2},{\theta _3}$ respectively. $\cos {\theta _1} = \dfrac{{(\vec a + \vec b + \vec c) \cdot \vec a}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec a\mid }} = \dfrac{{\vec a \cdot \vec a + \vec b \cdot \vec a + \vec c \cdot \vec a}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec a\mid }} = \dfrac{{|\vec a{|^2}}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec a|}} = \dfrac{{|\vec a|}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c|}}$
$\cos {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{(\vec a + \vec b + \vec c)\vec b}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec b\mid }} = \dfrac{{\vec a\vec b + \vec b\vec b + \vec c\vec b}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec b\mid }} = \dfrac{{|\vec b{|^2}}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec b|}} = \dfrac{{|\vec b|}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c|}}$
$\operatorname{os} {\theta _3} = \dfrac{{(\vec a + \vec b + \vec c) \cdot \vec c}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\bar c|}} = \dfrac{{\vec a\vec c + \vec b\vec c + \vec c\vec c}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec c\mid }} = \dfrac{{|\vec c{|^2}}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c||\vec c|}} = \dfrac{{|\vec c|}}{{|\vec a + \vec b + \vec c|}}$
Since, $|\vec a| = |\vec b| = |\vec c|\; \Rightarrow \;\cos {\theta _1} = \cos {\theta _2} = \cos {\theta _3}$, So, ${\theta _1} = {\theta _2} = {\theta _3}$
15. Prove that, $(\vec a + \vec b) \cdot (\vec a + \vec b) = \;|\vec a{|^2} + |\vec b{|^2}$ if and only if $\vec a,\vec b$ are perpendicular, given $\vec a \ne \vec 0,\vec b \ne 0$
Ans: $(\vec a + \vec b) \cdot (\vec a + \vec b) = |\vec a{|^2} + |\vec b{|^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \vec a \cdot \vec a + \vec a\;.\;\vec b + \vec b \cdot \vec a + \vec b\;.\;\vec b = |\vec a{|^2} + |\vec b{|^2}$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a{|^2} + 2\vec a\;.\;\vec b + |\vec b{|^2} = |a{|^2} + |\vec b{|^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2\vec a\;.\;\vec b = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \vec a\;.\;\vec b = 0$
So $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ are perpendicular.
16. If $\theta $ is the angle between two vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec b$, then $\vec a\vec b \geqslant 0$ only when
a. $0 < \theta < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
b. $0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
c. $0 < \theta < \pi $
d. $0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \pi $
Ans: $\therefore \vec a\vec b \geqslant 0$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a||\vec b|\cos \theta \geqslant 0$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta \geqslant 0\quad \because [|\vec a| \geqslant 0$ and $|\vec b| \geqslant 0]$
$ \Rightarrow 0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$\vec a \cdot \vec b \geqslant 0$ if $0 \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
So the right answer is B
17. Let $\vec a$ and $\vec b$ be two unit vectors and $\theta $ is the angle between them. Then $\vec a + \vec b$ is a unit vector if
a. $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$
b. $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
c. $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
d. $\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Ans: $|\vec a| = |\vec b| = 1$
$|\vec a + \vec b| = 1$
$ \Rightarrow (\vec a + \overrightarrow b )(\vec a + \overrightarrow b ) = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \vec a \cdot \vec a + \vec a\;.\;\vec b + \vec b\;.\;\vec a + \vec b\;.\;\vec b = 1$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a{|^2} + 2\vec a\;.\;\vec b + |\overrightarrow b {|^2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {1^2} + 2|\vec a||\vec b|\cos \theta + {1^2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow 1 + 2.1.1\cos \theta + 1 = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
So, $\vec a + \vec b$ is unit vector if $\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
The correct answer is D
18. The value of $\hat i.(\hat j \times \hat k) + \hat j \cdot (\hat i \times \hat k) + \hat k \cdot (\hat i \times \hat j)$ is
$\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{ a. }}0}&{{\text{ b. }} - 1}&{{\text{ c. }}1}&{{\text{ d. }}3} \end{array}$
Ans:
$\hat i \cdot (\hat j \times \hat k) + \hat j \cdot (\hat i \times \hat k) + \hat k \cdot (\hat i \times \hat j)$
$ = \hat i\;.\;\hat i + \hat j \cdot ( - \hat j) + \hat k\;.\;\hat k$
$ = 1 - 1 + 1$
$ = 1$
The correct answer is C.
19. If $\theta $ is the angle between any two vectors $\vec a$ and $\vec b$, then $|\vec a\vec b| = |\vec a \times \vec b|$ when $\theta $ is equal to
a. 0
b. $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
c. $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
d. n
Ans: $|\vec a\vec b| = |\vec a \times \vec b|$
$ \Rightarrow |\vec a|\vec b|\cos \theta = |\vec a||\vec b\mid \sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sin \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$
The correct answer is B
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 12 Maths Vector Algebra
Chapter | Dropped Topics |
Vector Algebra | 10.7 - Scalar Triple Product |
10.7.1 - Coplanarity of Three Vectors |
Class 12 Maths Chapter 10: Exercises Breakdown
Exercise | Number of Questions |
Exercise 10.1 | 5 Questions & Solutions (5 Short Answers) |
Exercise 10.2 | 19 Questions & Solutions (5 Short Answers, 14 Long Answers) |
Exercise 10.3 | 18 Questions & Solutions (5 Short Answers, 13 Long Answers) |
Exercise 10.4 | 12 Questions & Solutions (4 Short Answers, 8 Long Answers) |
Miscellaneous Exercise | 19 Questions & Solutions |
Conclusion
Vector Class 12 NCERT Solutions provides a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental concepts and applications of vectors. This chapter covers various essential topics such as vector addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, dot product, cross product, and their geometric interpretations. Through well-structured examples and step-by-step solutions, students gain a solid foundation in vector algebra, which is crucial for higher studies in mathematics, physics, and engineering. The exercises are designed to enhance problem-solving skills and analytical thinking. Typically 1 to 2 short answer questions and 1 to 2 long answer questions appear from Ch 10 Maths Class 12 in exams.
Other Study Material for CBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 10
S.No. | Important Links for Chapter 10 Vector Algebra |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths | Chapter-wise List
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT 12 Maths solutions PDF. Using these chapter-wise class 12th maths ncert solutions, you can get clear understanding of the concepts from all chapters.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter-wise List |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 |
Related Links for NCERT Class 12 Maths in Hindi
Explore these essential links for NCERT Class 12 Maths in Hindi, providing detailed solutions, explanations, and study resources to help students excel in their mathematics exams.
S.No. | Related NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths |
1 | |
2 |
Important Related Links for NCERT Class 12 Maths
S.No | Important Resources Links for Class 12 Maths |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra (2025-26)
1. What is the step-by-step approach to solving vector addition questions in Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 as per the NCERT Solutions methodology?
To solve vector addition questions as per the NCERT Solutions approach, follow these steps:
- Express each vector in component form (using i, j, k notation).
- Add respective components: add all i-components, all j-components, and all k-components separately.
- Combine the added components to get the resultant vector.
- Simplify the final result and, if required, calculate the magnitude using the Pythagorean formula.
2. How does understanding the difference between scalar and vector quantities help in solving NCERT Solutions for Vector Algebra?
Recognizing whether a quantity is a scalar (having only magnitude) or a vector (having both magnitude and direction) is crucial because:
- It determines the applicable algebraic operations—scalars use simple arithmetic, while vectors require component-wise methods.
- Vector solutions demand direction, so misidentifying a quantity can lead to incorrect answers.
- Exams may specifically ask you to classify or use the right quantity in physics or mathematical contexts.
3. What are the typical mistakes to avoid while solving NCERT Solutions for questions involving vector products?
When handling problems involving the dot (scalar) or cross (vector) product, avoid these common mistakes:
- Confusing the dot product (result is a scalar) with the cross product (result is a vector).
- Ignoring the angle between vectors—always use the correct trigonometric value (cos for dot, sin for cross products).
- Overlooking the order in cross products, which affects the direction of the resultant vector.
- Forgetting to simplify or write the final answer in the required form (magnitude, component, or both).
4. Why is the concept of direction cosines important in Class 12 Vector Algebra solutions?
Direction cosines are crucial because they specify the orientation of a vector with respect to the axes. Knowing them allows you to:
- Resolve vectors into components systematically.
- Calculate angles and projections accurately, which is frequent in CBSE exam questions.
- Apply geometric interpretations in three-dimensional space, as required by the syllabus.
5. How are NCERT Solutions for position vectors structured for step-wise learning?
Solutions for position vector problems are given in these steps:
- Identify the coordinates of the required points (e.g., P and Q).
- Use the section formula to find the ratio as per the question.
- Apply the formula for internal (or external) division to calculate the position vector.
- Simplify to the component form as per CBSE guidelines for clear representation.
6. What is the recommended methodology for tackling vector geometry problems in NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 10?
The recommended method is:
- Convert geometric entities (points, lines, triangles) into vectors using position vectors.
- Apply vector operations such as addition, subtraction, or scalar multiplication as required.
- For proving collinearity or perpendicularity, use conditions such as proportionality of components or dot product equal to zero.
- Show detailed steps as per the step-by-step format in the NCERT Solutions to enhance clarity and CBSE marking.
7. How can the stepwise approach in NCERT Solutions improve problem-solving skills for board examinations?
A structured, stepwise approach as presented in the official NCERT Solutions:
- Reduces errors by ensuring each part of the solution is logically derived.
- Makes complex vector questions manageable by breaking them into simple steps.
- Helps in achieving full marks, as each step is eligible for partial marking in CBSE board pattern for 2025–26.
8. What are the key pointers for writing solutions to projection and triple product questions as per CBSE exam requirements?
Key pointers include:
- Explicitly state the formulas for projection or the scalar/triple product.
- Substitute the given vectors in component form stepwise.
- Show intermediate calculations before presenting the answer.
- Final answers should be boxed or clearly highlighted as per CBSE subjective exam conventions.
9. In what way do NCERT Solutions prepare students for application-based and HOTS questions in vectors?
NCERT Solutions bridge conceptual gaps by:
- Demonstrating multiple-step reasoning for real-world or HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) problems involving vectors.
- Encouraging students to apply properties such as vector addition, section formula, and products to novel scenarios.
- Providing fully solved exemplar and miscellaneous exercise questions that mirror board exam patterns.
10. How do you verify if a vector is equally inclined to all coordinate axes using NCERT Solutions strategies?
To verify if a vector is equally inclined to OX, OY, and OZ axes:
- Find the direction cosines of the vector; for equal inclination, all three must be equal and each should be 1/√3.
- Show the calculation of the magnitude and corresponding cosine values stepwise, as per NCERT Solutions protocol.
- If the conditions are met, state clearly that the vector is equally inclined to each axis as per the CBSE marking scheme.
























