
$1 - $ Chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives: -
A) $1 - Butene$
B) $1 - $Butanol
C) $2 - Butene$
D) $2 - $Butanol
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: When alcoholic potash will react with an alkyl halide, elimination reaction will take place. Alcoholic potash is nothing but $KOH$ dissolved in alcohol, most preferably ethanol. Elimination reaction is the process by which organic compounds containing only single bonds (saturated compounds) are transformed to compounds containing double or triple bonds (unsaturated compounds). There are two types of elimination reaction: - ${E_1}\& {E_2}$
Complete solution:
As we already know that $alc.KOH$ is reacting with an alkyl halide to form alkene as a product so we name this reaction as Dehydrohalogenation as in the mechanism of the reaction one halogen and one hydrogen will be removed from the compound. Here $alc.KOH$ will act as a Dehydrohalogenating agent.
So, we write the reaction as: -
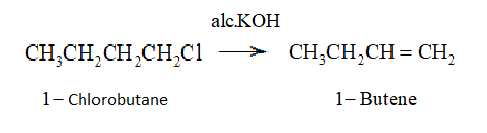
Here we see that ${E_2}$ elimination or $\beta $ elimination is taking place. In this case the removal of the halogen atom which $Cl$ in this case and removal of hydrogen atom attached to the $\beta $ carbon atom is taking place under the influence of highly basic metal hydroxide mixed with ethanol which is $alc.KOH$ in this case. This process finally leads to the formation of alkene.
Let us see which is the $\alpha \& \beta $ carbon: -
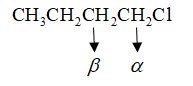
So, the correct answer is Option A i.e., $1 - Butene$
Additional information: Elimination reactions are commonly known by the kind of atoms or groups of atoms leaving the molecule. The removal of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom is known as dehydrohalogenation. When both the leaving atoms are halogens then the reaction is known as dehalogenation. Similarly, the elimination of water molecules, usually from an alcohol, is known as dehydrogenation.
Note:Elimination reaction is an important method for the preparation of alkenes. Here Saytzeff product is the major product formed. According to Saytzeff rule, the negative part that is the halogen will be removed from the $\alpha $ carbon and the positive part that is the hydrogen atom will be removed from $\beta $ carbon containing a minimum number of hydrogen atoms.
Complete solution:
As we already know that $alc.KOH$ is reacting with an alkyl halide to form alkene as a product so we name this reaction as Dehydrohalogenation as in the mechanism of the reaction one halogen and one hydrogen will be removed from the compound. Here $alc.KOH$ will act as a Dehydrohalogenating agent.
So, we write the reaction as: -
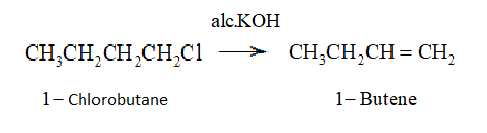
Here we see that ${E_2}$ elimination or $\beta $ elimination is taking place. In this case the removal of the halogen atom which $Cl$ in this case and removal of hydrogen atom attached to the $\beta $ carbon atom is taking place under the influence of highly basic metal hydroxide mixed with ethanol which is $alc.KOH$ in this case. This process finally leads to the formation of alkene.
Let us see which is the $\alpha \& \beta $ carbon: -

So, the correct answer is Option A i.e., $1 - Butene$
Additional information: Elimination reactions are commonly known by the kind of atoms or groups of atoms leaving the molecule. The removal of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom is known as dehydrohalogenation. When both the leaving atoms are halogens then the reaction is known as dehalogenation. Similarly, the elimination of water molecules, usually from an alcohol, is known as dehydrogenation.
Note:Elimination reaction is an important method for the preparation of alkenes. Here Saytzeff product is the major product formed. According to Saytzeff rule, the negative part that is the halogen will be removed from the $\alpha $ carbon and the positive part that is the hydrogen atom will be removed from $\beta $ carbon containing a minimum number of hydrogen atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




