




Understanding the Pharynx- Structure, Functions, and Importance of the Throat
The pharynx is a critical structure in the human body that connects the mouth, nasal cavity, and esophagus, playing a pivotal role in both the respiratory and digestive systems. For NEET aspirants, understanding the anatomy and function of the pharynx is essential for excelling in Biology. Divided into three regions – the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx – the pharynx facilitates the passage of air to the lungs and food to the stomach. It also plays an important role in voice production and swallowing reflexes. In this detailed guide, we will explore the structure, function, and significance of the pharynx, helping you strengthen your NEET Biology preparation with clear, concise information.
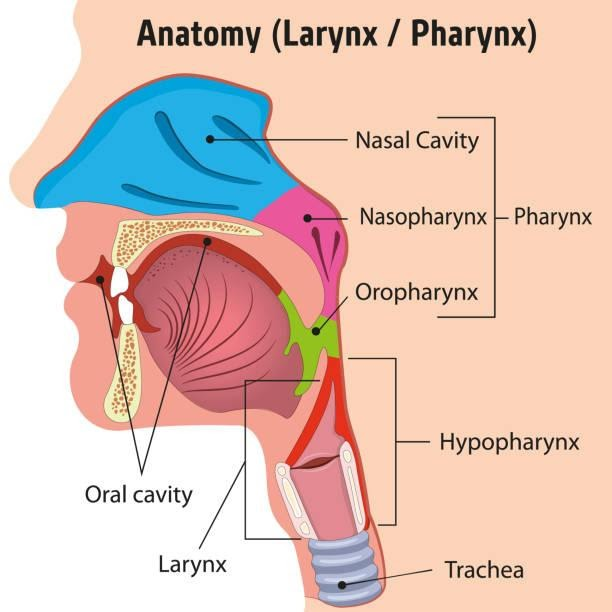
Pharynx Location
The pharynx is located behind the oral and nasal cavities, serving as a part of the throat and acting as a shared passage for both the digestive and respiratory systems. It opens into the oesophagus in the digestive system and the larynx in the respiratory system.
The pharynx is also found in certain invertebrates, with variations in shape and size across different species. In some cases, it may be thick and muscular or have unique structural adaptations such as rotation or outward expansion.
Pharynx Structure and Parts
The pharynx can be divided into three primary sections based on its location-
Nasopharynx- Positioned posterior to the nasal cavity.
Oropharynx- Located behind the oral cavity, extending down to the hyoid bone.
Laryngopharynx- The lowest part, starting at the epiglottis and continuing to the oesophagus.
Key Features of the Pharynx
The pharynx is composed of both longitudinal and circular muscles, which help shape the lumen.
The isthmus connects the oropharynx to the nasopharynx, assisting with mouth breathing and the movement of food into the oesophagus via the nasal tube when necessary.
Pharyngeal adenoids or tonsils are located in the nasopharynx.
The nasopharynx is lined with pseudostratified, columnar, and ciliated respiratory epithelium.
Eustachian tubes link the middle ear to the pharynx, aiding in equalising air pressure on the eardrum.
Palatine tonsils are located in the lateral walls of the oropharynx.
The oropharynx’s walls are made of non-keratinised, stratified squamous epithelium.
The opening from the pharynx to the larynx is regulated by the epiglottis, a muscular flap that prevents food from entering the trachea.
The wall of the laryngopharynx consists of stratified squamous epithelium and helps control the movement of air to the lungs and food to the oesophagus.
Lymphoid tissues, including pharyngeal, tubal, palatine, and lingual tonsils, form Waldeyer’s ring, which acts as the body’s first defense against microorganisms in both the digestive and respiratory systems.
Pharynx Function
The pharynx serves as a conduit for both air and food, with several key functions-
It warms and humidifies air before it enters the lungs.
It aids in the passage of food into the oesophagus. Circular muscles push food down, while longitudinal muscles help in swallowing by lifting and widening the pharyngeal walls.
The pharynx also plays a role in speech, amplifying sound produced by the larynx.
The lymphoid tissues within the pharynx provide an important defense mechanism, acting as the first line of defense against harmful microorganisms in the digestive and respiratory tracts.
Pharynx Diseases
Several conditions can affect the pharynx, including-
Pharyngitis- Inflammation of the pharynx, often resulting in a sore throat.
Tonsillitis- Inflammation of the tonsils, which are located in the pharynx.
Pharyngeal Cancer- Malignant growths that can occur in the pharynx.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on Pharynx- Definition, Functions and Structure for NEET
1. What is the pharynx?
The pharynx is a muscular tube located behind the oral and nasal cavities, serving as a common passage for both the respiratory and digestive systems. It helps in the movement of air to the lungs and food to the stomach.
2. What are the main parts of the pharynx?
The pharynx is divided into three main parts-
Nasopharynx- Located behind the nasal cavity.
Oropharynx- Located behind the oral cavity.
Laryngopharynx- The lower portion, extending from the epiglottis to the oesophagus.
3. What is the function of the pharynx?
The pharynx serves multiple purposes, including-
Facilitating the passage of air to the lungs and food to the oesophagus.
Warming and humidifying air before it reaches the lungs.
Aiding in swallowing and speech production.
Acting as a defense mechanism against harmful microorganisms.
4. What are some diseases associated with the pharynx?
Some common pharyngeal diseases include-
Pharyngitis- Inflammation of the pharynx, often causing a sore throat.
Tonsillitis- Inflammation of the tonsils.
Pharyngeal Cancer- Malignant tumors in the pharynx.
5. What are the lymphoid tissues in the pharynx?
The pharynx contains lymphoid tissues such as pharyngeal, tubal, palatine, and lingual tonsils. These tissues form Waldeyer’s ring, which plays a crucial role in defending the body against infections.
6. How does the pharynx contribute to speech?
The pharynx amplifies the sound produced by the larynx, playing an important role in voice production.
7. Can pharyngeal diseases affect breathing?
Yes, conditions like pharyngitis or tonsillitis can lead to swelling and discomfort, which may affect the passage of air and make breathing difficult.
8. How is pharyngeal cancer diagnosed?
Pharyngeal cancer is typically diagnosed through physical examinations, imaging tests, and biopsy procedures. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
9. What is the role of the Eustachian tube in the pharynx?
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the pharynx, helping equalise air pressure on the eardrum and ensuring proper ear function.
10. How can pharyngeal diseases be prevented?
Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can help prevent infections in the pharynx.























