
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Answer
520.9k+ views
Hint: We will take a closer look at all the parts of a human eye and will study about different parts, their location and their function in the human eye as a sense organ. We will then make a human eye diagram locating different parts of the eye.
Complete step by step answer:
The human eye is a sense organ that reacts with light and allows light perception, colour vision and depth perception. The eye is made up of a number of parts, including the Iris, Pupil, Cornea and Retina. The eye has a total of six muscles that control the eye movement, all providing different tension and torque.
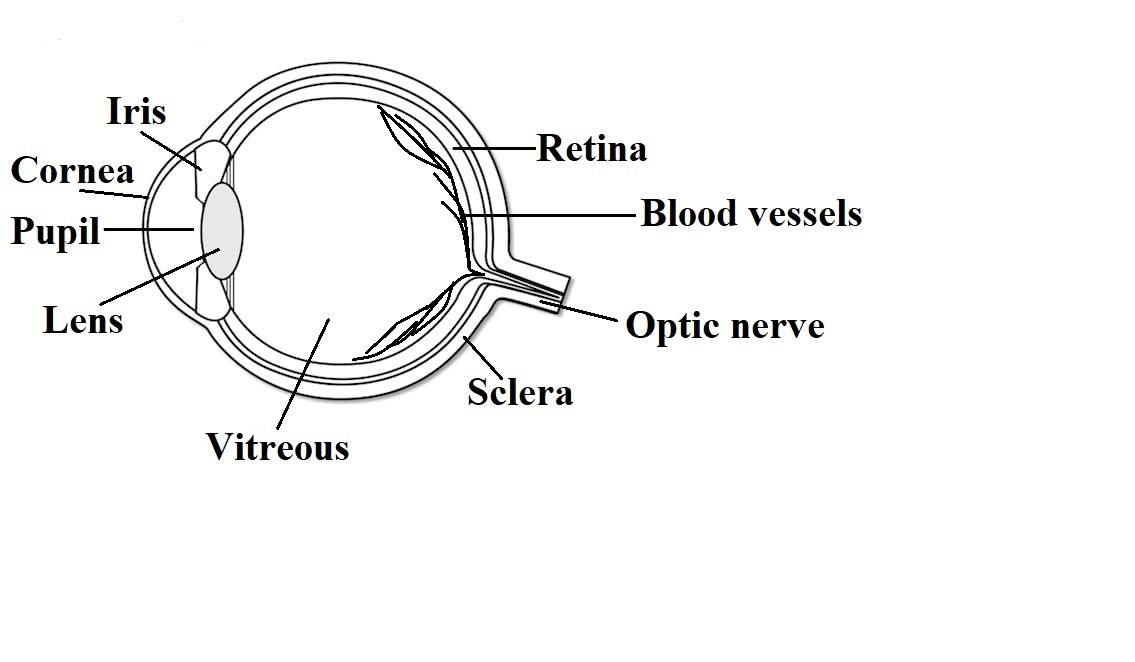
Different parts of Human eye:
Cornea – Light is focussed primarily by the Cornea, which is the clear front of the eye. Cornea acts like a camera lens for the human eye.
Iris – The Iris of the eye controls the amount of light reaching the back of the eye, by automatically adjusting the size of the aperture.
Eye lens – The eye’s crystalline lens is located directly behind the pupil and further focuses light.
Pupil – The pupil is a hole located in the centre of the Iris of the eye which allows the light to strike the retina.
Retina – Light focussed by the cornea and crystalline lens then reaches the retina, the light sensitive inner lining of the back of the eye. The purpose of the retina is to receive the light focussed by the lens, converting it into neural signals and sending these signals to the brain for visual recognition.
Sclera – It is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some elastic fibre.
Blood vessels – Blood vessels provide blood to the eye and veins drain blood from the eye.
Vitreous – It is a gel like structure that fills the interior of the eye and helps to preserve its round shape.
Optic nerve – Optic nerves transfer visual information from the retina to the vision centres of the brain via electrical impulses.
Note: Human eye is one of the most complex organ systems in the human body. It is a type of natural optical instrument which is used to see the objects by human beings. It also gives us the ability to differentiate between colours and depth. Human eye functions like a digital camera which has a lens and screen system.
Complete step by step answer:
The human eye is a sense organ that reacts with light and allows light perception, colour vision and depth perception. The eye is made up of a number of parts, including the Iris, Pupil, Cornea and Retina. The eye has a total of six muscles that control the eye movement, all providing different tension and torque.

Different parts of Human eye:
Cornea – Light is focussed primarily by the Cornea, which is the clear front of the eye. Cornea acts like a camera lens for the human eye.
Iris – The Iris of the eye controls the amount of light reaching the back of the eye, by automatically adjusting the size of the aperture.
Eye lens – The eye’s crystalline lens is located directly behind the pupil and further focuses light.
Pupil – The pupil is a hole located in the centre of the Iris of the eye which allows the light to strike the retina.
Retina – Light focussed by the cornea and crystalline lens then reaches the retina, the light sensitive inner lining of the back of the eye. The purpose of the retina is to receive the light focussed by the lens, converting it into neural signals and sending these signals to the brain for visual recognition.
Sclera – It is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some elastic fibre.
Blood vessels – Blood vessels provide blood to the eye and veins drain blood from the eye.
Vitreous – It is a gel like structure that fills the interior of the eye and helps to preserve its round shape.
Optic nerve – Optic nerves transfer visual information from the retina to the vision centres of the brain via electrical impulses.
Note: Human eye is one of the most complex organ systems in the human body. It is a type of natural optical instrument which is used to see the objects by human beings. It also gives us the ability to differentiate between colours and depth. Human eye functions like a digital camera which has a lens and screen system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




