Class 8 Social Science Social And Political Life Chapter 4 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Social Science Chapter 4 Judiciary (2025-26)
1. What is the main function of the judiciary as explained in the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
The main function of the judiciary is to uphold the law and enforce fundamental rights. It does this by interpreting laws, resolving disputes, and ensuring that all actions of the government and citizens are in line with the Constitution of India, as per the CBSE 2025–26 guidelines.
2. How does the independence of the judiciary ensure justice as per NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
An independent judiciary means that judges are free from the influence of other branches of government or powerful individuals. This independence helps courts deliver fair judgments, protect citizens' rights, and act as a check on misuse of power, ensuring justice for all.
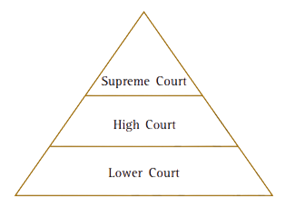
3. Discuss the structure of courts in India outlined in Class 8 Civics Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions.
According to NCERT Solutions, India's judiciary is organized in a hierarchical structure with the Supreme Court at the top, followed by High Courts in each state, District Courts, and lower Magistrate Courts. This structure allows appeals and ensures all cases can be addressed at the appropriate level.
4. Why is the Right to Constitutional Remedies called the ‘heart and soul’ of the Constitution in Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
The Right to Constitutional Remedies enables citizens to approach courts if any of their fundamental rights are violated. As per NCERT Solutions, this right is essential because it ensures legal protection and enforces all other rights, making it the 'heart and soul' of the Constitution (CBSE 2025–26 reference).
5. What are the key differences between civil and criminal cases, as explained in the Judiciary chapter of Class 8 Civics?
NCERT Solutions define civil cases as disputes between people or organizations over rights or agreements, usually seeking compensation. Criminal cases involve actions against society or the state (like theft, assault), where penalties can include fines or imprisonment.
6. How does the judiciary safeguard fundamental rights according to NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
The judiciary safeguards fundamental rights by using its authority to issue writs, hear petitions, and overturn laws or actions by the government that violate constitutional guarantees. Courts can direct authorities to restore rights when breached, ensuring citizens' protection.
7. Why was the introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) significant in Indian judiciary history, as per Class 8 Civics NCERT Solutions?
The introduction of PIL allowed even those who could not afford lawyers to approach the courts about issues affecting the community or the poor, removing financial and technical barriers and improving access to justice for all (CBSE 2025–26 compliant content).
8. What role does the Supreme Court play as the guardian of the Constitution, as stated in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
The Supreme Court acts as the guardian of the Constitution by interpreting its provisions, reviewing legislative actions, and ensuring no law or action violates constitutional rights. It also settles constitutional disputes and protects fundamental rights.
9. In Class 8 Civics Chapter 4, why is ‘justice delayed is justice denied’ an important principle of the Indian judiciary?
This principle, emphasized in NCERT Solutions, means that if legal redress or relief is not given promptly, it becomes meaningless. Delays harm those awaiting justice and weaken faith in the judicial system, highlighting the need for courts to resolve cases efficiently.
10. How does the judiciary prevent the misuse of power by other branches of government, as explained in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
The judiciary checks misuse of power by reviewing actions of the executive and legislative branches. Through judicial review, courts can strike down unconstitutional acts and maintain a balance of power, upholding the rule of law (as per CBSE 2025–26 pattern).
11. What are the main duties of the government to uphold the Right to Food according to Chapter 4 Civics Class 8 NCERT Solutions?
The government should ensure food availability, prevent wastage, support poor communities through schemes like PDS, and make food accessible and affordable to all. These steps are essential for upholding the Right to Food, as detailed in the chapter solutions.
12. Explain the concept of judicial review as per NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4.
Judicial review empowers courts to examine laws and government actions to check whether they conform to the Constitution. If a law or act is found unconstitutional, courts can nullify it, safeguarding citizens' rights and upholding constitutional supremacy.
13. How does the glossary term ‘acquit’ apply in the context of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4?
To ‘acquit’ means a court finds the accused not guilty after a trial. In the judiciary context, if there is insufficient evidence, the accused is acquitted and released, as explained in the chapter’s glossary exercises and stepwise NCERT Solutions.
14. What is the meaning of ‘violation’ in legal terms, based on Class 8 Civics Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions?
‘Violation’ refers to breaking or disregarding a law or a right. According to NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4, not every violation is a crime, but it does mean that someone has acted against a legal duty or protected right.
15. How can studying NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics Chapter 4 Judiciary help students perform better in social science exams?
Stepwise NCERT Solutions clarify concepts, reinforce CBSE answer-writing methods, offer practical examples, and help students develop clear, concise, and accurate exam responses, boosting understanding and scores in Class 8 social science.