
(1) Is $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)?$
(2) Is $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)?$
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are asked to prove the commutative property of the unions and the intersections of sets. Begin by assuming set A, B and C. Then find out the LHS of the given equation first and then the RHS step by step. If LHS = RHS, then the given statements are correct, otherwise not.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(1) In this question, we have to prove that $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)$.
We will prove it by assuming certain sets.
Let $A = \{ 1,2,3\} $,$B = \{ 4,5,6\} $and $C = \{ 7,8,9\} $.
Let us start with LHS first.
LHS = $(A \cup B) \cup C$
We will find $(A \cup B)$ and using it, we will find $(A \cup B) \cup C$. $(A \cup B)$ includes all the elements in A and B.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cup B) = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6\} $
Now let us find $(A \cup B) \cup C$ using $(A \cup B)$ and set C. $(A \cup B) \cup C$ includes all the elements in $(A \cup B)$and C.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cup B) \cup C = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9\} $ …..…. (1)
Next, we will find the RHS of the given equation, beginning with finding $(B \cup C)$. It will include all the elements in B and C.
$ \Rightarrow (B \cup C) = \{ 4,5,6,7,8,9\} $
Now let us find $A \cup (B \cup C)$ using $(B \cup C)$. $A \cup (B \cup C)$ will include all the elements in $(B \cup C)$ and A.
$ \Rightarrow A \cup (B \cup C) = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9\} $....…. (2)
From (1) and (2), we can infer that LHS = RHS.
Hence, $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)$.
(2) In this part, we have to prove that $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$.
Using the same approach as in the above question, let us assume some sets.
Let $A = \{ 1,2,3,4\} $, $B = \{ 2,3,4,5\} $ and $C = \{ 3,4,5,6\} $.
Let us start with LHS first.
LHS =$(A \cap B) \cap C$
We will find $(A \cap B)$ first and using it we will find $(A \cap B) \cap C$. $(A \cap B)$ will include only those elements which are common in A and B.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cap B) = \{ 2,3,4\} $
Next, we will find $(A \cap B) \cap C$ using $(A \cap B)$. It will include the common elements of $(A \cap B)$ and C.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cap B) \cap C = \{ 3,4\} $ …..…. (3)
Now we will find the RHS of the given equation. Let us find \[(B \cap C)\]. \[(B \cap C)\] will include only those elements which are common in B and C.
$ \Rightarrow (B \cap C) = \{ 3,4,5\} $
Using this we will find $A \cap (B \cap C)$. It will include the common elements of \[(B \cap C)\] and A.
$ \Rightarrow A \cap (B \cap C) = \{ 3,4\} $ …..…. (4)
From (3) and (4), we can infer that LHS = RHS.
Hence, $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$.
Note: This question can also be solved using Venn diagrams.
(1) We have to prove that $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)$. On the LHS, we will mark the $(A \cup B)$ using yellow colour and on RHS, we will mark $(B \cup C)$ using yellow colour. Then we will mark the area covered by $(A \cup B) \cup C$ and $A \cup (B \cup C)$ using blue colour on both the sides, (when blue is mixed with yellow, it gives green).
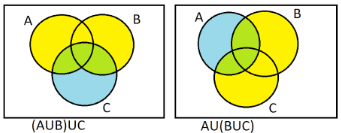
As a result, we can see that the entire figure is covered using colours. The space covered on the LHS figure and on the RHS figure is the same. Therefore, LHS=RHS.
(2) We have to prove that $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$. On the LHS, we will mark the $(A \cap B)$ with yellow colour and on RHS, we will mark $(B \cap C)$ with yellow colour.
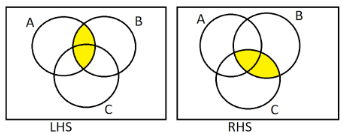
Then we will mark the area covered by $(A \cap B) \cap C$ and $A \cap (B \cap C)$ using green colour on both sides.
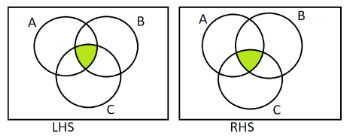
As a result, we can see that the common part (green coloured area) on both sides is the same. Hence, $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(1) In this question, we have to prove that $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)$.
We will prove it by assuming certain sets.
Let $A = \{ 1,2,3\} $,$B = \{ 4,5,6\} $and $C = \{ 7,8,9\} $.
Let us start with LHS first.
LHS = $(A \cup B) \cup C$
We will find $(A \cup B)$ and using it, we will find $(A \cup B) \cup C$. $(A \cup B)$ includes all the elements in A and B.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cup B) = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6\} $
Now let us find $(A \cup B) \cup C$ using $(A \cup B)$ and set C. $(A \cup B) \cup C$ includes all the elements in $(A \cup B)$and C.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cup B) \cup C = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9\} $ …..…. (1)
Next, we will find the RHS of the given equation, beginning with finding $(B \cup C)$. It will include all the elements in B and C.
$ \Rightarrow (B \cup C) = \{ 4,5,6,7,8,9\} $
Now let us find $A \cup (B \cup C)$ using $(B \cup C)$. $A \cup (B \cup C)$ will include all the elements in $(B \cup C)$ and A.
$ \Rightarrow A \cup (B \cup C) = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9\} $....…. (2)
From (1) and (2), we can infer that LHS = RHS.
Hence, $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)$.
(2) In this part, we have to prove that $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$.
Using the same approach as in the above question, let us assume some sets.
Let $A = \{ 1,2,3,4\} $, $B = \{ 2,3,4,5\} $ and $C = \{ 3,4,5,6\} $.
Let us start with LHS first.
LHS =$(A \cap B) \cap C$
We will find $(A \cap B)$ first and using it we will find $(A \cap B) \cap C$. $(A \cap B)$ will include only those elements which are common in A and B.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cap B) = \{ 2,3,4\} $
Next, we will find $(A \cap B) \cap C$ using $(A \cap B)$. It will include the common elements of $(A \cap B)$ and C.
$ \Rightarrow (A \cap B) \cap C = \{ 3,4\} $ …..…. (3)
Now we will find the RHS of the given equation. Let us find \[(B \cap C)\]. \[(B \cap C)\] will include only those elements which are common in B and C.
$ \Rightarrow (B \cap C) = \{ 3,4,5\} $
Using this we will find $A \cap (B \cap C)$. It will include the common elements of \[(B \cap C)\] and A.
$ \Rightarrow A \cap (B \cap C) = \{ 3,4\} $ …..…. (4)
From (3) and (4), we can infer that LHS = RHS.
Hence, $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$.
Note: This question can also be solved using Venn diagrams.
(1) We have to prove that $(A \cup B) \cup C = A \cup (B \cup C)$. On the LHS, we will mark the $(A \cup B)$ using yellow colour and on RHS, we will mark $(B \cup C)$ using yellow colour. Then we will mark the area covered by $(A \cup B) \cup C$ and $A \cup (B \cup C)$ using blue colour on both the sides, (when blue is mixed with yellow, it gives green).

As a result, we can see that the entire figure is covered using colours. The space covered on the LHS figure and on the RHS figure is the same. Therefore, LHS=RHS.
(2) We have to prove that $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$. On the LHS, we will mark the $(A \cap B)$ with yellow colour and on RHS, we will mark $(B \cap C)$ with yellow colour.

Then we will mark the area covered by $(A \cap B) \cap C$ and $A \cap (B \cap C)$ using green colour on both sides.

As a result, we can see that the common part (green coloured area) on both sides is the same. Hence, $(A \cap B) \cap C = A \cap (B \cap C)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




