Mechanical Properties of Solids for NEET
The chapter Mechanical properties of solids is one of the easiest chapters in physics as far as the NEET exam is concerned. As the name of the chapter implies, we deal with the properties of solids and their behaviour under applied stress and some concept-oriented problems from this chapter.
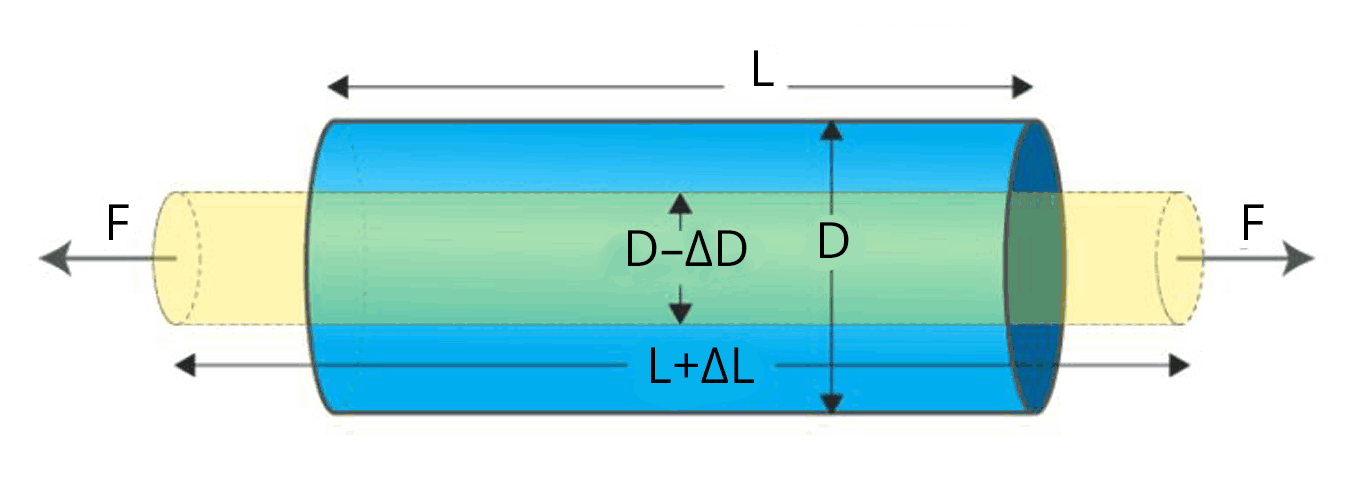
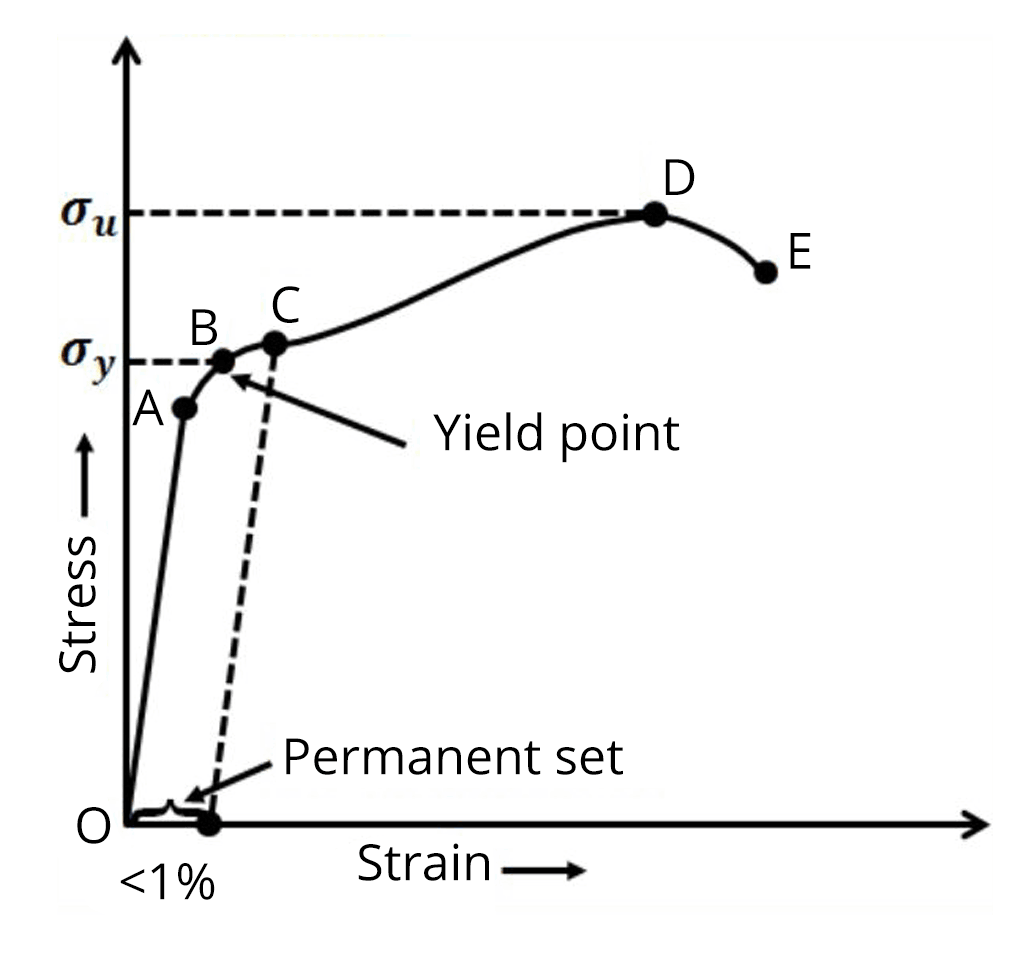
In the chapter Mechanical properties of solids, first, we will learn about different types of stress like longitudinal stress and bulk stress along with different types of strain. The stress-strain curve of a wire under longitudinal stress is studied in detail. Hooke's law and types of modulus of elasticity are very important in this chapter. Problems related to young’s modulus, bulk modulus and rigidity modulus are discussed in this chapter.
Let us see the important concepts, mechanical properties of solids formulas in this chapter Mechanical properties of solids needed for the NEET exam with solved mechanical properties of solids numerical examples.
Mechanical Properties of Solids- Important Topics
Elastic behaviour of solids
Longitudinal stress and Longitudinal strain
Volume stress and volume strain
Volume stress and volume strain
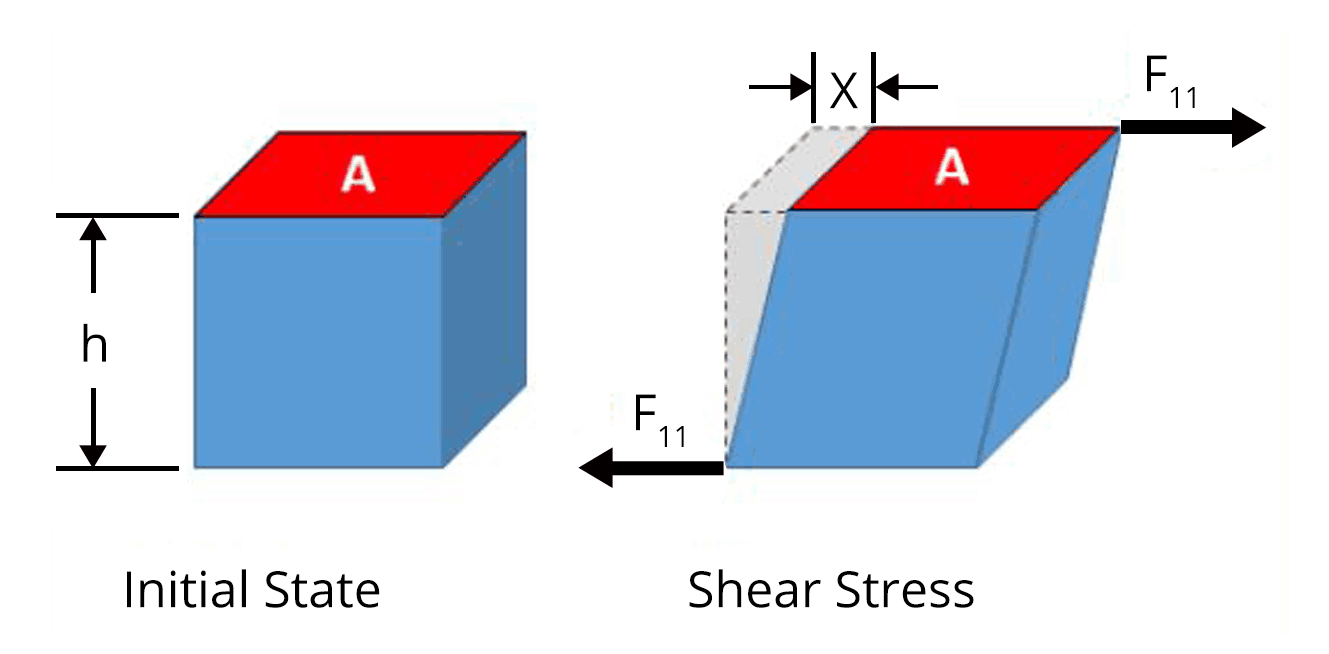
Shear or tangential stress or shearing strain
Young’s modulus
Bulk modulus
Modulus of rigidity
Work done in stretching a strain
Important Concepts of Mechanical Properties of Solids
List of Important Formulae
Solved Examples
A long elastic spring is stretched by 2 cm and its potential energy is U. If the spring is stretched by 10 cm, then the P.E will be,
a. U
b. 98U/5
c. 3U
d. 25U
Ans:
Given, Potential energy of spring stretched by 2 cm = U
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}K(2~cm)^2$....(1)
The potential energy of the spring stretched by 10 cm can be calculated using the formula given by,
$U'=\dfrac{1}{2}K(10~cm)^2$....(2)
Divide equation (2) by equation (1) to calculate the potential energy of the spring stretched by 10 cm
$\dfrac{U'}{U}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}K(10~cm)^2}{\dfrac{1}{2}K(2~cm)^2}$
$U'=25U$
Therefore, the correct answer is option d).
Key point: The potential energy of the spring depends on the spring constant and the elongation.
A cube of aluminium of 0.1 m is subjected to a shearing force of 100 N? The top face of the cube is displaced through 0.02 cm with respect to the bottom face. The shearing strain will be
Ans: Given,
The height of the cube, h = 0.1 m = 10 cm
The displacement of the top face due to the tangential force of 100 N, x = 0.02 cm
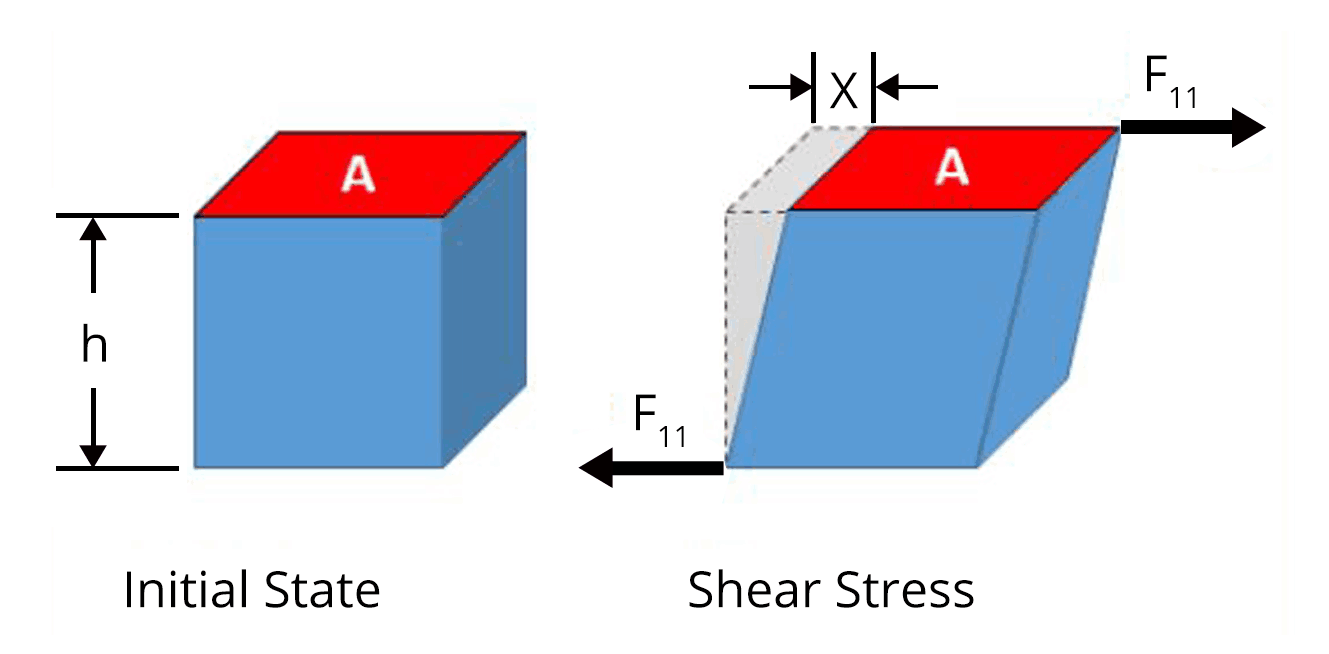
The shearing strain can be calculated using the formula,
$\text{Shearing strain}=\dfrac{\text{x}}{h}$
$\text{Shearing strain}=\dfrac{\text{0.02 cm}}{10 \text{ cm}}$
$\text{Shearing strain}=0.002$
Key point: Shearing strain is equal to the ratio of displacement of the top face to the height of the cube.
Previous Year Questions from NEET paper
When a block of mass M is suspended by a long wire of length L, the length of the wire becomes (L+l). The elastic potential energy stored in the extended wire is (NEET 2019)
a. Mgl
b. 2Mgl
c. Mgl/2
d. Mgl/4
Ans:
The force acting on the wire is related to the extension of the wire
$F=Kl$
$K=\dfrac{F}{l}$
$K=\dfrac{Mg}{l}$....(1)
The energy stored in the wire is given by,
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}Kl^2$....(2)
Put equation (1) in equation (2)
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{Mg}{l}l^2$
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}Mgl$
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Key point: When a wire is suspended by a mass, then weight acting on the mass acts as the deforming force.
The bulk modulus of a spherical object is ‘B’. If it is subjected to uniform pressure ‘p’, the fractional decrease in radius will be (NEET 2017)
a. B/3p
b. 3p/B
c. p/3B
d. p/B
Ans:
The fraction volume of a spherical object having radius r is given by,
$V=\dfrac{4\pi r^3}{3}$
$\dfrac{\Delta V}{V}=3\dfrac{\Delta r}{r}$...(1)
The formula to calculate the bulk modulus is given by,
$B=\dfrac{p}{\Delta V/V}$
${\Delta V/V}=\dfrac{p}{B}$...(2)
Put equation(1) in equation (2) to calculate the fractional decrease in radius
${3\dfrac{\Delta r}{r}}=\dfrac{p}{B}$
${\dfrac{\Delta r}{r}}=\dfrac{p}{3B}$
Key point: Fractional decrease in radius can be obtained from the formula for the volume of the sphere.
Practice Questions
1. If the volume of the wire remains constant when subjected to tensile stress, then the value of Poisson's ratio of the material of the wire is,
(Ans: 0.5 )
2. What increase in pressure is required to decrease the volume of 200 litres of water by 0.004 per cent? Given bulk modulus of water is 2100 MPa
(Ans: 84 KPa)
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed important topics, and important formulas in the mechanical properties of solids chapter from the NEET point of view. Students must make sure that they do not miss any of the above important topics to obtain a good score on the NEET exam.
FAQs on NEET Important Chapter- Mechanical Properties of Solids
1. How many questions are asked about the Mechanical properties of solids in NEET?
Only 1 question from this chapter is asked for NEET. It corresponds to around 4 marks in the NEET exam. Mechanical properties of solid solutions of previous year NEET questions are available in Vedantu.
2. Is the Mechanical properties of solids a tough chapter for the NEET exam?
No, mechanical properties of solids are any chapter as far as the NEET exam is concerned. The quantity of the chapter is small and the level of questions asked is moderate. So, students must definitely not miss this chapter while preparing for the NEET exam. Students must make short notes of mechanical properties of solids chapter after studying the chapter for later reference.
3. What should be the strategy in preparing for the NEET exam?
The strategy the students should follow while preparing for the NEET exam is simple. Understand the concepts clearly and do all the problems given in the NCERT textbooks and other study materials. Then, move to solve the previous year's questions for the last 20 years' NEET exam.