
1-Chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives:
A. 1-Butene
B. 1-Butanol
C. 2-Butene
D. 2-Butanol
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: Remember that this is one of the elimination reactions, as alcoholic potash is involved. So, while solving such reactions, we should try to look for $\text{ }\!\!\beta\!\!\text{ }$ carbon atoms, so that this base reacts on it.
Complete step by step solution:
Since alcoholic potash is a dehydrohalogenation agent, it will $\text{ }\!\!\beta\!\!\text{ }$ allow the process of dehydrohalogenation to take place.
- We should remove the hydrol atom from the $\text{ }\!\!\beta\!\!\text{ }$ -carbon of the alkyl halide in order to form an alkene.
- So, in this question when 1-chlorobutane reacts with alcoholic potash,the hydrogen atom from beta carbon eliminates and combines with OH ion to form a water molecule.
- On account of this,halogen being a leaving group,here we have chlorine that departs, and thus 1-butene is formed.
-The below equation will explain that:
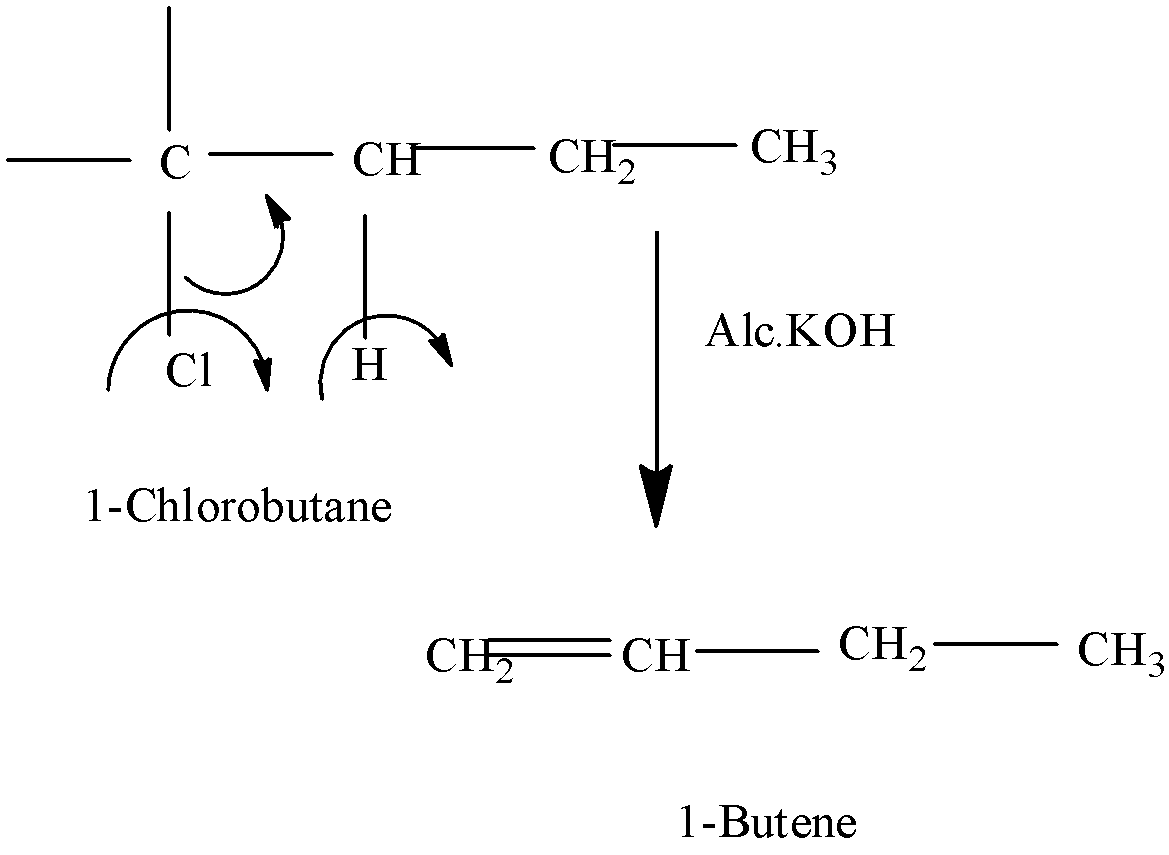
- As this product is formed, this is only the major product, as there are no chances of rearrangement to take place.
- So, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
Now there might be doubts arising here that if there were two beta carbon atoms attached, during the isomers of tertiary and secondary alkyl halide, then which one would be the major product.
So in that case we follow the Satyzeff rule,which states that the more substituted alkene or the one with more hyperconjugation is more stable and thus that will be the major product.
Note: We must focus that the reaction of dehydrohalogenation does not take place in a stepwise manner, but it involves a concerted mechanism. This means that all the bond breaking between the carbon- halide, carbon-hydrogen and the bond making while forming an alkene takes place in only a single step.
Complete step by step solution:
Since alcoholic potash is a dehydrohalogenation agent, it will $\text{ }\!\!\beta\!\!\text{ }$ allow the process of dehydrohalogenation to take place.
- We should remove the hydrol atom from the $\text{ }\!\!\beta\!\!\text{ }$ -carbon of the alkyl halide in order to form an alkene.
- So, in this question when 1-chlorobutane reacts with alcoholic potash,the hydrogen atom from beta carbon eliminates and combines with OH ion to form a water molecule.
- On account of this,halogen being a leaving group,here we have chlorine that departs, and thus 1-butene is formed.
-The below equation will explain that:

- As this product is formed, this is only the major product, as there are no chances of rearrangement to take place.
- So, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
Now there might be doubts arising here that if there were two beta carbon atoms attached, during the isomers of tertiary and secondary alkyl halide, then which one would be the major product.
So in that case we follow the Satyzeff rule,which states that the more substituted alkene or the one with more hyperconjugation is more stable and thus that will be the major product.
Note: We must focus that the reaction of dehydrohalogenation does not take place in a stepwise manner, but it involves a concerted mechanism. This means that all the bond breaking between the carbon- halide, carbon-hydrogen and the bond making while forming an alkene takes place in only a single step.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




