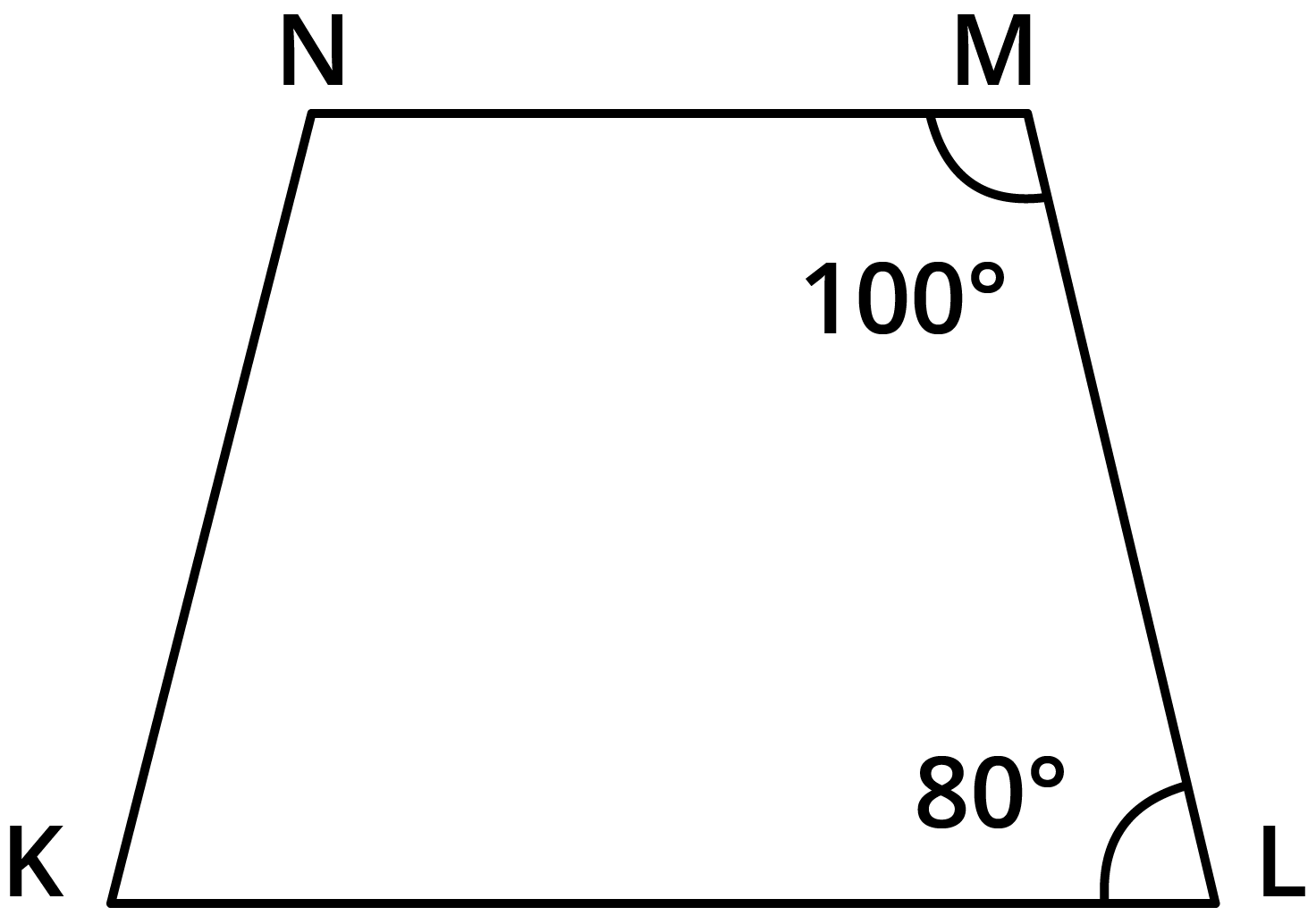
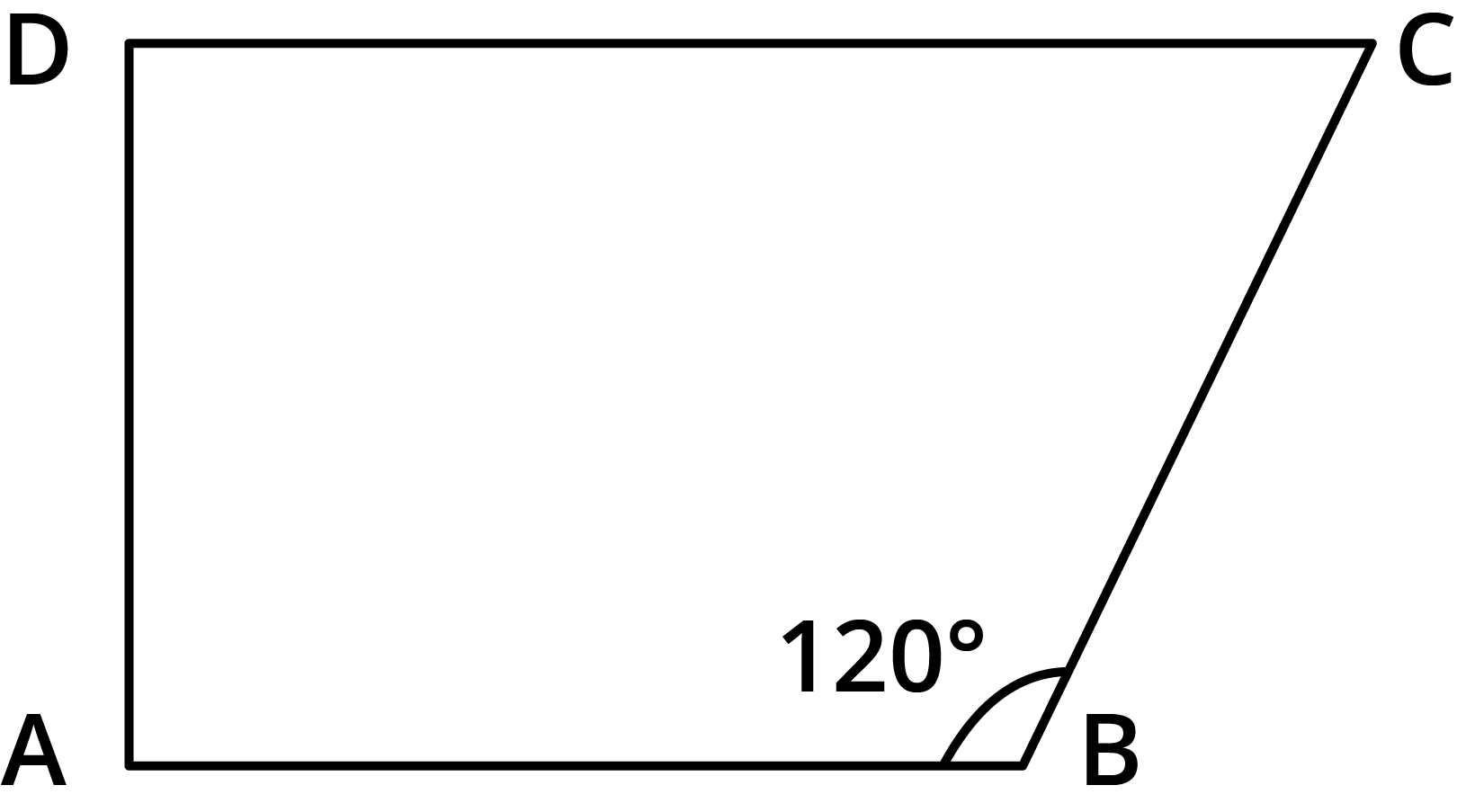
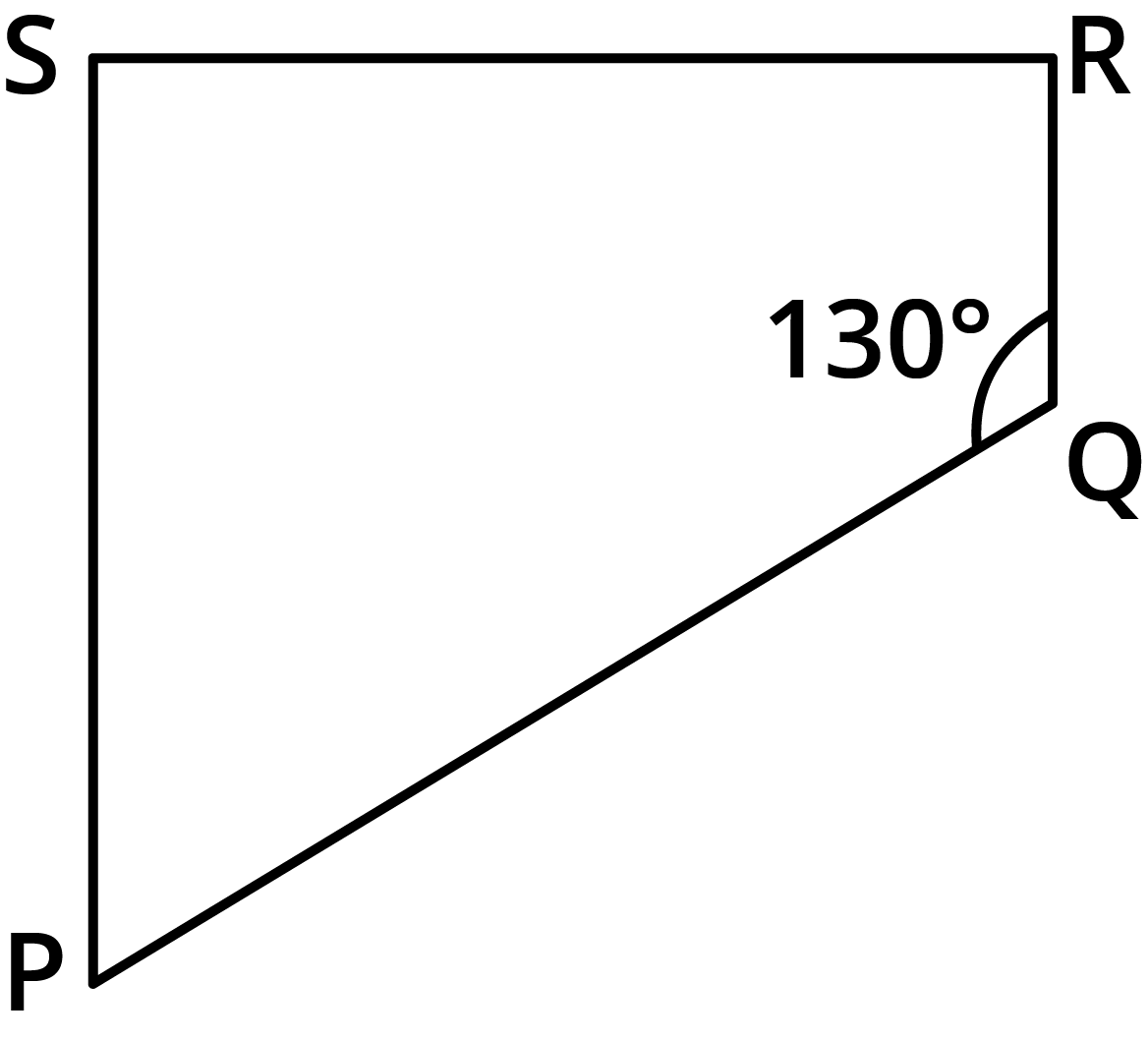
Understanding Quadrilaterals - Exercise-wise Questions and Answers For Class 8 Maths - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals (2025-26)
1. What are the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals?
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals provide step-by-step, CBSE-aligned answers to all textbook questions on polygons, quadrilaterals, their types (like parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square, kite, trapezium), and their properties. Each solution follows the correct methodology and in-depth explanations as per the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus, ensuring clarity for every exercise.
2. How do the NCERT Solutions help in solving Exercise 3.3 of Class 8 Maths Chapter 3?
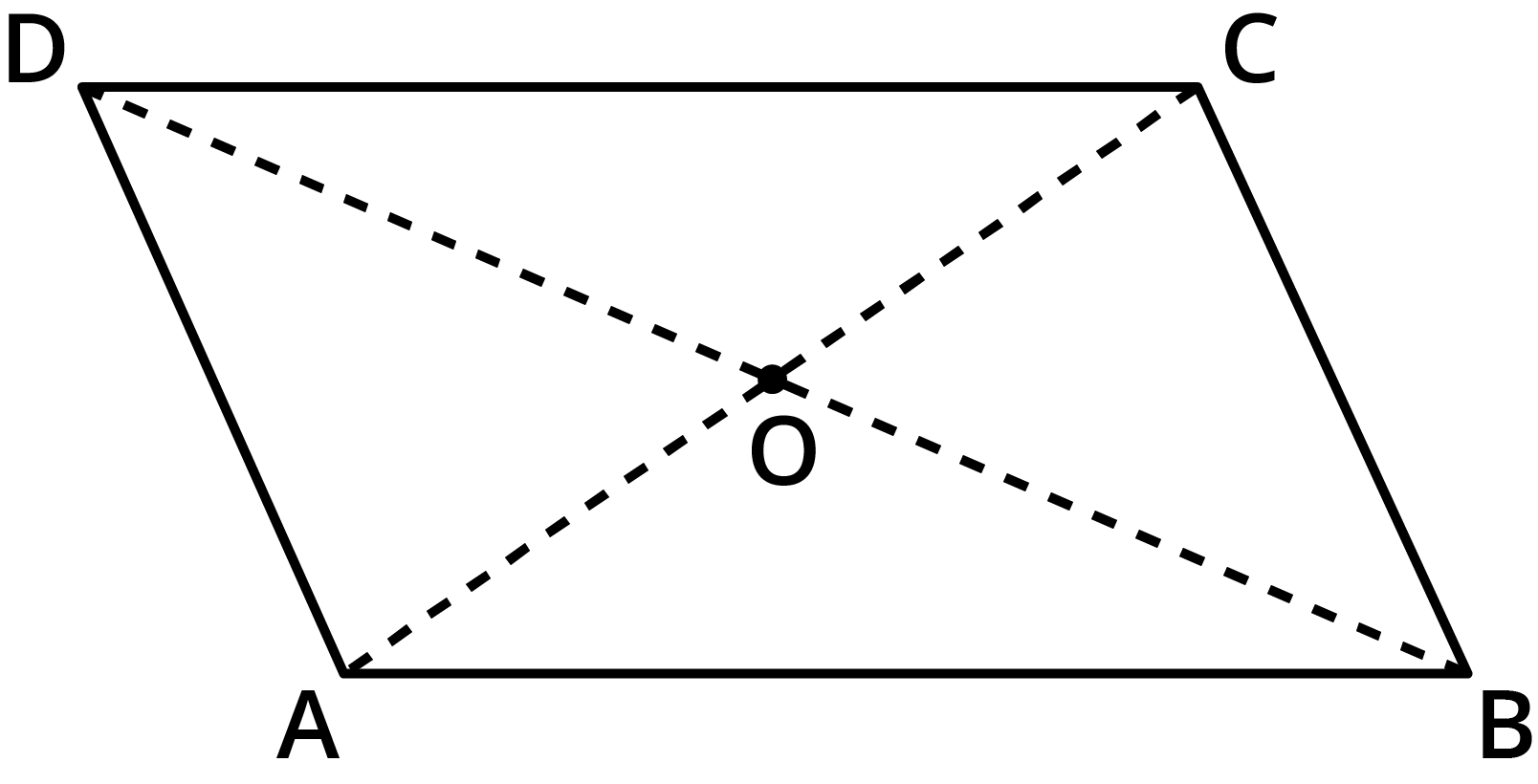
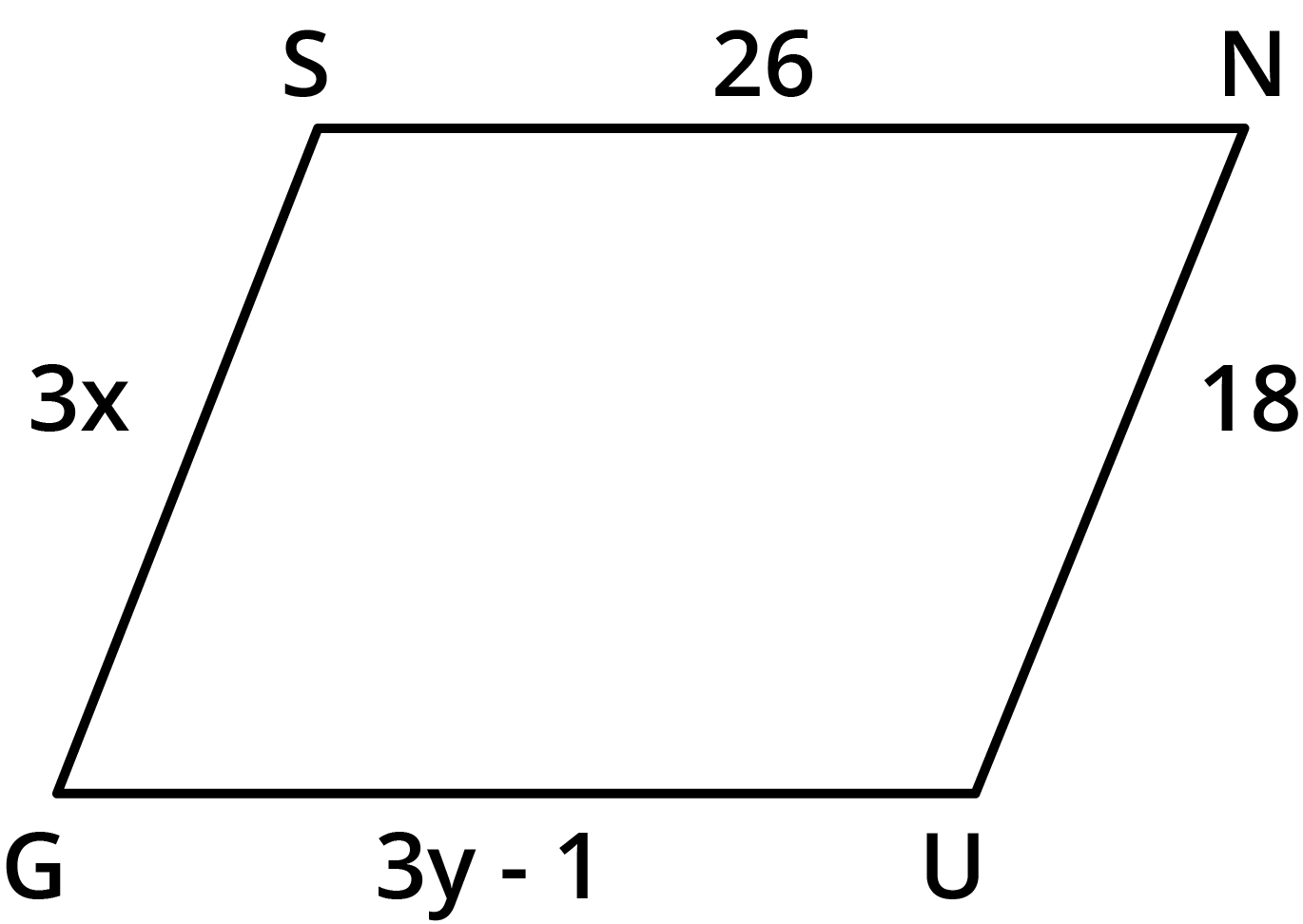
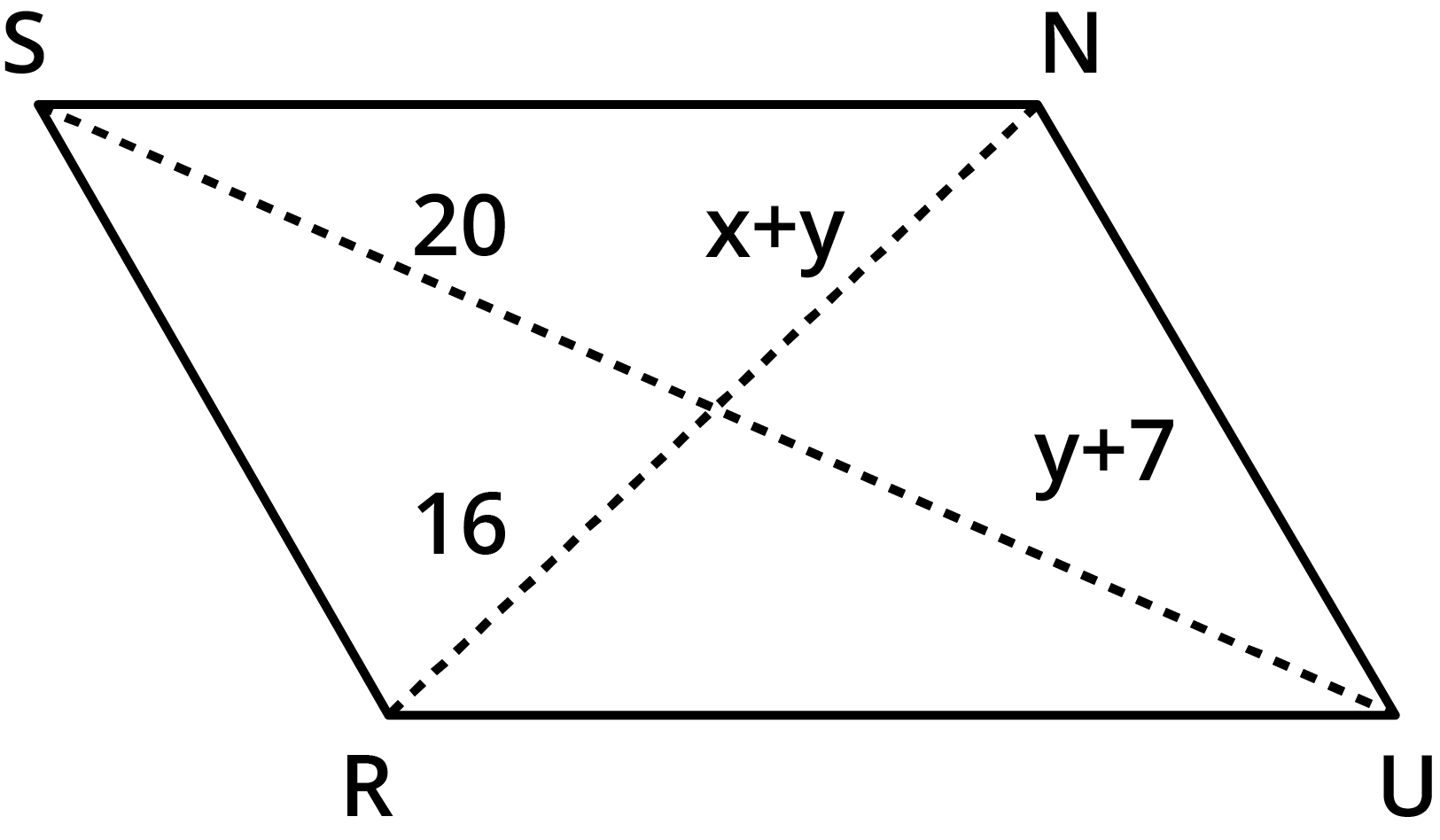
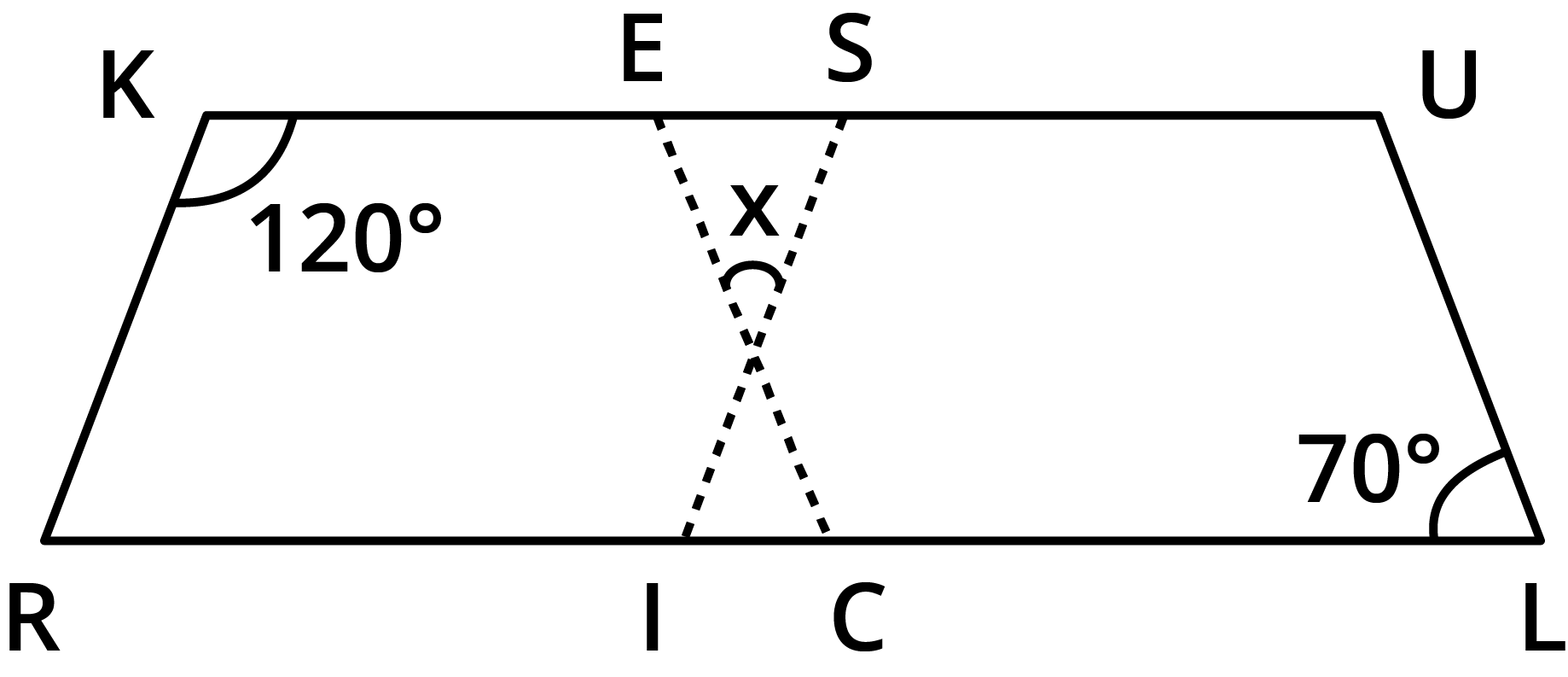
The NCERT Solutions guide students through each question in Exercise 3.3 by clearly breaking down the proof or calculation steps involving properties of parallelograms, such as equal opposite angles, supplementary adjacent angles, and diagonal bisectors. Each answer follows CBSE marking schemes and includes reasoning for every property used.
3. What key properties of quadrilaterals should students remember for Class 8 Maths exams?
Students must remember the following properties for exams:
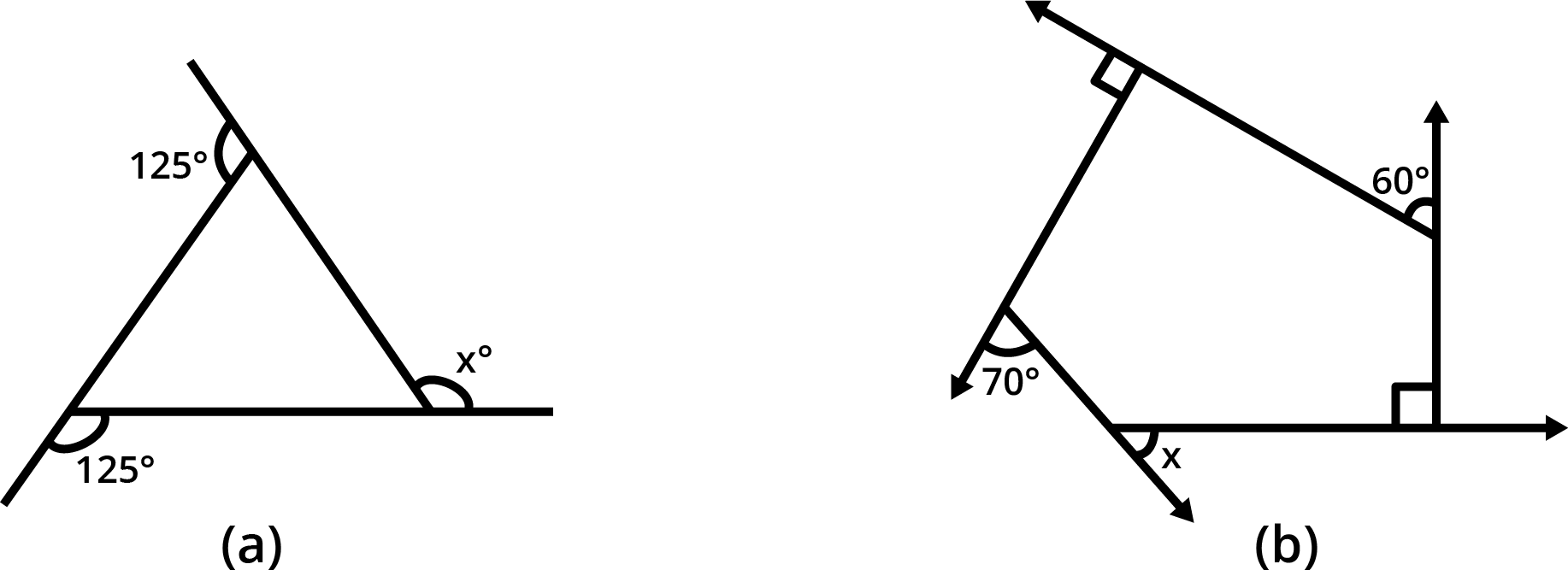
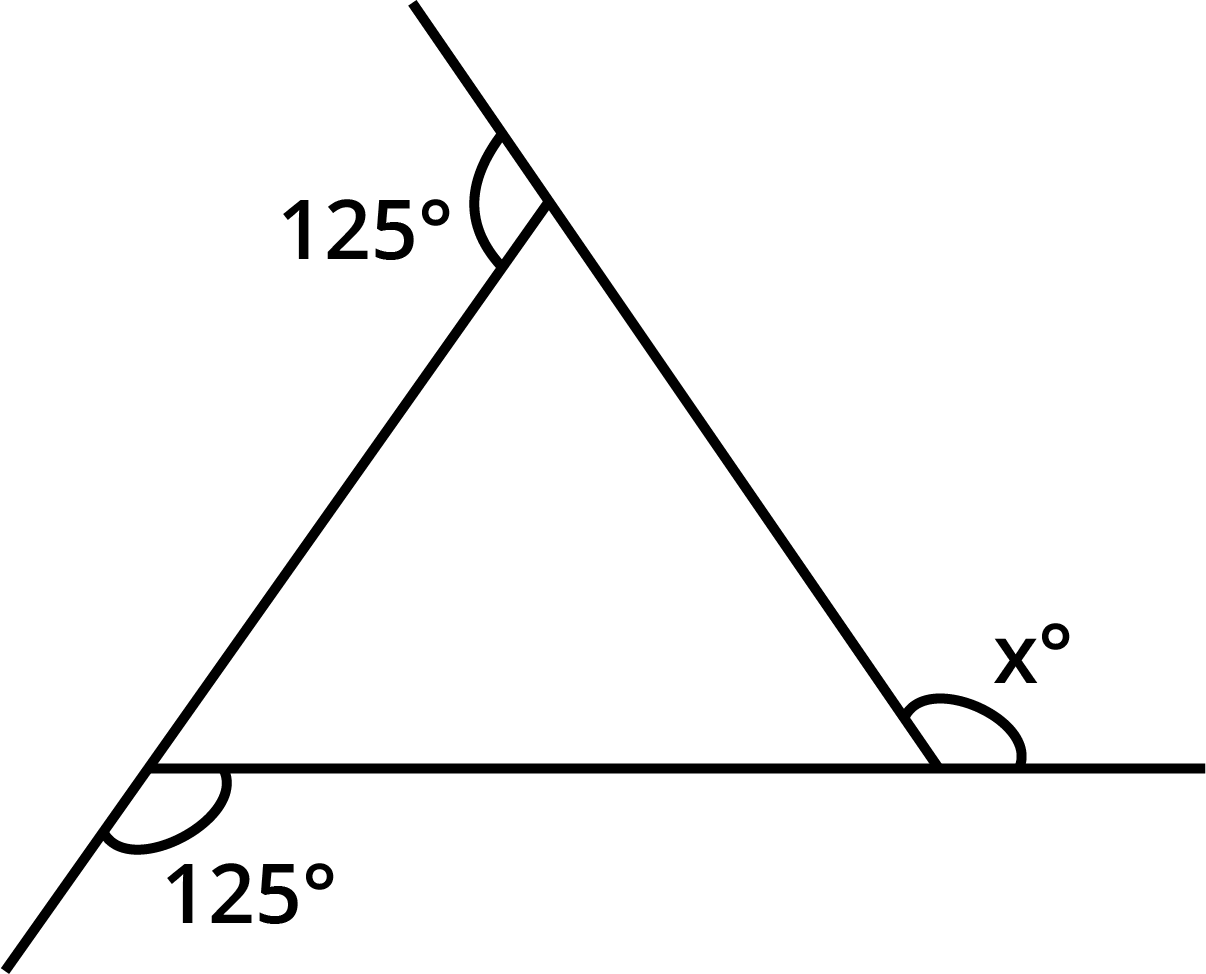
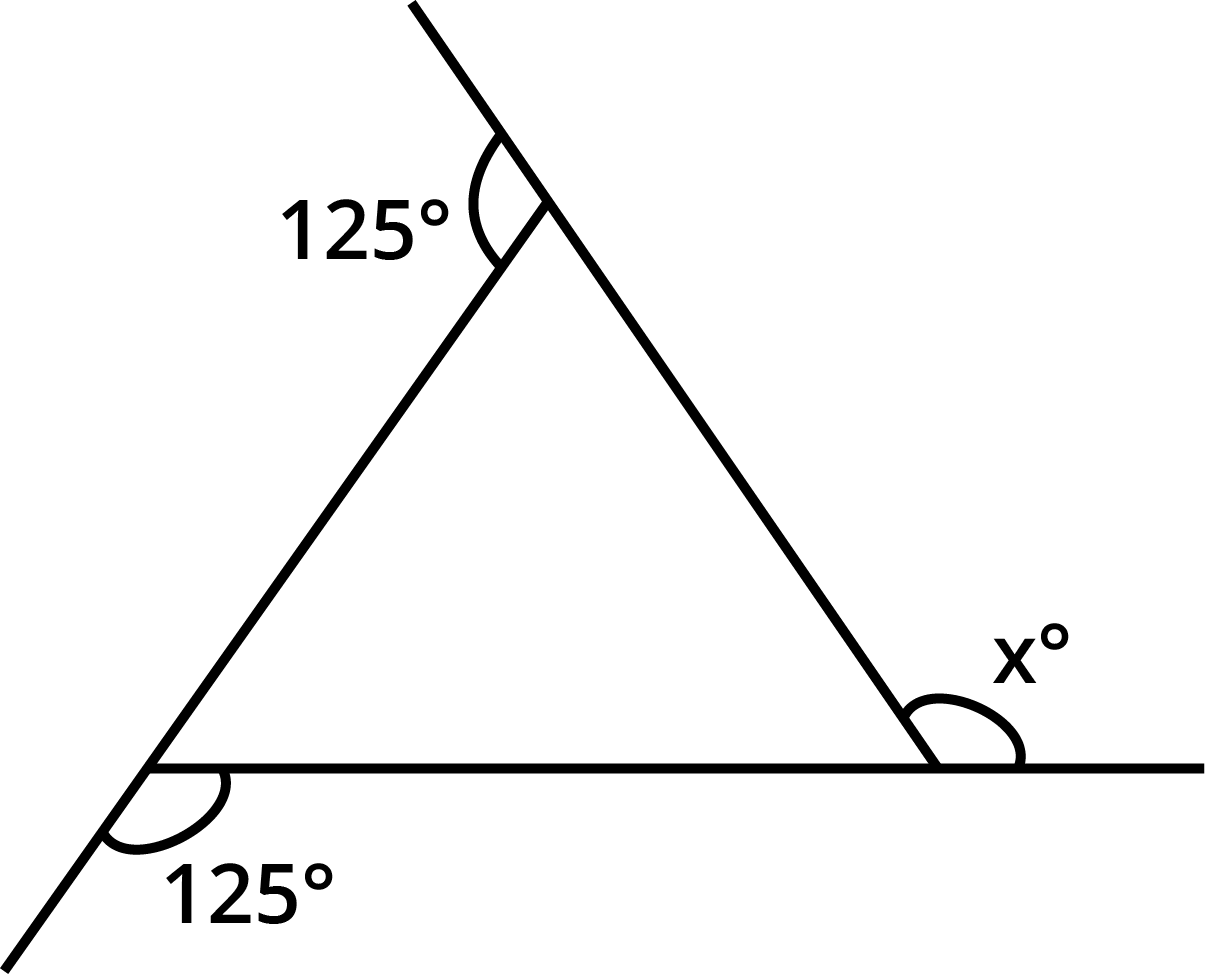
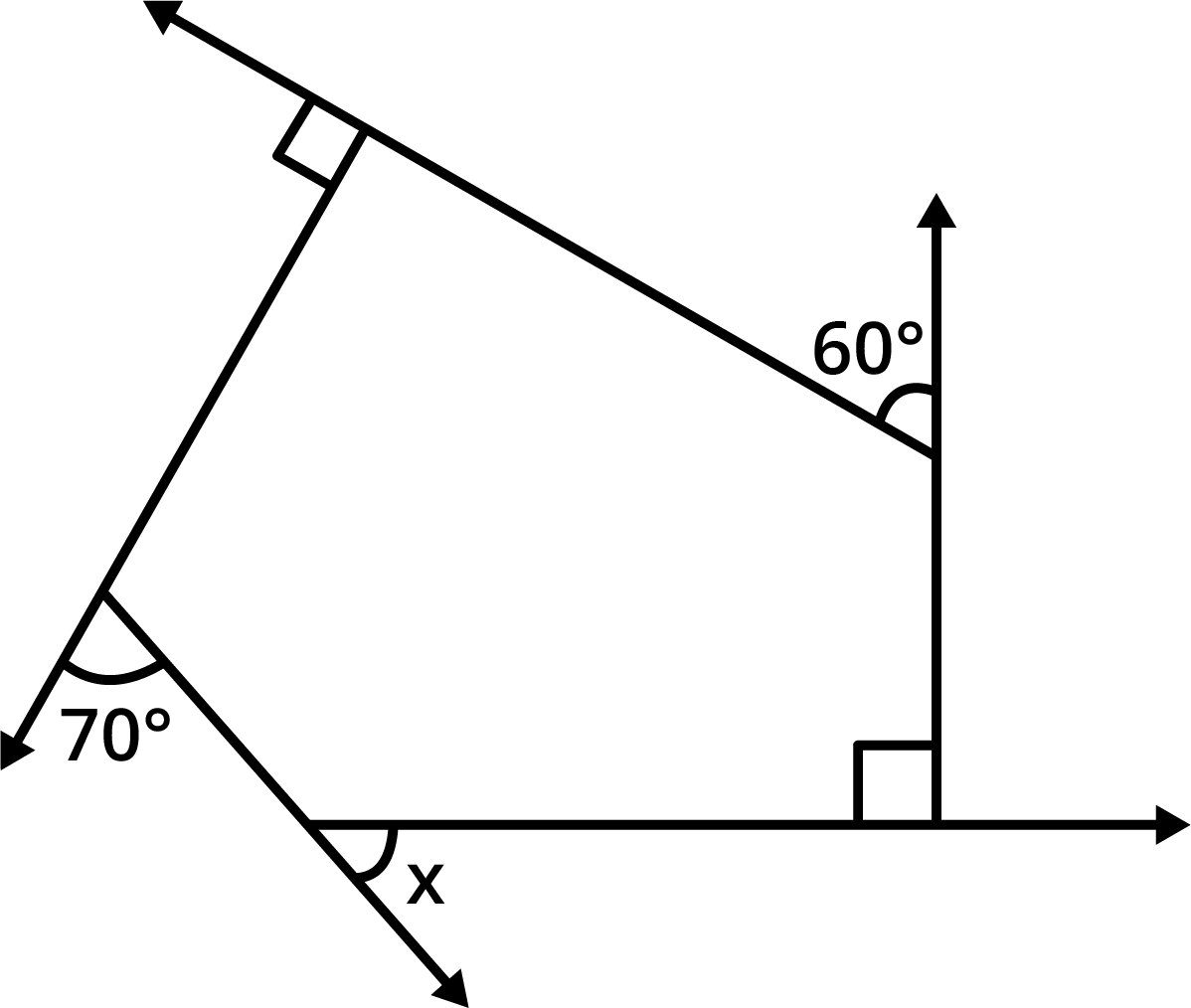
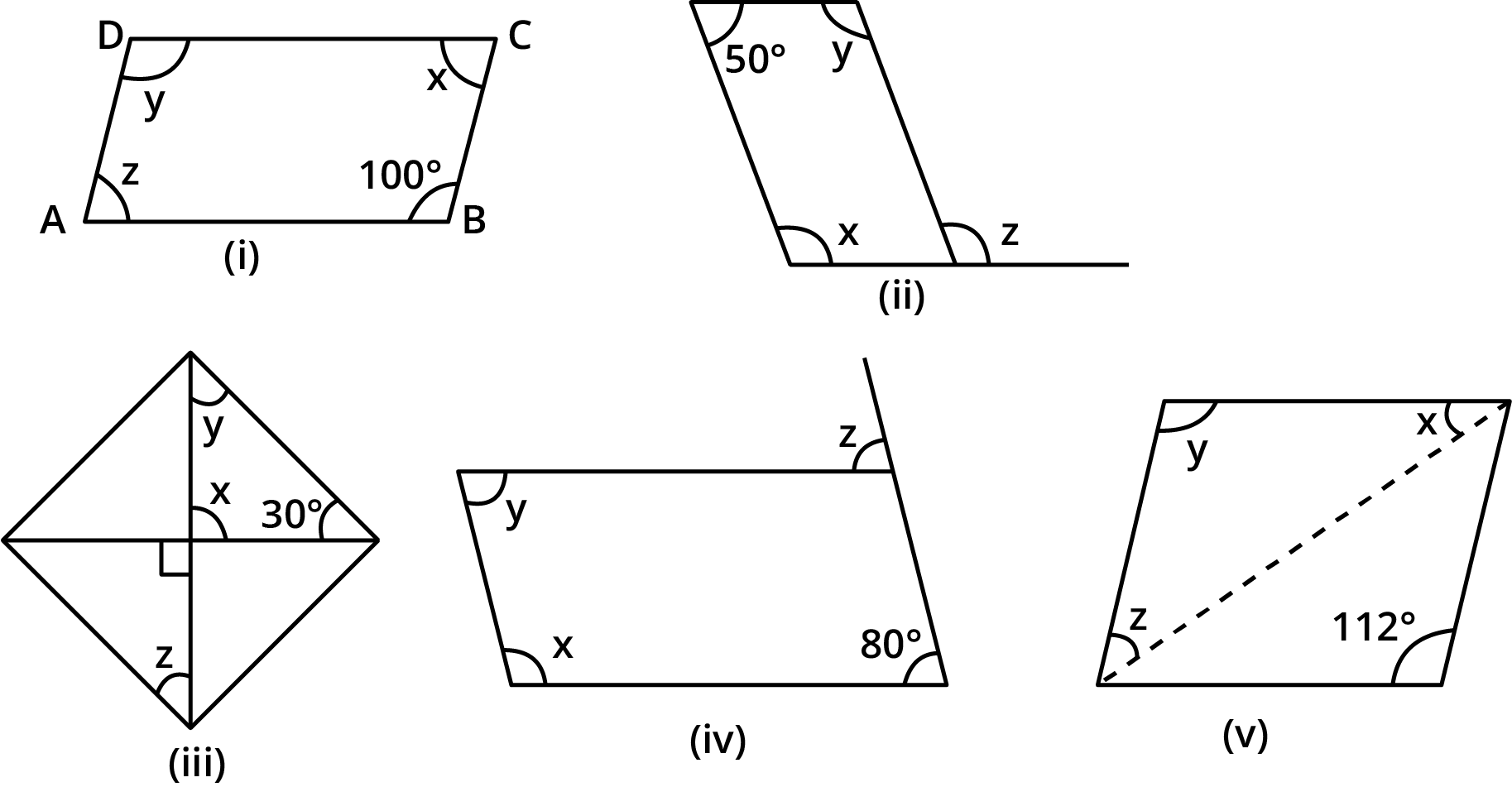
- Sum of all interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360°.
- Opposite sides of parallelograms are equal and parallel.
- Diagonals of a rectangle and square are equal and bisect each other.
- All angles of a square and rectangle are right angles.
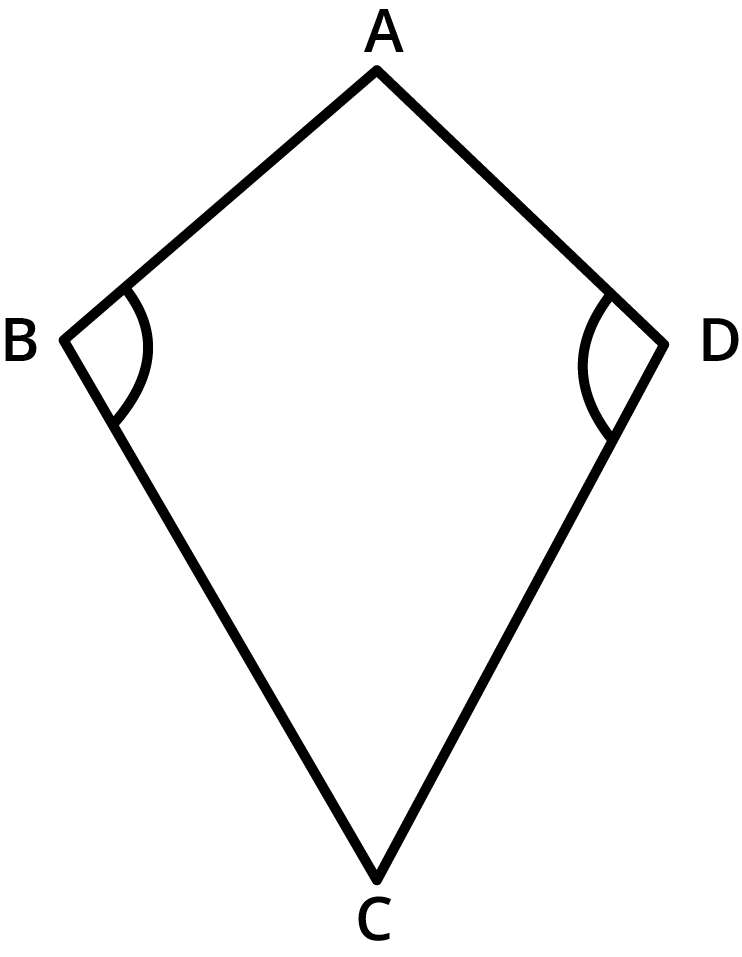
- In rhombus and kite, diagonals intersect at right angles.
4. Why is understanding the difference between convex and concave polygons important in Chapter 3?
Knowing the difference between convex and concave polygons helps in classifying shapes correctly and understanding their angle properties, which is fundamental for accurate polygon identification, problem-solving, and avoiding confusion in competitive or board exams.
5. How can you find the number of sides in a regular polygon if each exterior angle is given?
Use the formula: Number of sides = 360° ÷ measure of each exterior angle. This formula is essential for Class 8 Chapter 3 and is frequently applied in NCERT exercise questions for regular polygons.
6. What is the significance of the angle sum property of quadrilaterals in CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3?
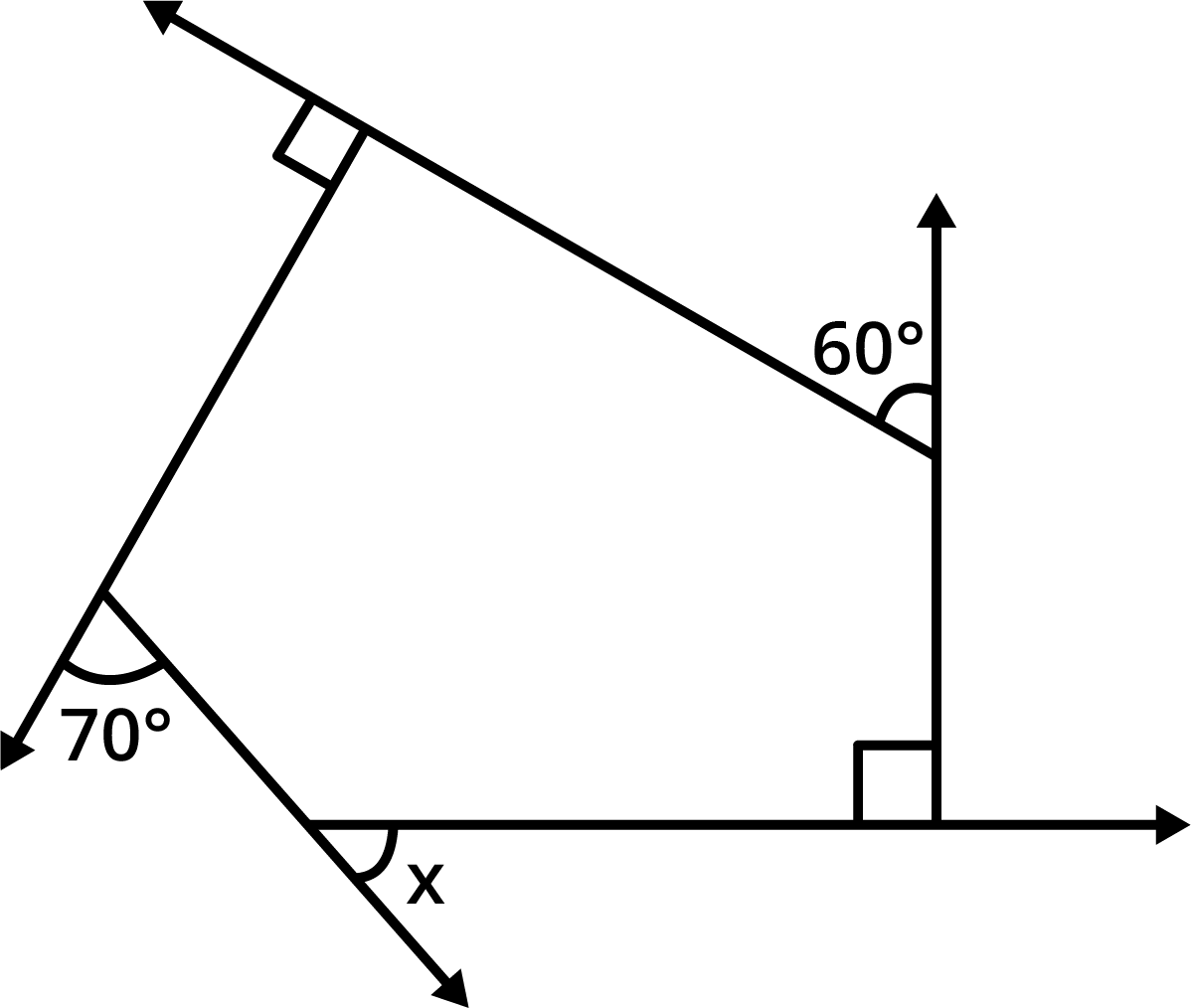
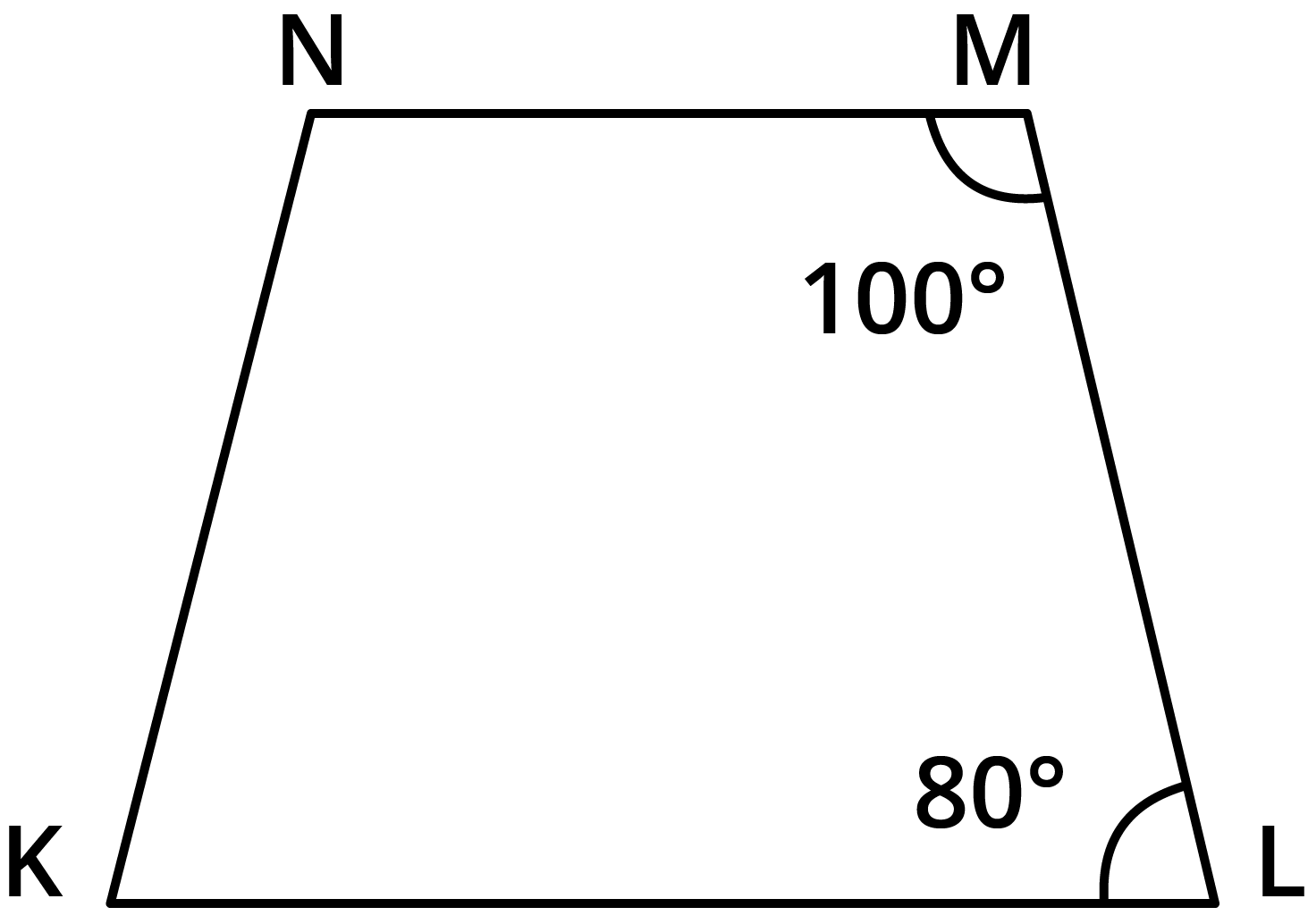
The angle sum property states that the sum of all interior angles in any quadrilateral equals 360°. This concept is central for solving angle-finding questions and is highlighted in multiple exercises and higher-order thinking questions in Chapter 3.
7. Can a quadrilateral with two pairs of equal-length adjacent sides always be a parallelogram? Justify as per NCERT Solutions.
No, such a quadrilateral could be a kite but not necessarily a parallelogram. In parallelograms, opposite sides must be equal and parallel, whereas in a kite, only two pairs of adjacent sides are equal. NCERT solutions provide reasoning-based answers to distinguish these cases.
8. What formulas are recommended to memorize for perimeter and area of quadrilaterals in Class 8 Chapter 3?
Key formulas include:
- Perimeter of Rectangle = 2 × (Length + Breadth)
- Area of Rectangle = Length × Breadth
- Area of Square = Side × Side
- Area of Parallelogram = Base × Height
- Area of Rhombus/Kite = (1/2) × Diagonal 1 × Diagonal 2
9. How do NCERT Solutions ensure CBSE board pattern compliance in Chapter 3 answers?
NCERT Solutions strictly follow CBSE board marking guidelines, provide logical stepwise explanations, state which property/theorem is being applied, and give concise, direct answers instead of only final results. This maximizes marks and strengthens conceptual clarity for board exams.
10. What common mistakes should students avoid when answering Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Quadrilateral questions?
Common pitfalls include:
- Confusing properties of similar-looking quadrilaterals (e.g., parallelogram vs. rhombus vs. kite).
- Missing that angle sum is always 360° for any quadrilateral.
- Not justifying each answer with a specific property or theorem, as required in NCERT Solutions.
- Misapplying area or perimeter formulas to irregular quadrilaterals.
11. Why is it essential to solve all exercise questions from NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3?
Practicing all exercise questions builds a thorough understanding of each concept and prepares students for a wide variety of exam problems, reducing errors and improving speed. NCERT Solutions also expose students to CBSE board style and expected reasoning steps.
12. How is the concept of diagonal bisection used in solving parallelogram problems in NCERT Solutions for Class 8?
For parallelograms, the diagonals bisect each other, meaning they cut each other into two equal halves. This property is frequently used in NCERT exercises to set up equations and solve for unknown side lengths, coordinates, or angles.
13. What should a student do if they find certain quadrilateral questions tricky in NCERT Chapter 3?
Students should:
- Revisit the solution steps and identify which property or theorem was applied.
- Draw neat, labelled diagrams for visual clarity.
- Practice similar questions from the NCERT Solutions to reinforce understanding.
- Seek clarification from teachers or reliable explanations as per CBSE pattern.
14. How is Class 8 Chapter 3 on Understanding Quadrilaterals important for higher classes?
This chapter forms the basis for advanced topics in geometry such as congruence, similarity, coordinate geometry, and surface areas in later classes. Mastery here enables easier and deeper understanding of mathematical concepts in Class 9, 10, and beyond.
15. What real-life examples help in understanding quadrilaterals, as discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 8?
Common objects like doors (rectangle), chessboards (square), kites (kite), tabletop (rectangle), diamond warning signs (rhombus), and trapezium-shaped benches help students relate quadrilaterals to daily life, aiding practical understanding and retention of properties.