




Introduction to Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notes
In NEET Chemistry, the topic “Aldehydes, Ketones and carboxylic acids” is very essential. Aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids (COOH) are found in large amounts in both plants and animals. They (R-CHO. R-CO-R and COOH) serve a crucial function in life's metabolic processes. They are used to flavour a variety of foods and medications.
As a result, the total weightage of this chapter in the NEET exams is up to 4 percent. In this aldehydes ketones and carboxylic acids notes, aldol condensation, Grignard reaction and Cannizzaro Reaction are a few of the concepts that are covered in this article.
Important Topics of Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Acid anhydride
Aldehydes
Ester
Aldol Condensation
ketone
Acyl halide
Cannizzaro reaction
Carboxylic acid
Amide
Important Concepts of Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
The carbonyl group is one of the most important functional groups in organic chemistry because it contains a carbon-oxygen double bond (>C=O). The carbonyl group is connected to a carbon and hydrogen in aldehydes, while it is bonded to two carbon atoms in ketones. Carboxylic acids are carbonyl compounds in which the carbonyl group is linked to oxygen.
Aldehydes and ketones belong to a class of compounds having general formula CnH2nO and are represented as RCHO and RR'CO respectively.
Methods of Preparation of Aldehydes
1. Oxidation of Primary Alcohols
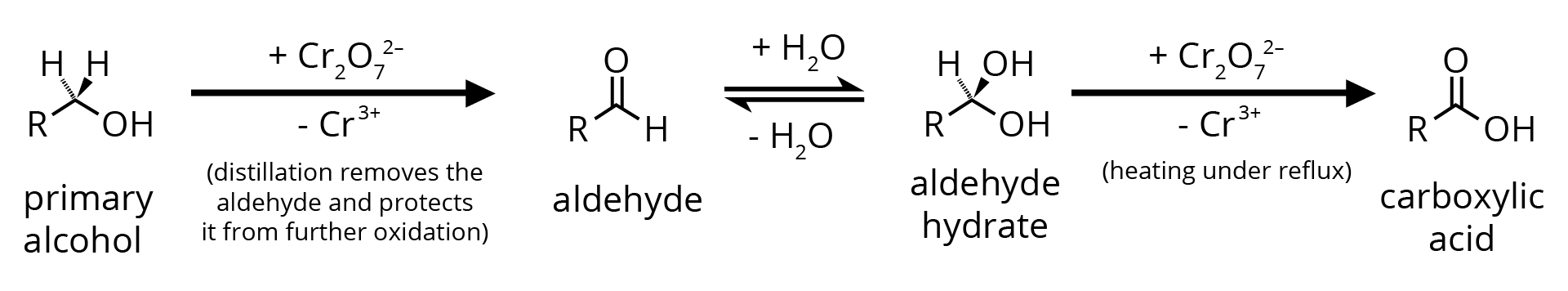
Oxidation can be affected with acidic K2Cr2O7 or with PCC (Pyridine Chlorochromate, mild oxidising agent) in CH2Cl2
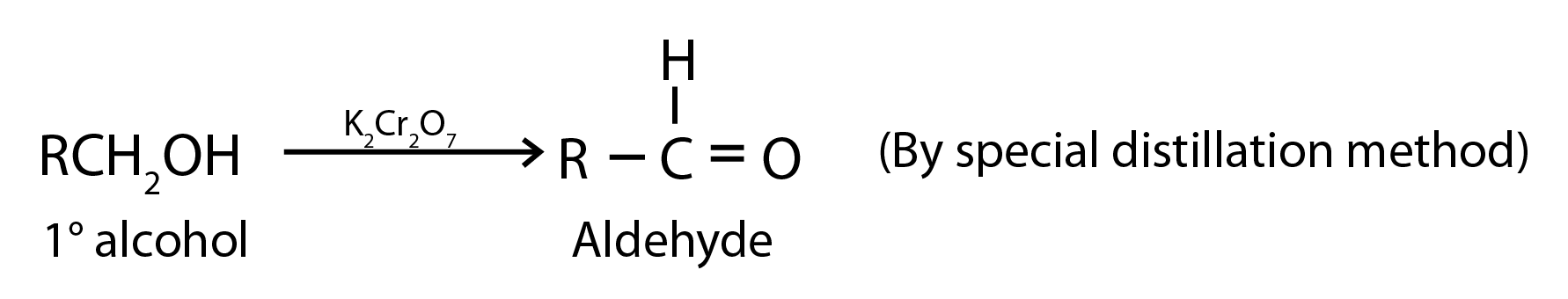
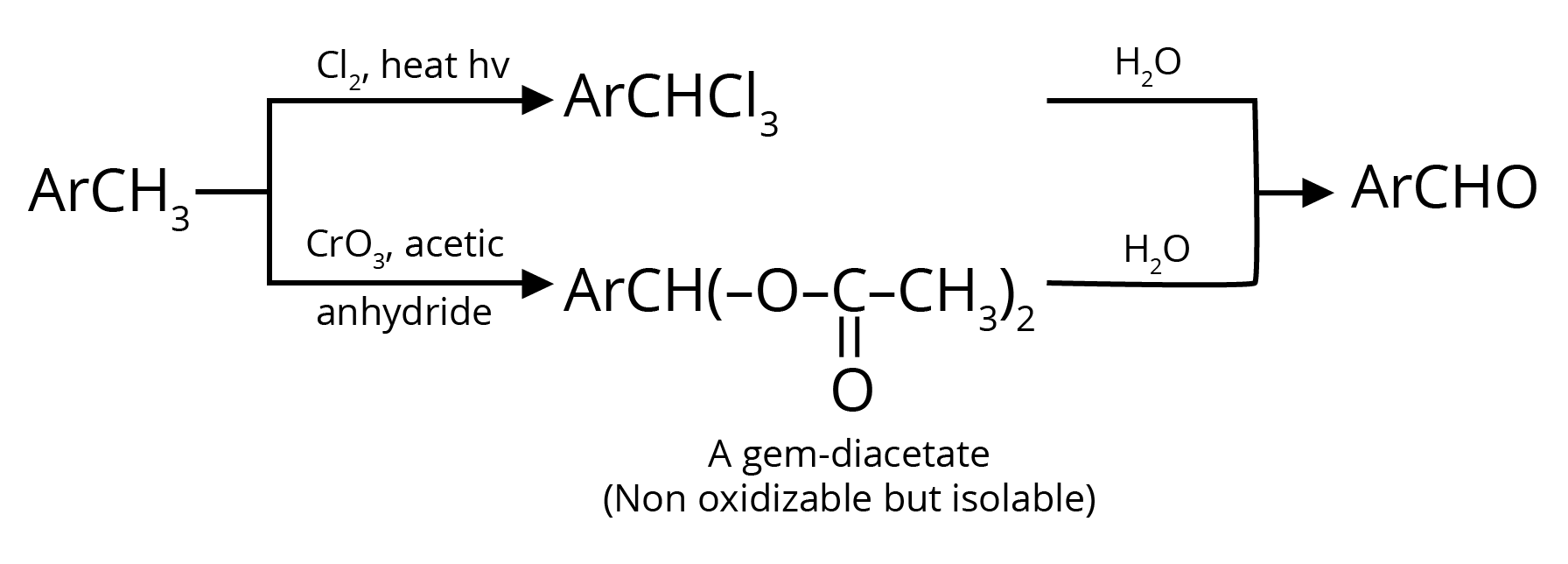
2. Oxidation of Methylbenzenes
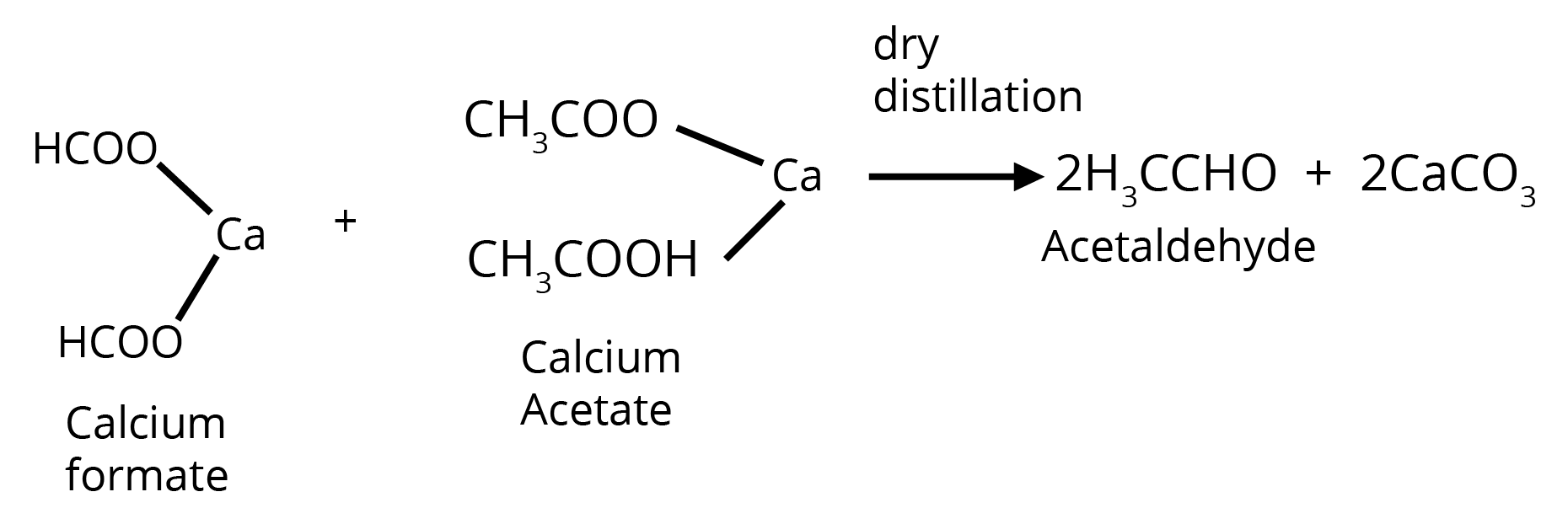
3. By Heating a Mixture of the Calcium Salts of Formic Acid and any one of its Homologues
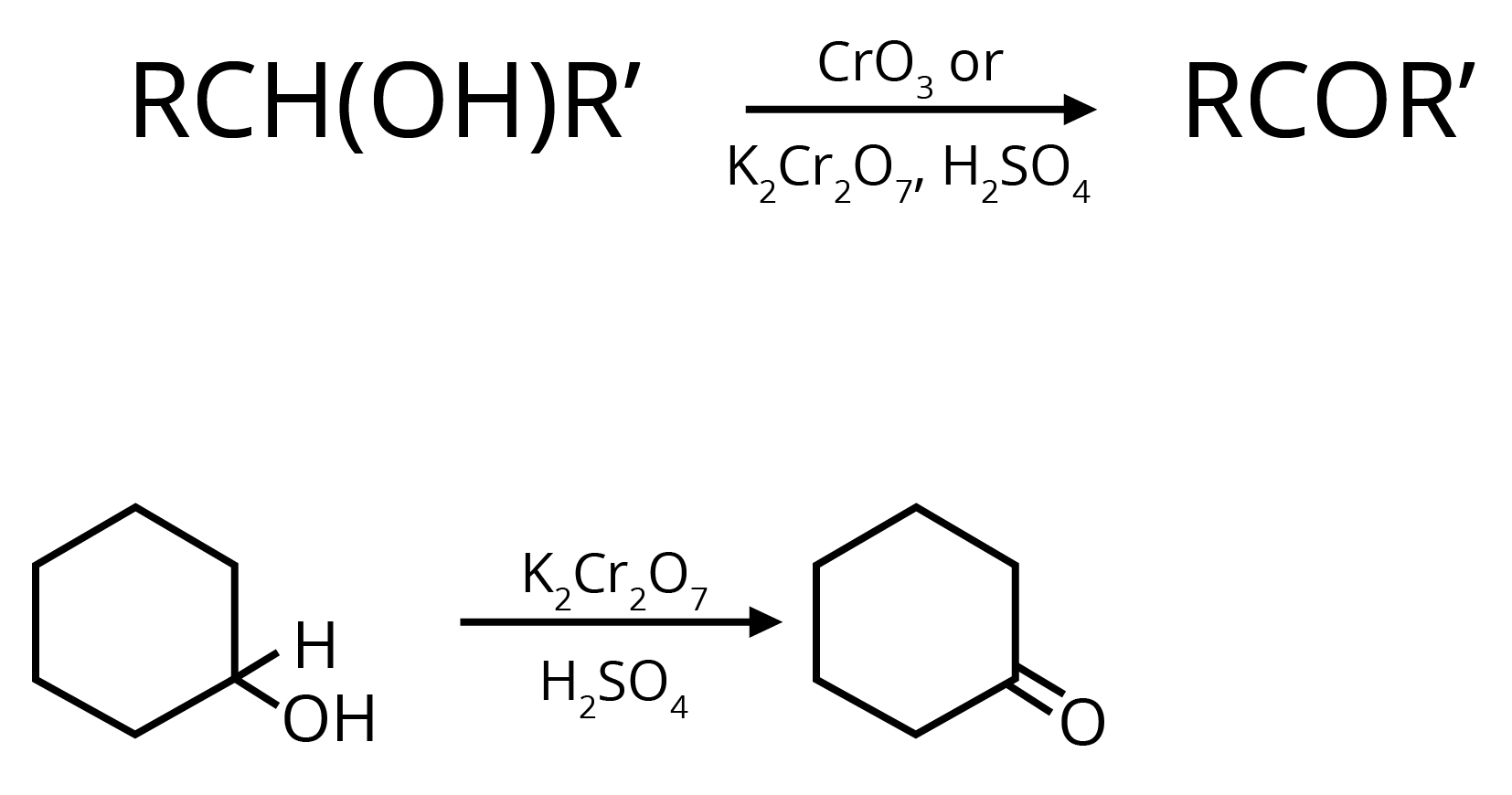
Methods of Preparation of Ketones
1. Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols
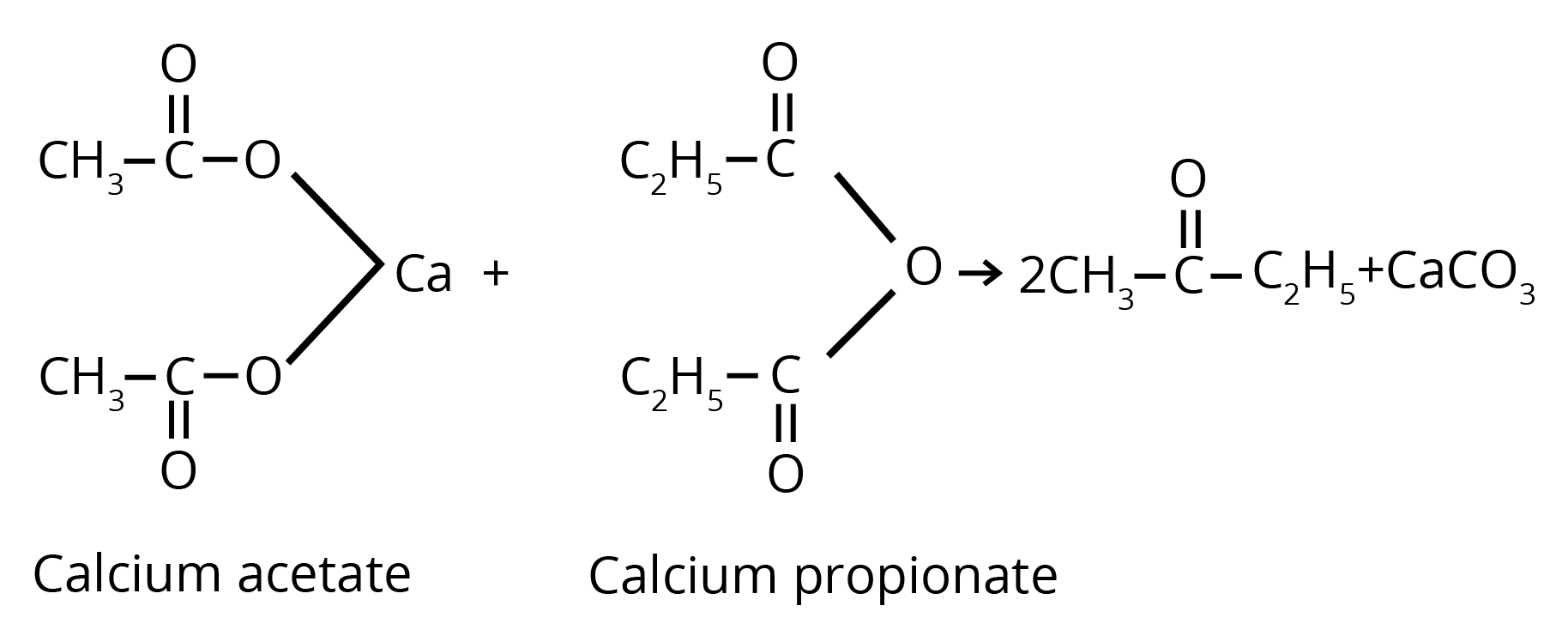
2. By Heating the Calcium Salt of any Monocarboxylic Acid other than Formic Acid
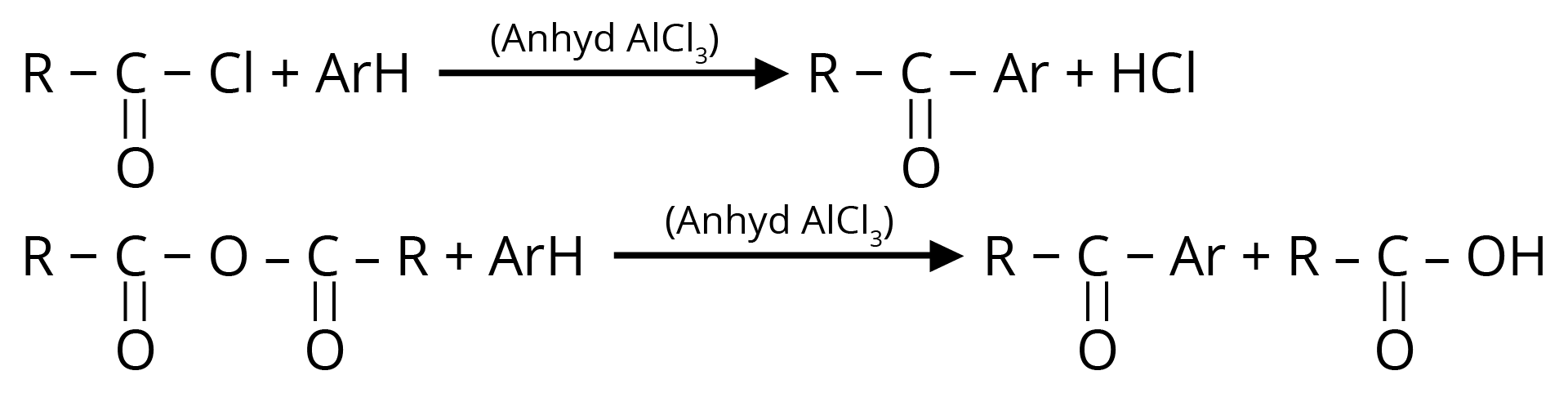
3. Friedel – Crafts Acylation
Used for the preparation of aliphatic aromatic ketones or aromatic ketones.
Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
1. By Oxidation of Primary Alcohol
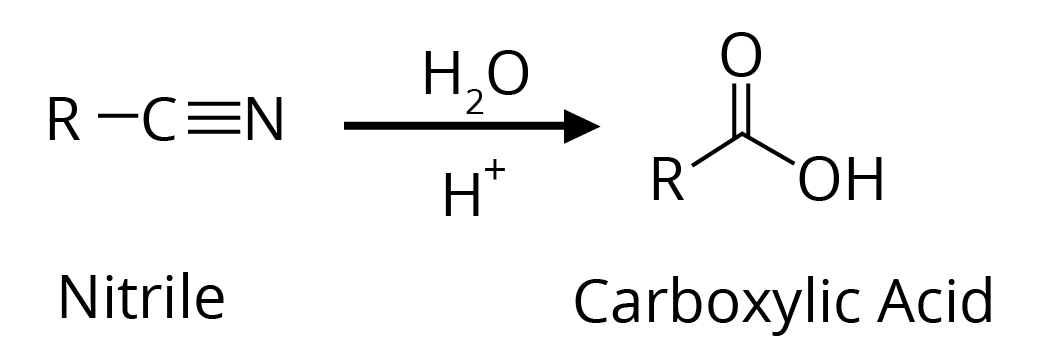
2. By hydrolysis of Cyanides
Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
These are the polar compounds due to the presence of a carbonyl group.
They have higher boiling points than non-polar compounds of comparable molecular weights.
They are soluble in water.
Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids have polar molecules that form hydrogen bonds.
The first four members are water miscible. The greater the acid, the less soluble it is. Benzoic acid, the most basic aromatic acid, has far too many carbon atoms to be soluble in water.
Chemical Properties of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
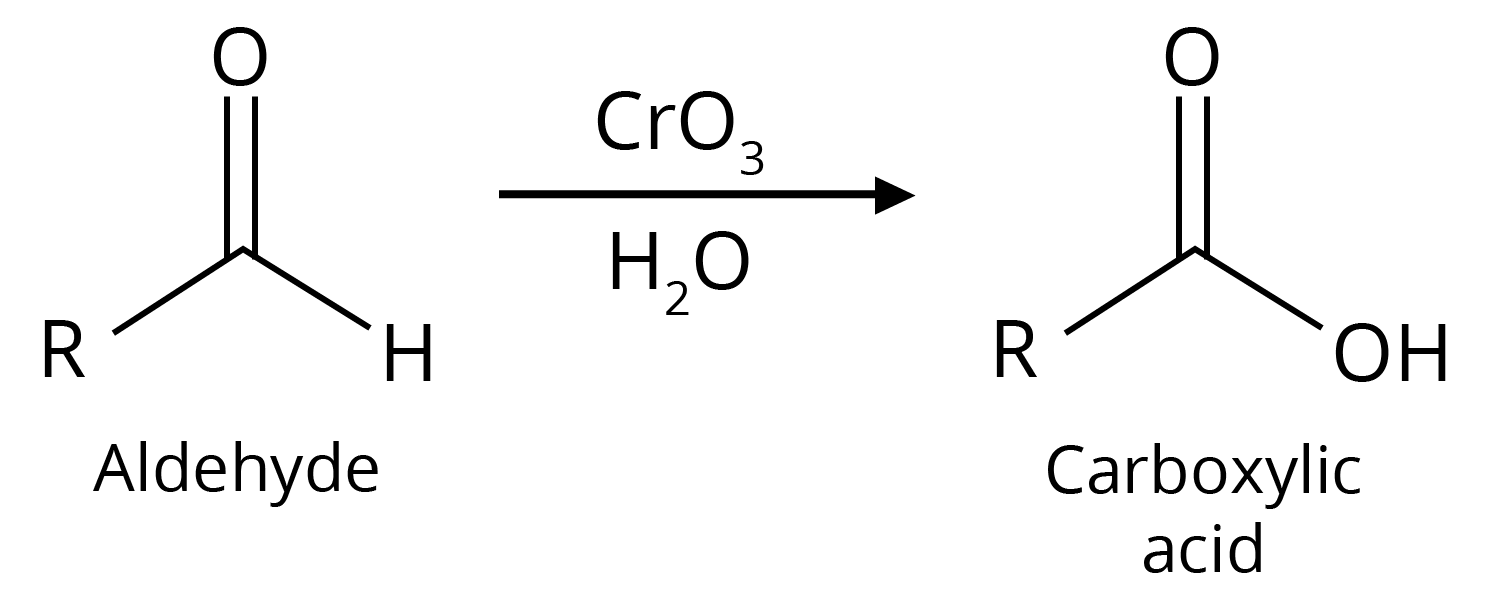
1. Oxidation
(a)
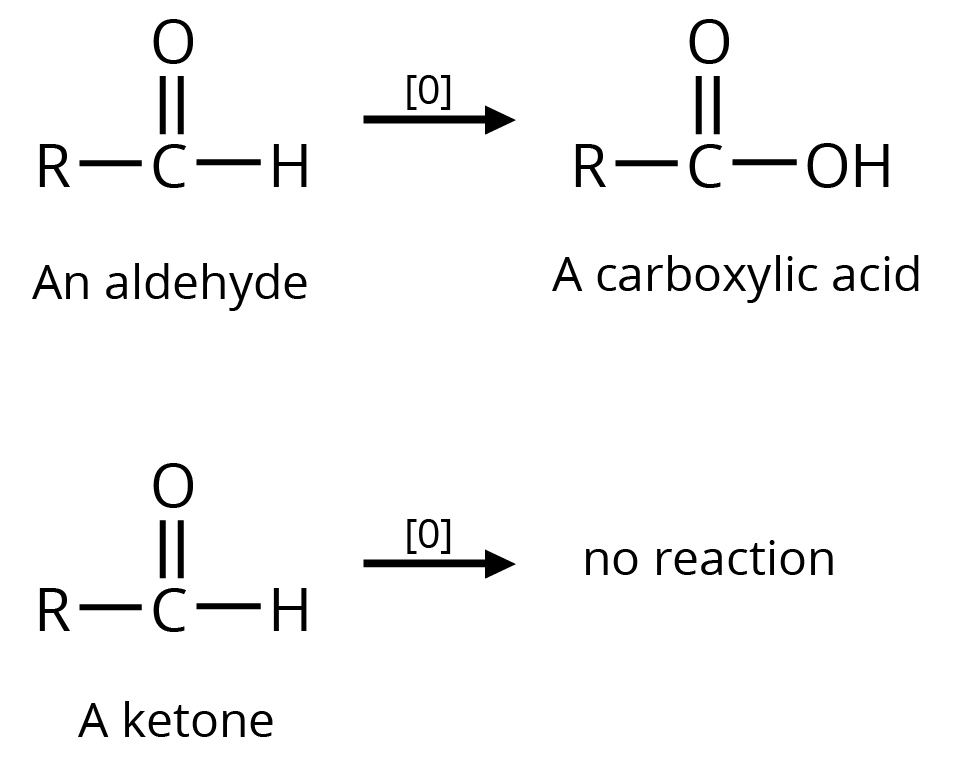
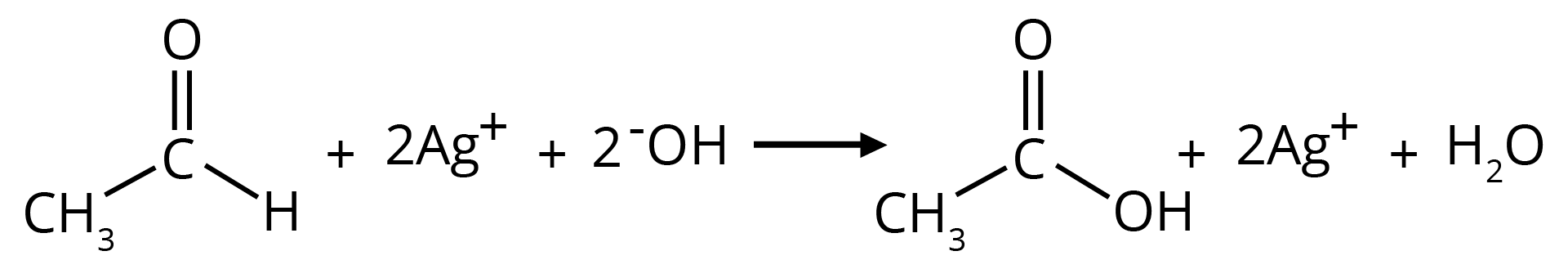
(b) Tollen's Reagent
A specific oxidant for RCHO is Ag(NH3)2+. Ketones do not give this reaction
(c) Strong Oxidants
Ketones resist mild oxidation, but with strong oxidants at a high temperature, they undergo cleavage of the C-C bond on either side of the carbonyl group.
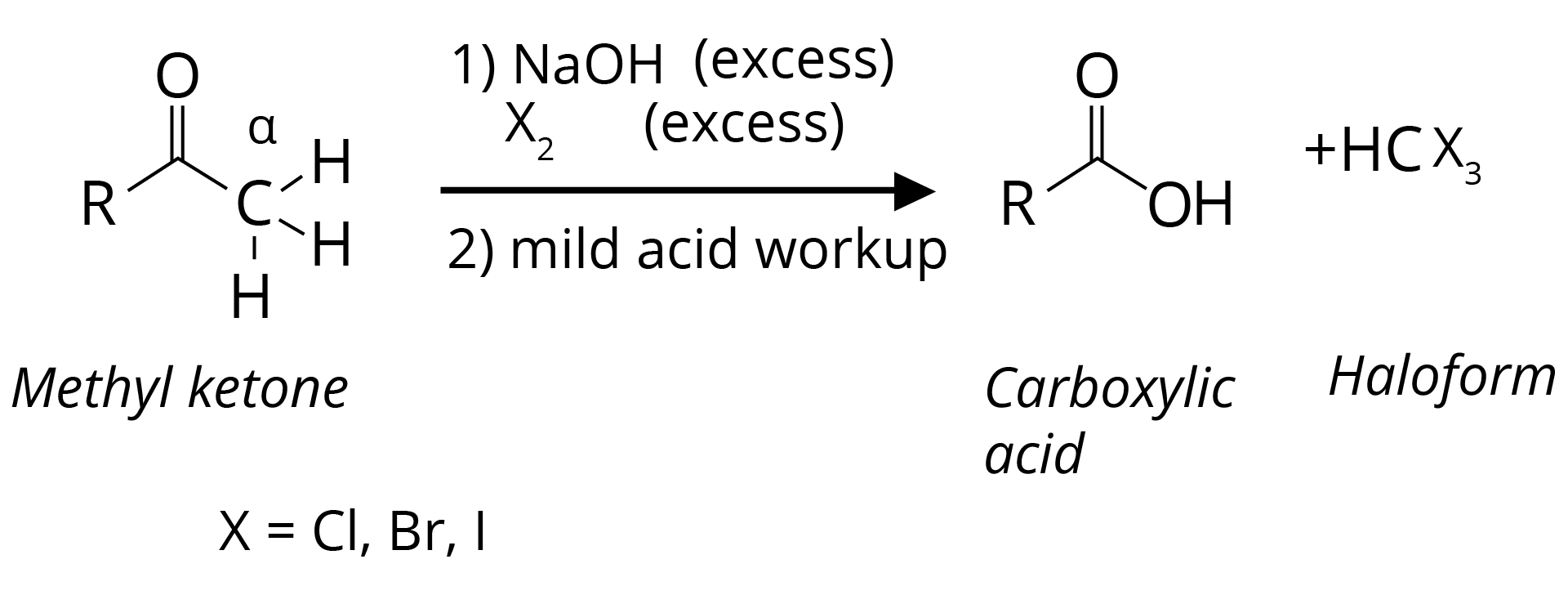
(d) Haloform Reaction is Shown by Methyl Ketones.
CH3COR are readily oxidized by NaOI (NaOH + I2) to iodoform, CHI3, and RCO2Na.
2. Reduction
(a) Reduction to Alcohols
Reduction to alcohols can be achieved either by hydrogenation in the presence of Pt or Pd or by LiAlH4/NaBH4.
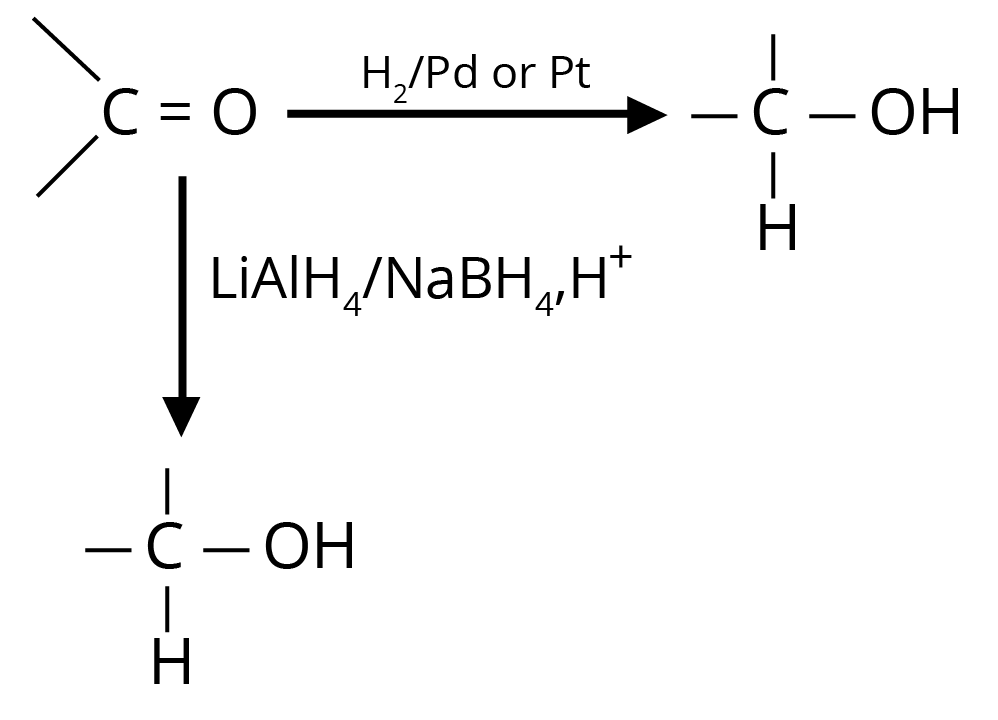
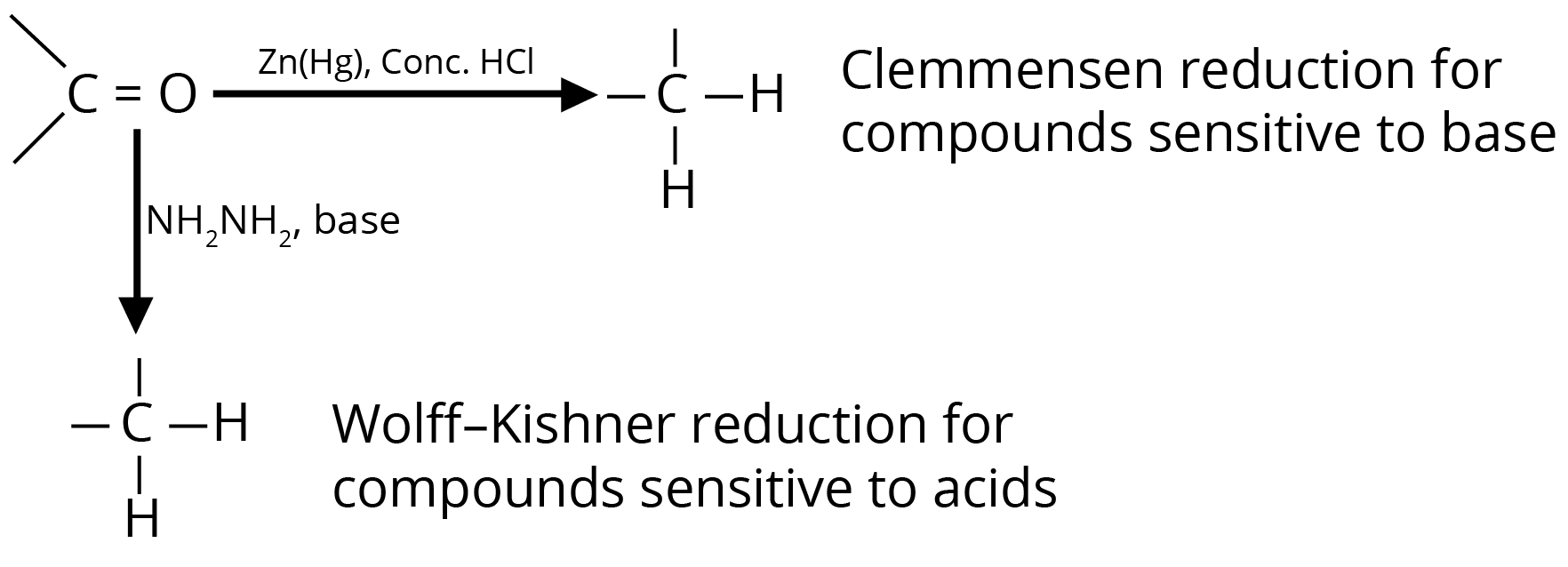
(b) Reduction to Hydrocarbons
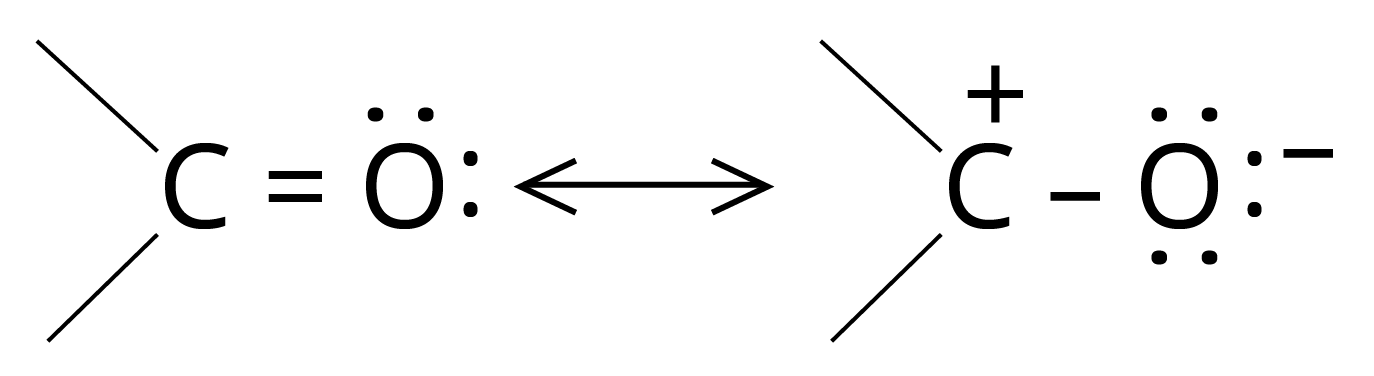
3. Addition Reactions of Nucleophiles
The carbon of the carbonyl group is electrophilic and thus initially attacked by a nucleophile.
(a) Addition of Grignard Reagent
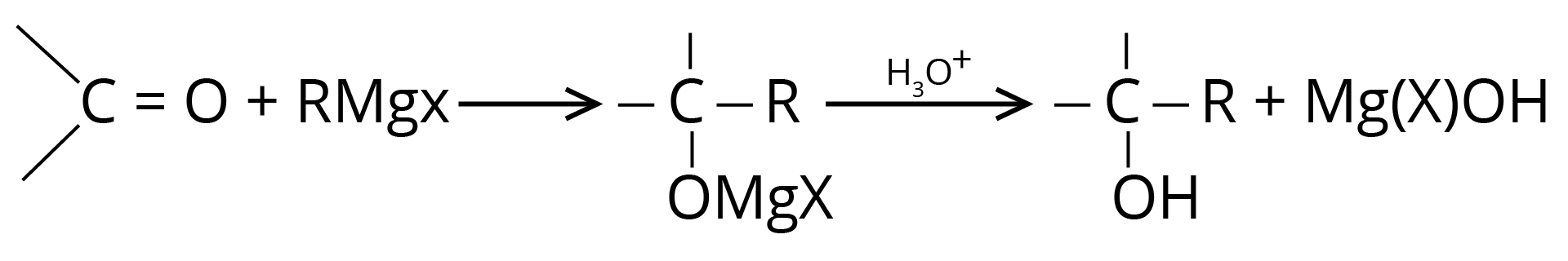
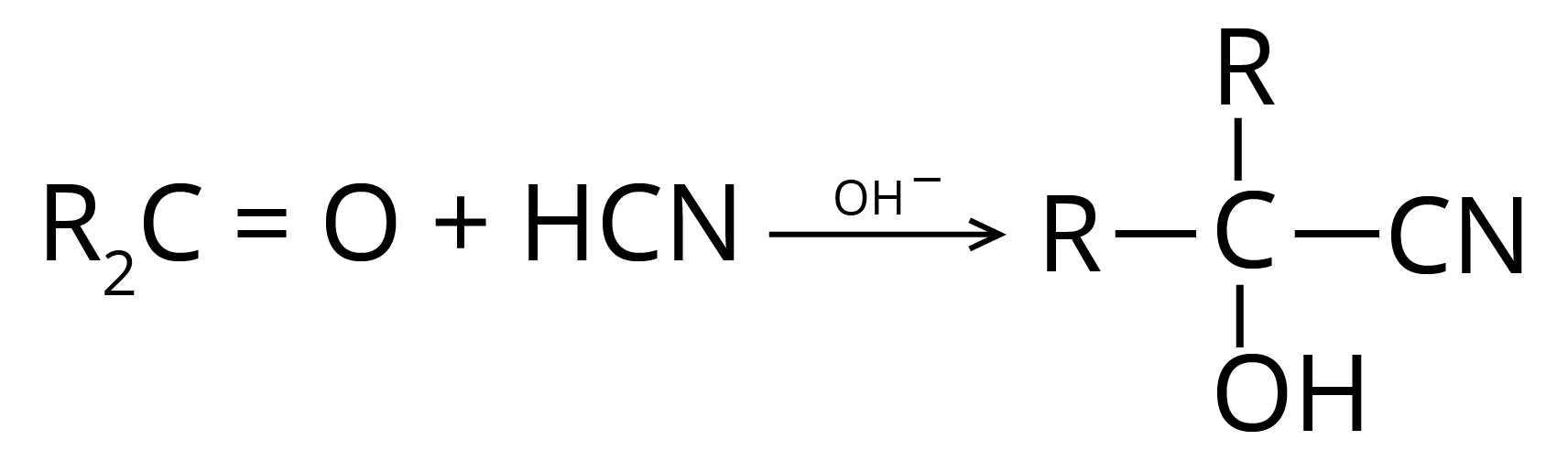
(b) Addition of Hydrogen Cyanide
(c) Addition of Sodium Bisulfite
Bisulfite compound formation is confined to aldehydes, methyl ketones and some cyclic ketones.
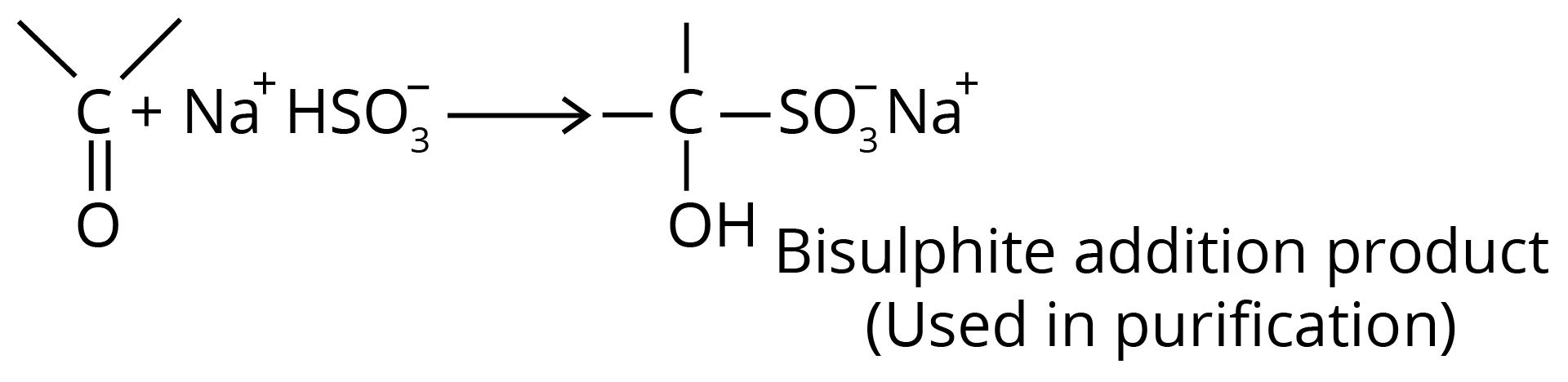
(d) Nucleophilic Addition of Derivatives of Ammonia
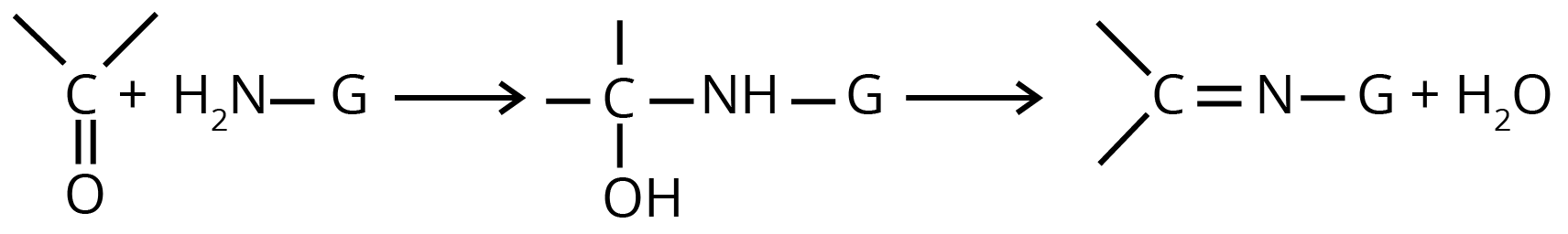
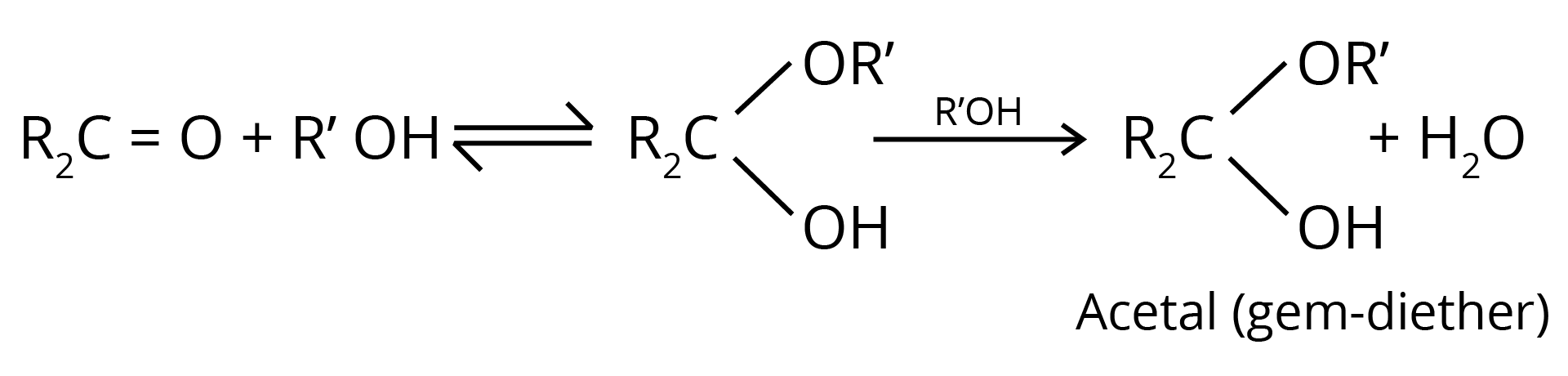
4. Addition of Alcohols
The carbonyl compounds react with alcohols, R'OH, to yield hemiacetals.
5. Cannizzaro Reaction
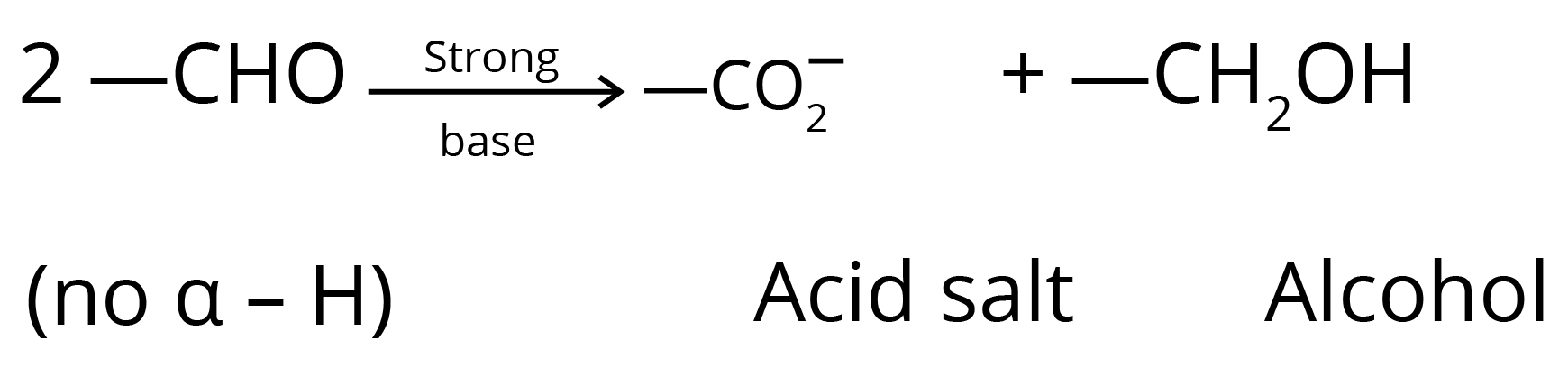
6. Aldol Condensation
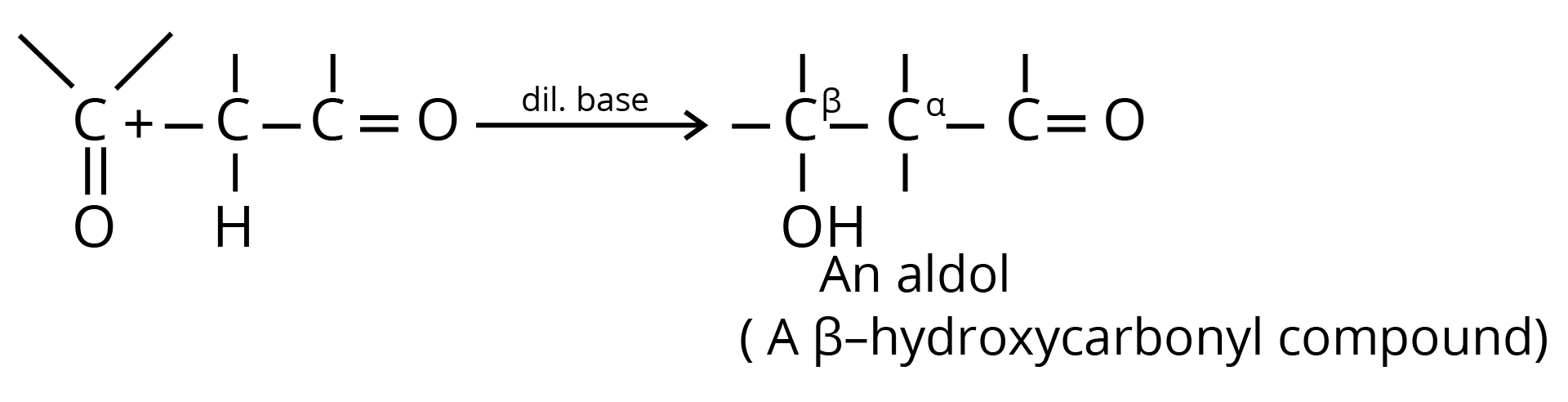
7. Perkin Condensation
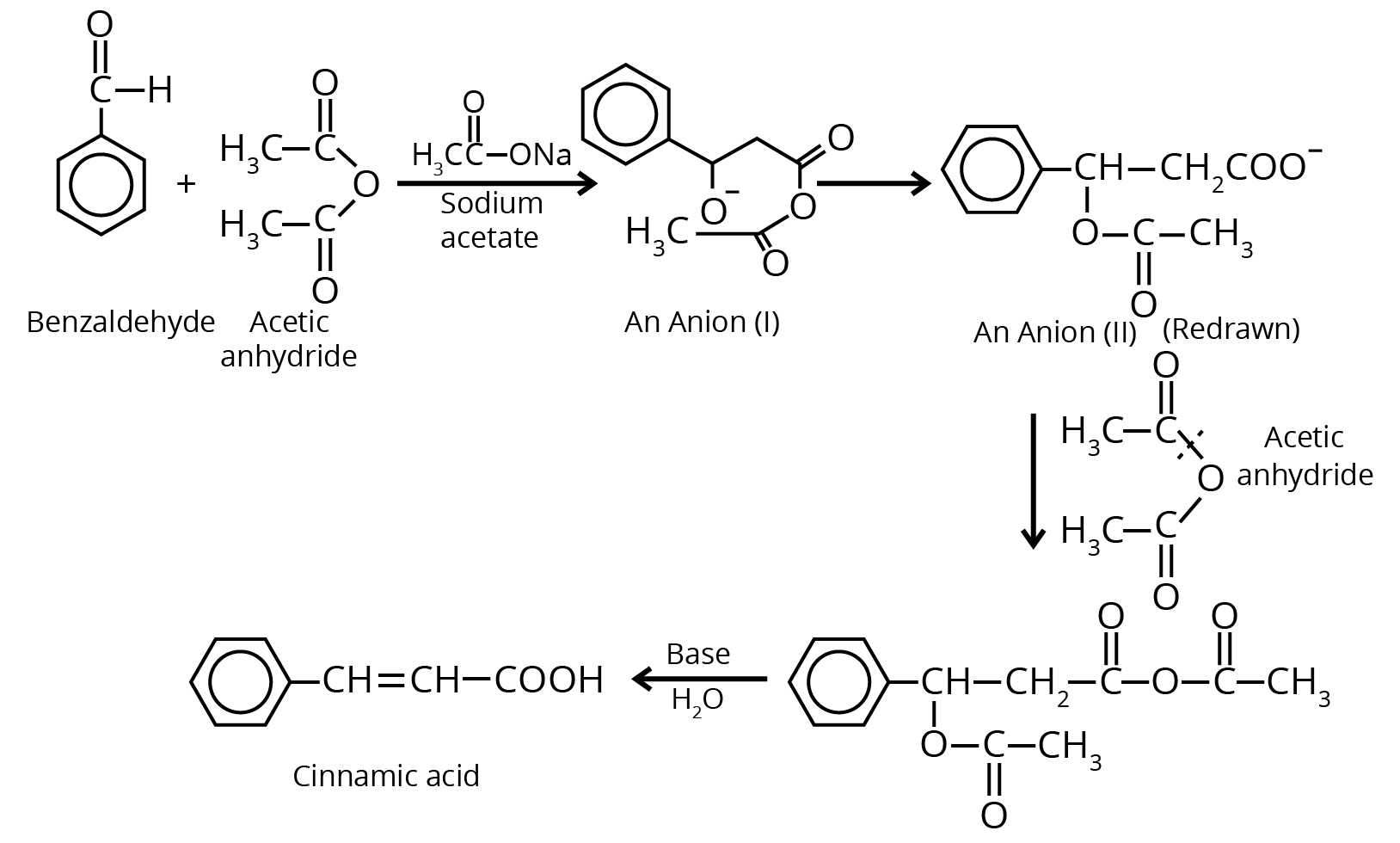
8. Beckmann Rearrangement
The acid-catalyzed conversion of ketoximes to N substituted amides is known as Beckmann rearrangement.
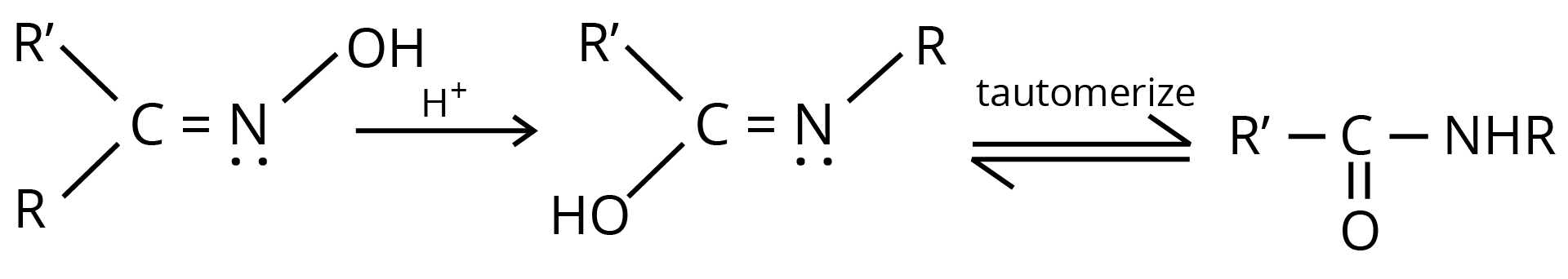
Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acid
1. The carboxylic acids react with metal to liberate hydrogen and are soluble in NaOH and NaHCO3 solutions.
2. Carboxylic acid reacts with halogenated compounds and forms acid halide.
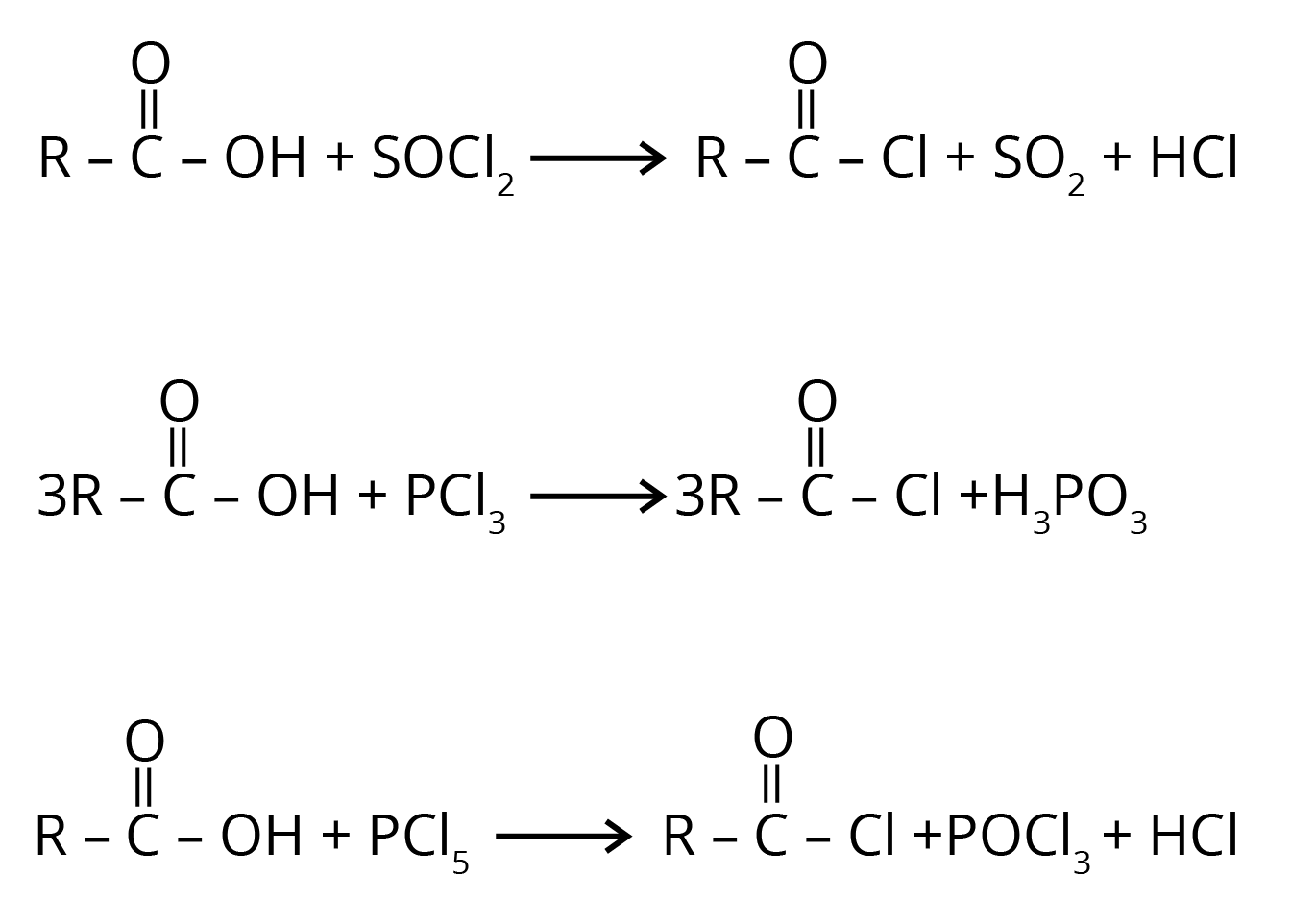
3. Carboxylic acid gets reduced to alcohol.
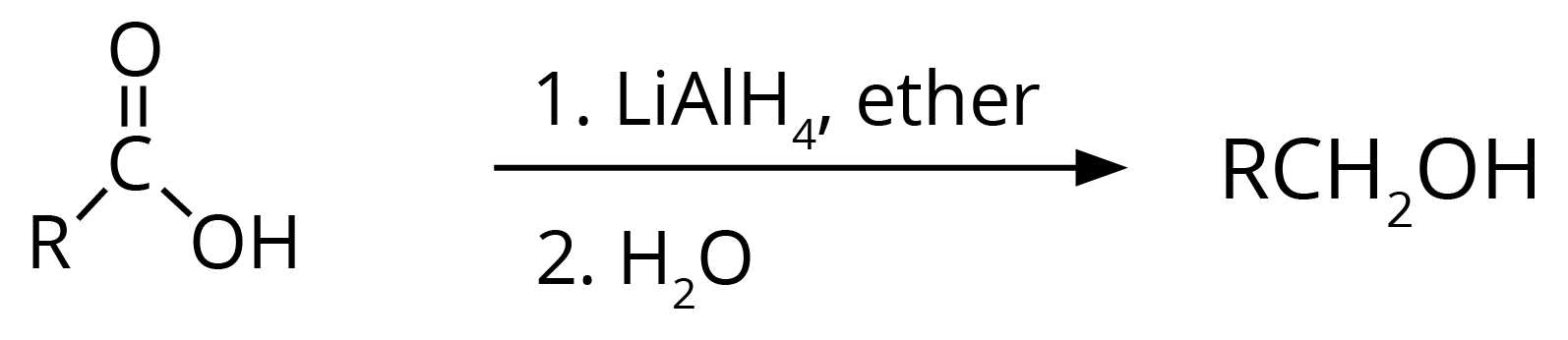
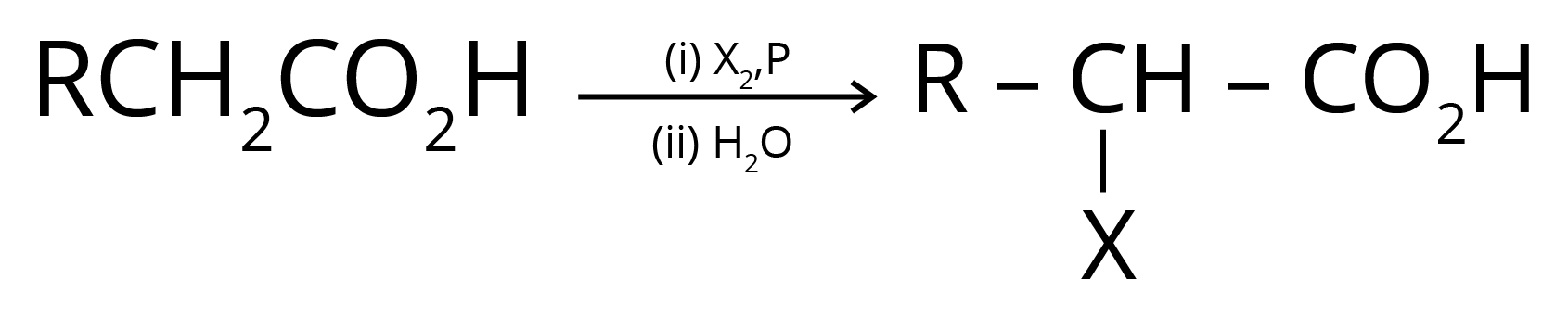
4. Hell Volhard Zelinsky Reaction- Aliphatic carboxylic acids react with Br2 or Cl2 in presence of phosphorus (or phosphorus halides) to give haloacids.
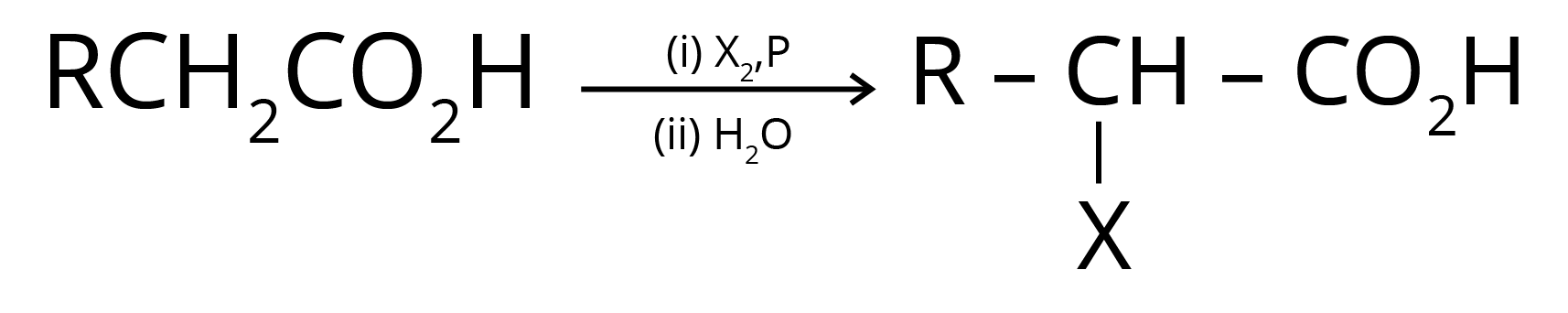
5. Schmidt Reaction- Carboxylic acids react with hydrazoic acid in presence of concentrated H2SO4 to give amine.
6. Benzoic acid is attacked by the usual electrophilic reagents Chlorine, Bromine, Nitric and sulphuric acids to give m-derivatives.
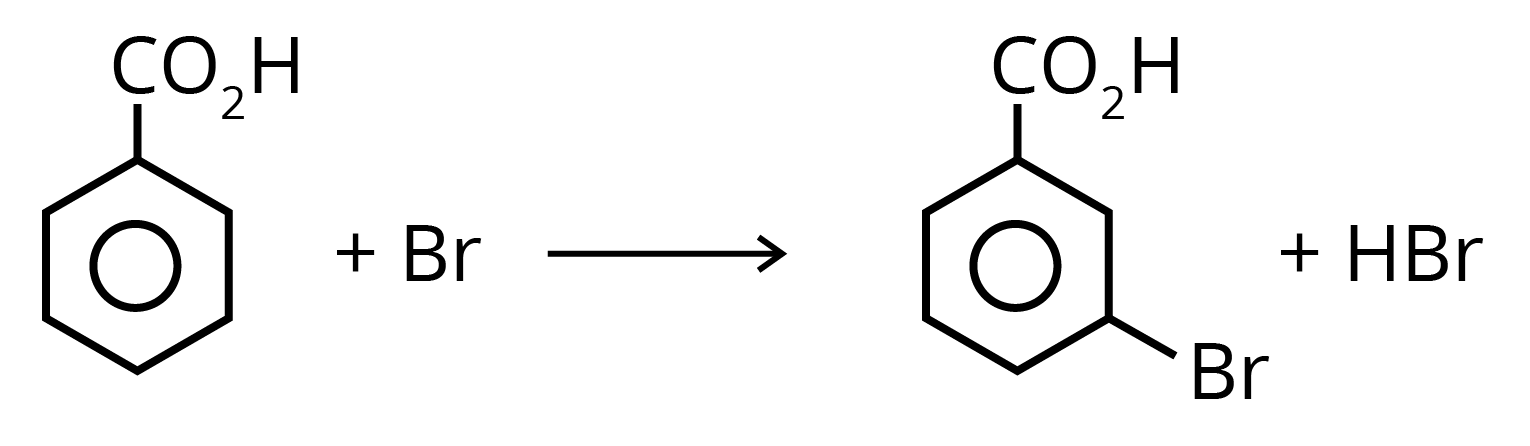
Solved Examples/Problems From the Chapter: Organic Compound Containing Oxygen
1. Names the reagent that is use in the transformation of Hexan-1-ol to hexanal:
Sol: The oxidation of Hexan-1-ol to hexanal takes place in the presence of a mild oxidizing agent. One of the most widely used mild oxidizing agents is PCC (Pyridinium chlorochromate). Its structural formula is C5H5NH+CrO3Cl-
Key Points: Mild oxidizing agent is used for the conversion of alcohol to aldehyde or ketone While strong oxidizing agent is used to convert alcohol to carboxylic acid.
2. Write structures of the products of the given reaction.
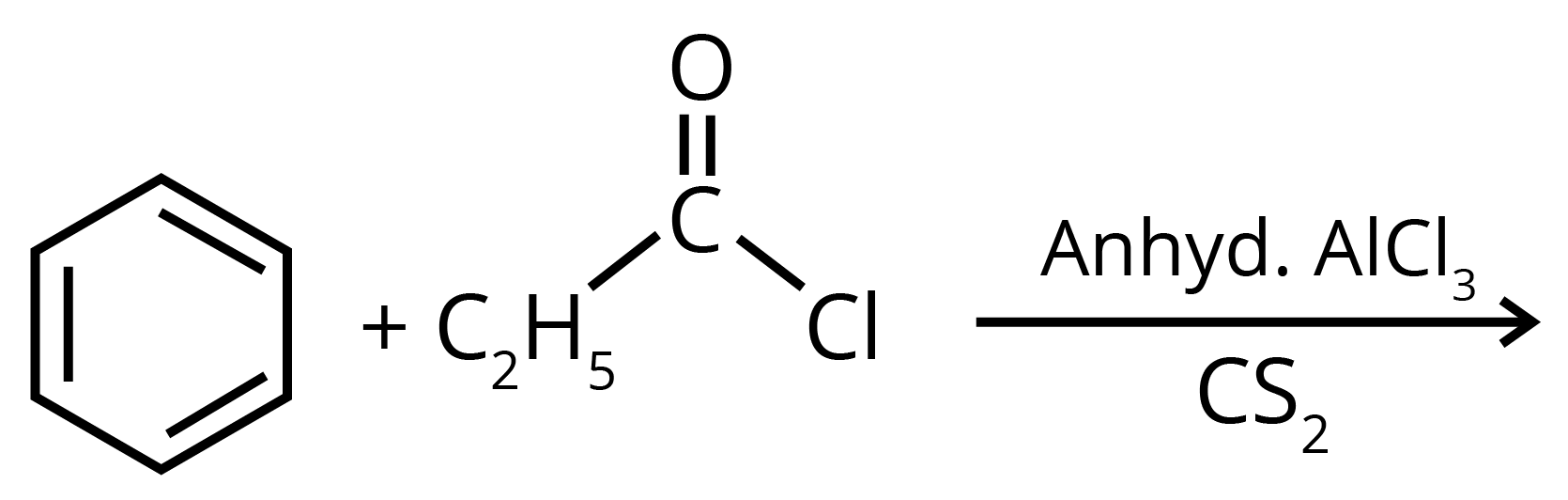
Sol: The product formed in the above reaction will be propiophenone. The structure of this compound is given below. This reaction takes place in the presence of lewis acid and non polar medium.
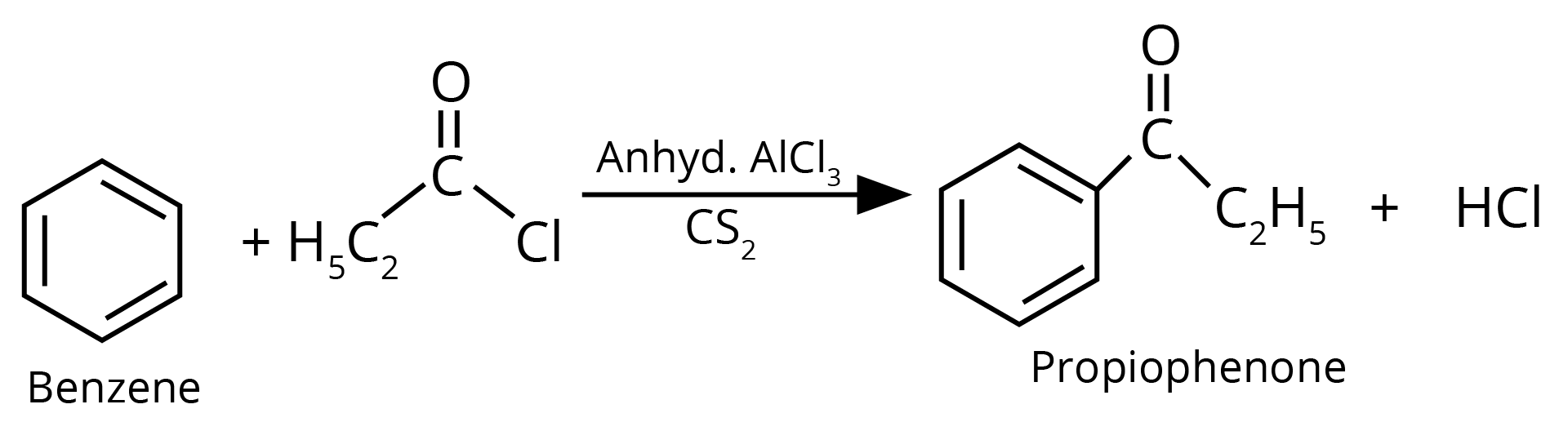
Key Points: The reaction given above is an acylation reaction.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Question from the Chapter: Aldehyde, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acid
1. An alkene on ozonolysis gives methanal as one of the products. Its structure is :
Options:
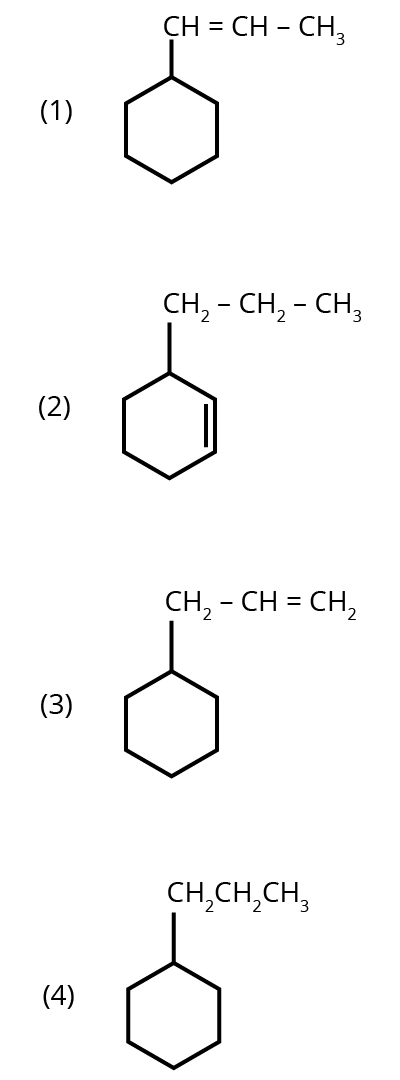
Ans: The correct answer is option 3.
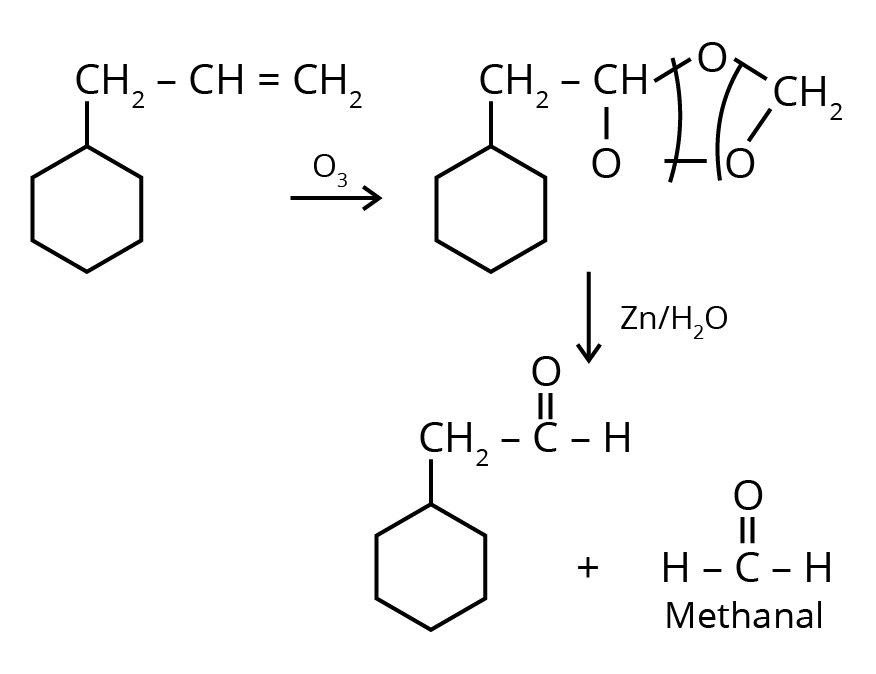
Trick: The given reaction is an ozonolysis reaction. The trick to solve this question in less time is just break the double bond and attach oxygen with the double bonded carbon molecules.
2. Identify compound X in the following sequence of reactions :
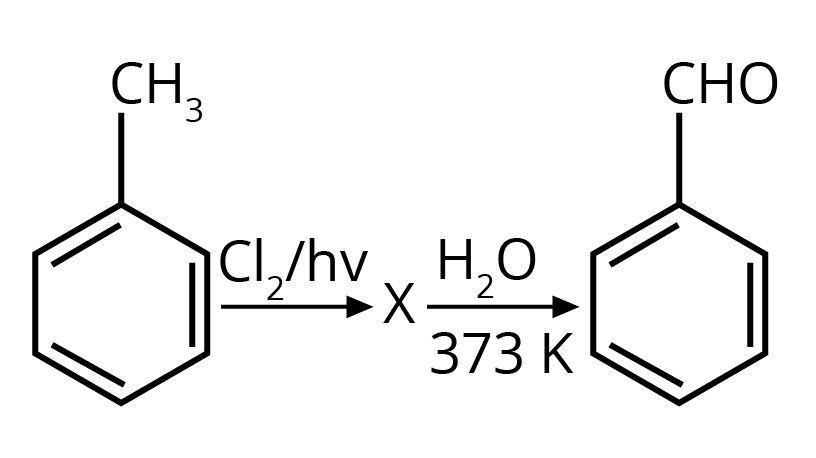
Options:
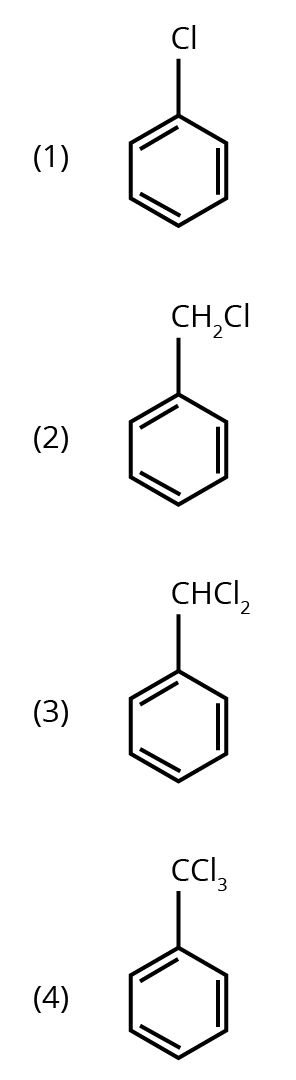
Ans: The correct answer is option 3.
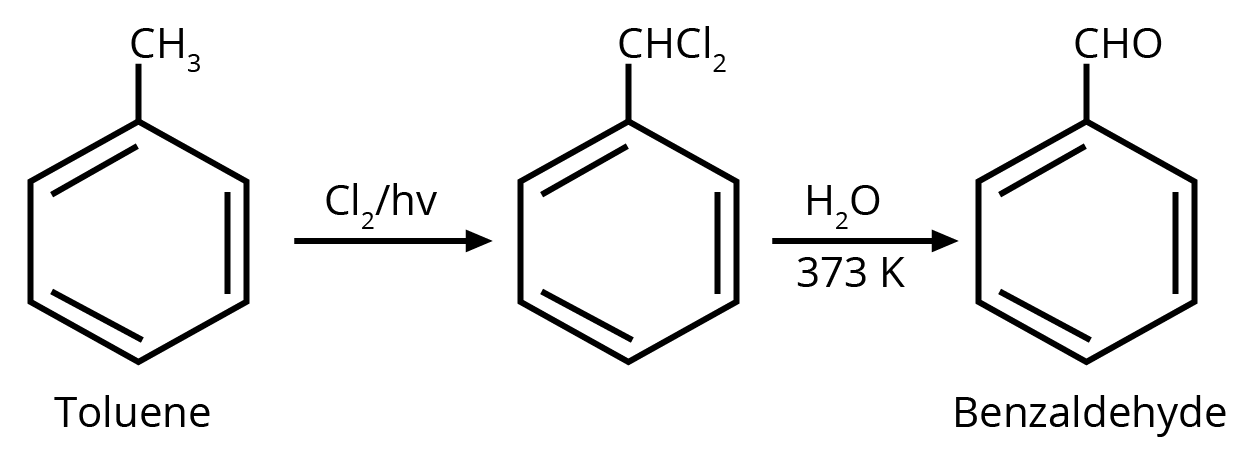
Trick: Two hydroxyl groups on the same carbon are unstable and lead to dehydration and form an aldehyde or ketone (formation of double bond oxygen).
3. What is the IUPAC name of the organic compound formed in the following chemical reaction?
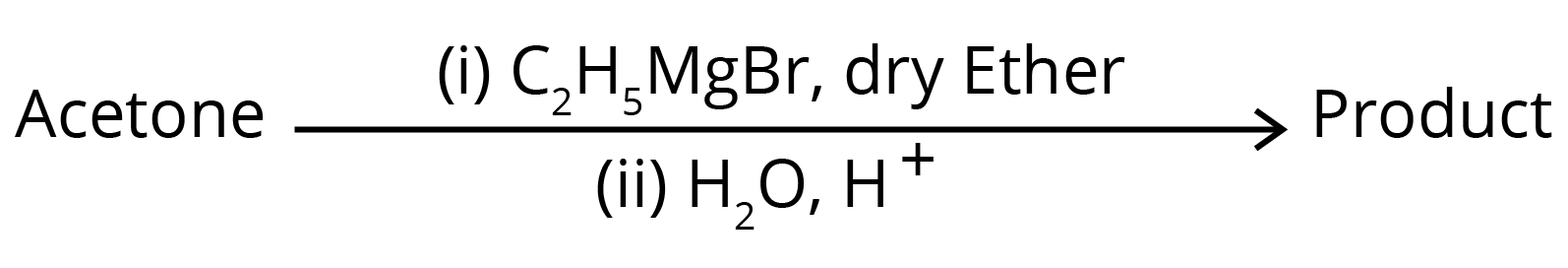
(1) 2-methyl propan-2-ol
(2) pentan-2-ol
(3) pentan-3-ol
(4) 2-methyl butan-2-ol
Ans: The correct answer is option 4.
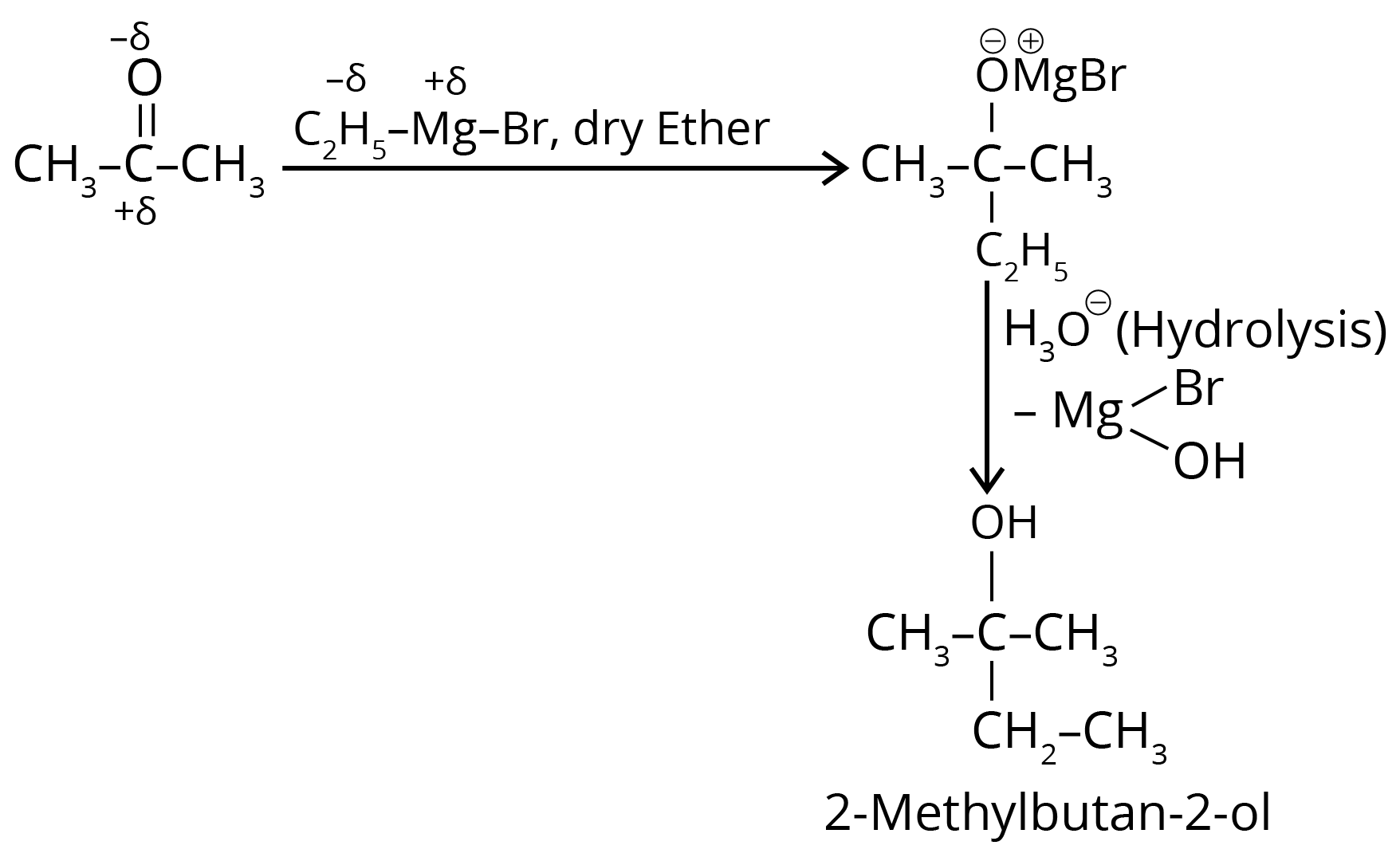
Trick: The given reaction is a grignard reaction.
Practice Questions
1. Give names of the reagents that is used to bring the given transformations:
Cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone
(Ans: PCC.)
2. Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more reactive or less reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions than propanal? Explain your answer.
(Ans: Less reactive due to resonance)
Conclusion:
In this article, we have provided important information regarding the chapter aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acid such as important concepts, reactions, etc. Students should work on more solved examples and previous year question papers for securing good grades in the NEET exams.
NEET Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Chapter

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Chapter
1. In the NEET examination, what is the contribution of the aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acids chapter?
Approximately 2-3 questions from this chapter appear on the exam, covering roughly 12 marks and accounting for 3-4 percent of the total marks.
2. What are the main points to remember while tackling problems involving aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acids?
Students should practice writing the mechanism of the reaction for solving the questions in the NEET exam. By practicing the mechanism of the reaction, the concept behind the product formation will become clear thus giving answers will take less time in exam.
3. What are the important topics that need to be covered from this chapter to score good marks in the NEET exam?
Canizaro reaction, aldol condensation reaction, ozonolysis of alkenes and reaction with grignard reagent are the main topics from this chapter that comes in NEET exam.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


