




Understand What Is RO and Why is it Important
RO stands for Reverse Osmosis, a widely used water purification process that removes contaminants, dissolved solids, and impurities from water.
This technology is essential for providing clean and safe drinking water by filtering out harmful chemicals, bacteria, and salts. The article covers how RO works, its benefits, and its applications in daily life.
What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is an advanced water purification process that removes contaminants using high-pressure filtration.
Uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter impurities.
Eliminates bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and dissolved salts.
Provides safe and purified drinking water.
Used in homes, industries, and large-scale water treatment plants.
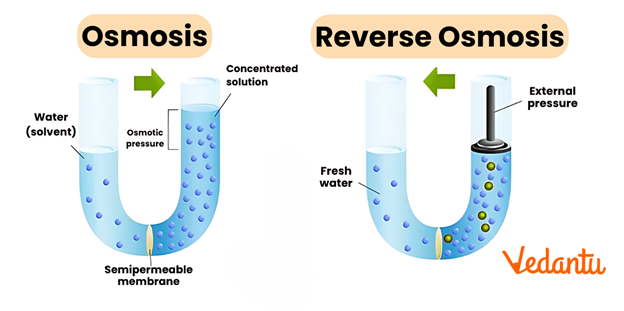
Osmosis Vs Reverse Osmosis
Here's a concise tabular comparison of Osmosis vs. Reverse Osmosis (RO):
How Does RO Work?
The RO process involves multiple filtration stages to purify water effectively.
Step-by-Step Process:
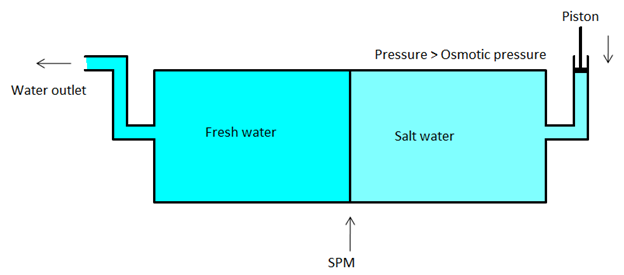
Reverse osmosis is a process which is exactly the reverse to the osmosis. We know that in osmosis, the solvent flows from the less concentrated side to the side which has a higher concentration of solutes.
In reverse osmosis, we reverse the flow of solvent and this is made possible by applying external pressure on the concentrated solution.
We need to give such a pressure which is larger than the Osmotic pressure to the side which has a higher concentration of solutes.
The pure solvent will flow through the semipermeable membrane. We can use porous membranes such as a film of cellulose acetate placed over certain suitable supports.
Cellulose acetate can flow water through it but it is impermeable to the ions and other impurities in the water. The diagram of reverse osmosis is given below.
Benefits of RO Water Purification
RO purification offers multiple advantages, making it one of the most reliable water filtration methods.
Eliminates up to 99% of dissolved solids, bacteria, and toxins.
Reduces chlorine, heavy metals, and foul odours.
Protects against bacteria, viruses, and chemical pollutants.
Eco-Friendly Alternative to Bottled Water: Reduces plastic waste and promotes sustainable water consumption.
Applications of Reverse Osmosis Technology
RO is widely used in various sectors due to its efficient purification capabilities.
Ensures safe drinking water at home.
Used in manufacturing and chemical industries.
Converts seawater into fresh drinking water.
Ensures ultra-pure water for laboratory and medical purposes.
Used in bottled water production and food processing.
RO vs. Other Water Purification Methods
RO technology is often compared with other filtration methods like UV and UF purification.
Limitations of RO Purification
While RO technology is highly effective, it also has certain drawbacks.
RO systems reject some water as waste during filtration.
Along with contaminants, beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium are also removed.
RO purifiers need a power supply to function.
How to Maintain an RO Water Purifier?
Regular maintenance ensures the efficiency and longevity of an RO system.
Replace Filters Regularly: Change sediment, carbon, and RO membranes every 6-12 months.
Clean Storage Tanks: Prevent bacterial growth by cleaning the storage tank periodically.
Check Water Pressure: Ensure adequate water pressure for efficient filtration.
Service the System Annually: Get professional servicing to maintain optimal performance.
Conclusion
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a highly effective water purification technology that ensures safe and clean drinking water. It is used extensively in homes, industries, and large-scale filtration plants to remove contaminants, bacteria, and harmful chemicals. Proper maintenance and regular servicing can help maximise the benefits of an RO purifier.
FAQs on RO Full Form - Reverse Osmosis
1. What does RO stand for?
RO stands for Reverse Osmosis, a water purification process that removes contaminants through a semi-permeable membrane.
2. How does an RO purifier work?
An RO purifier filters water through multiple stages, including sediment filtration, carbon filtration, reverse osmosis, and post-filtration.
3. Is RO water safe to drink?
Yes, RO water is safe and free from harmful impurities, but it may require remineralisation to restore essential minerals.
4. What are the disadvantages of RO purification?
RO filtration wastes some water, removes beneficial minerals, and requires electricity to function.
5. Can RO remove bacteria and viruses?
Yes, RO can eliminate bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and dissolved salts, ensuring purified water.
6. Is RO better than UV filtration?
RO is better for removing dissolved solids and heavy metals, while UV is effective against bacteria and viruses.
7. How often should RO filters be replaced?
RO filters should be replaced every 6-12 months depending on water quality and usage.
8. Does RO remove fluoride from water?
Yes, RO removes fluoride along with other dissolved solids and contaminants.
9. Is RO required for soft water areas?
If water quality is good, an RO system may not be necessary, but it is beneficial for removing chemicals and heavy metals.
10. Can RO purifiers be used for borewell water?
Yes, RO purifiers are effective for borewell water, removing high TDS, hardness, and microbial contaminants.























